眼科护理干预在糖尿病性视网膜病变中的应用探讨
崔琳琳
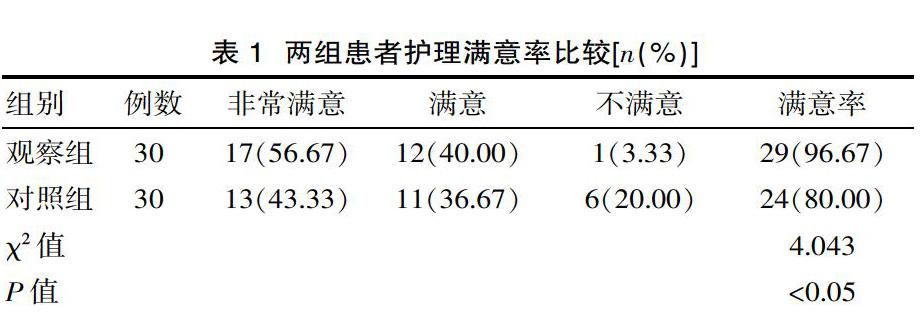
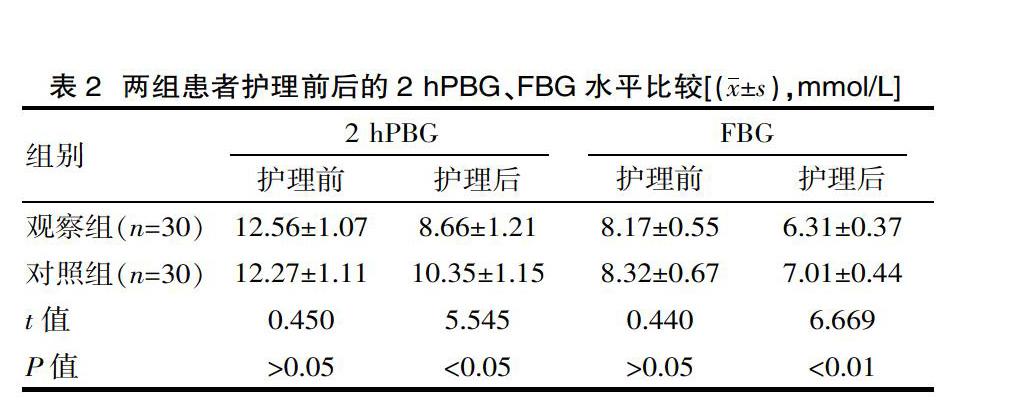
[摘要] 目的 探讨眼科护理干预在糖尿病性视网膜病变中的应用效果。方法 选取2018年3月—2019年3月期间于该院接受治疗的60例糖尿病性视网膜病变患者为研究对象,将其分为观察组(2018年10月—2019年3月收治)与对照组(2018年3—9月收治),每组30例。对照组实施常规护理,观察组在此基础上实施整体眼科护理,比较两组护理满意率、血糖水平及护理前后视力变化。结果 观察组护理满意率高于对照组;两组护理后的2 hPBG、FBG均有降低,观察组的2 hPBG、FBG低于对照组;两组护理后的视力水平均有提高,观察组高于对照组(P<0.05)。结论 对糖尿病性视网膜病变患者实施整体眼科护理干预,能够有效控制患者血糖,并能改善其视力水平,提高其护理满意率。
[关键词] 眼科护理干预;糖尿病;视网膜病变
[中图分类号] R473.77 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-4062(2020)08(a)-0157-03
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of ophthalmic nursing intervention in diabetic retinopathy. Methods 60 patients with diabetic retinopathy who were treated in the hospital from March 2018 to March 2019 were selected as study subjects. They were divided into the observation group (admitted from October 2018 to March 2019) and the control group (admitted from March to September 2018), with 30 cases in each group. The control group carried out routine nursing, and the observation group carried out overall eye care on this basis, and compared the nursing satisfaction rate, blood glucose level and visual changes before and after nursing in the two groups. Results The nursing satisfaction rate of the observation group was higher than that of the control group. After nursing, 2 hPBG and FBG were decreased in both groups, while 2 hPBG and FBG in the observation group were lower than those in the control group. The visual acuity level of the two groups after nursing was improved, the observation group was higher than the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion The whole eye care intervention for diabetic retinopathy patients can effectively control the patients' blood glucose, improve their vision level and improve their nursing satisfaction rate.
[Key words] Eye care intervention; Diabetes; Retinopathy
糖尿病性視网膜病变是糖尿病微血管病变中的重要表现,是糖尿病严重并发症之一[1]。该疾病在控制血糖稳定的情况下使用药物、手术等方法治疗,可改善患者视力情况。而为了长期稳定血糖水平,在患者治疗过程中需要进行一定的护理干预,以维护患者眼部健康[2]。常规的护理对糖尿病性视网膜病变患者的眼部干预不强,其效果不够理想,整体眼科护理是在控制患者血糖水平的同时对其进行针对性眼部护理的模式,其能够改善患者视力,并有效控制患者血糖水平[3]。为探讨整体眼科护理干预在糖尿病性视网膜病变中的应用效果,笔者选取2018年3月—2019年3月期间于该院接受治疗的60例患者进行观察,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取于该院接受治疗的60例糖尿病性视网膜病变患者为研究对象,将其分为观察组(2018年10月—2019年3月收治)与对照组(2018年3—9月收治),每组30例。对照组男女例数比为17:13;年龄50~78岁,均数(64.09±6.13)岁;病程3~9年,均数(6.03±2.21)年。观察组男女例数比为16:14;年龄50~79岁,均数(64.55±6.22)岁;病程3~10年,均数(6.51±2.05)年。两组一般资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。研究已取得院伦理委员会的同意。纳入标准:符合《眼科学》中糖尿病性视网膜病变的诊断标准;未做过眼部激光手术;患者或其家属已签署知情同意书。排除标准:伴有恶性肿瘤、肝肾功能不全者;其他眼部疾病者。

