LAD1和P-ERK在乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中的表达及临床意义
安淑香 雷丽 赵丹



【摘要】 目的:研究LAD1和P-ERK蛋白在乳腺组织中的表达,探讨LAD1和P-ERK蛋白在乳腺浸润性导管癌发展及预后中的作用。方法:选取2013年1月-2014年12月于本院進行手术治疗的20例乳腺导管原位癌患者及其导管原位癌组织、癌旁正常组织标本,另选取同期80例乳腺浸润性导管癌患者及其组织标本。采用免疫组织化学方法检测并比较LAD1和P-ERK蛋白在癌旁正常、导管原位癌及浸润性导管癌组织中的表达。比较不同临床病理特征的浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK的表达。分析浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK表达的相关性。采用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线比较不同LAD1和P-ERK表达的乳腺浸润性导管癌患者的生存情况。结果:乳腺导管原位癌、乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK蛋白阳性表达率均高于癌旁正常组织(P<0.05)。不同组织学分级、临床分期、淋巴结转移情况浸润性导管癌患者LAD1蛋白和P-ERK蛋白阳性表达率比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同年龄、肿瘤大小及ER、PR表达情况者LAD1蛋白和P-ERK蛋白阳性表达率比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK表达之间呈正相关(P<0.05)。LAD1表达阳性的乳腺浸润性导管癌患者5年生存率为66.0%低于LAD1阴性患者的90.0%(P<0.05)。P-ERK表达阳性的乳腺浸润性导管癌患者5年生存率为67.9%低于P-ERK阴性患者的91.7%(P<0.05)。结论:LAD1和P-ERK的过表达在乳腺癌的发展及浸润转移中协同发挥重要作用,并与患者的不良预后有关。
【关键词】 LAD1 P-ERK 乳腺浸润性导管癌
[Abstract] Objective: To study the expression of LAD1 and P-ERK protein in breast tissue, and to explore the role of LAD1 and P-ERK protein in the development and prognosis of breast infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Method: A total of 20 cases of ductal carcinoma in situ patients and their ductal carcinoma in situ tissues and adjacent normal tissue specimens who underwent surgical treatment in our hospital from January 2013 to December 2014 were selected, and another 80 cases of infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast and their tissue specimens were selected during the same period. Immunohistochemical method was used to detect and compare the expression of LAD1 and P-ERK protein in adjacent normal, ductal carcinoma in situ and infiltrating ductal carcinoma. The expressions of LAD1 and P-ERK in infiltrating ductal carcinoma with different clinicopathologic features were compared. The correlation between LAD1 and P-ERK expression in infiltrating ductal carcinoma was analyzed. Survival curve was drawn by Kaplan-Meier method to compare the survival of patients with infiltrating ductal carcinoma with different LAD1 and P-ERK expression. Result: The positive expression rates of LAD1 and P-ERK in ductal carcinoma in situ and infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast were higher than those in adjacent normal tissues (P<0.05). The positive expression rates of LAD1 protein and P-ERK protein in breast infiltrating ductal carcinoma patients with different histological grade, clinical stage and lymph node metastasis were statistically significant (P<0.05); there were no significant differences in the positive expression rates of LAD1 and P-ERK protein among different age, tumor size and ER and PR expression (P>0.05). There was a positive correlation between LAD1 and P-ERK expression in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast (P<0.05). The 5-year survival rate of infiltrating ductal carcinoma patients with LAD1 positive expression was 66.0% lower than 90.0% of LAD1 negative expression patients (P<0.05). The 5-year survival rate of infiltrating ductal carcinoma patients with P-ERK positive expression was 67.9% lower than 91.7% of P-ERK negative expression patients (P<0.05). Conclusion: The over expressions of LAD1 and P-ERK might play an important role in progression, invasion and metastasis of breast cancer, and related to the poor prognosis of the patient.
[Key words] LAD1 P-ERK Breast infiltrating ductal carcinoma
First-author’s address: Fuxin Center Hospital, Fuxin 123000, China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2021.22.007
細胞骨架是一系列细胞结构蛋白的统称,它们不仅为细胞塑形,更在细胞的通讯、迁移、浸润转移中发挥着重要的作用,细胞骨架蛋白如微管蛋白抑制剂可用于癌症的治疗[1-2]。LAD1是一个细胞骨架相关蛋白,蛋白分子量59 kD,LAD1首先从小鼠皮肤cDNA文库中克隆,除了富含精氨酸的N端延伸序列和6个丝氨酸-谷氨酸-赖氨酸(SEK)三肽基序以外,编码的蛋白质没有可识别的结构域,其可作为基底膜的分泌成分。人类LAD1基因位于染色体1号上,其外显子区域在哺乳动物中保存良好[3]。关于其报道的内容不多,较早的研究报道与正常卵巢上皮相比,LAD1是卵巢浆液性乳头状癌中表达最高的基因之一[4]。最新的研究发现,LAD1和人的恶性侵袭性乳腺肿瘤相关,LAD1蛋白是媒介EGF激活ERK信号通路的重要因子[5]。丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)途径中的细胞外激酶(ERK)是MAPK家族的重要成员,P-ERK是ERK的活化形式,ERK信号途径以正调节的方式调控肿瘤生长并可用于肿瘤的治疗[6-7]。LAD1蛋白与ERK信号通路相关,在乳腺癌组织中LAD1是否通过调节活化ERK途径发挥作用,两者在乳腺癌组织中的表达是否存在一定的相关性并协同发挥作用具有研究意义。本研究分析了LAD1和P-ERK在乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中的表达及临床意义,旨在为乳腺癌的研究开辟新途径,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2013年1月-2014年12月于本院进行手术治疗的20例乳腺导管原位癌患者及其导管原位癌组织、癌旁正常组织标本,另选取同期80例乳腺浸润性导管癌患者及其组织标本。纳入标准:均已确诊为乳腺导管原位癌与乳腺浸润性导管癌;女性,年龄25~70岁;入组前无放疗、化疗、免疫及内分泌治疗史。排除标准:患有其他系统恶性肿瘤病史;患有严重内外科疾病;临床资料不完整。所有患者及家属均知情同意并签署知情同意书,本研究已经医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 方法 (1)实验试剂。LAD1兔多克隆抗体(PA5-55966)购买自Thermo Fisher Scientific、P-ERK鼠单克隆抗(sc-7383)购自 Santa CruzBiotech Inc。S-P 超敏免疫组化试剂盒、DAB 酶底物显色试剂盒购自北京中山生物技术有限公司。(2)LAD1和P-ERK蛋白的表达。标本经10%中性福尔马林固定,石蜡包埋,4 μm厚连续切片,采用免疫组织化学(SP)法,按试剂盒说明书步骤进行抗LAD1(1︰500)、P-ERK(1︰200)抗体免疫组织化学染色,PBS代替一抗作为阴性对照,用已知阳性片作阳性对照。结果判定:LAD1蛋白阳性表达位于乳腺癌细胞质和膜内,P-ERK蛋白阳性表达主要分布于乳腺癌细胞质。每张切片在光镜下随机选取5个视野,每个视野计数100个细胞,0分,无阳性细胞;1分,阳性细胞<25%;2分,阳性细胞25%~50%;3分,阳性细胞51%~75%;4分,阳性细胞>75%。染色强度评分,0分为无阳性细胞;1分为浅黄色;2分为黄色;3分为棕黄色。阳性细胞数评分与染色强度评分相乘后得出综合评分。综合评分>3为阳性表达[8]。(3)随访。80例浸润性导管癌患者术后进行5年定期随访,随访开始时间为接受手术时间,截止时间为2019年12月。采用门诊随访及电话随访,平均每6个月随访1次,终止时间为患者死亡时间,中途失访者的终止时间为最后1次随访时间。
1.3 统计学处理 采用SPSS 25.0软件对所得数据进行统计分析;计数资料以率(%)表示,比较采用字2检验;LAD1和P-ERK的相关性用Pearson列联系数;Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线及log-rank检验进行生存分析。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 20例乳腺导管原位癌患者与80例乳腺浸润性导管癌患者一般资料比较 乳腺导管原位癌患者年龄≤45岁者9例,年龄>45岁者11例;肿瘤直径<2 cm者7例,>2 cm者13例。乳腺浸润性导管癌患者年龄≤45岁者32例,年龄>45岁者48例;肿瘤直径<2 cm者30例,>2 cm者50例。依据WHO2012年所推荐的乳腺肿瘤标准进行分级、分期,并结合第5版WHO乳腺肿瘤分类解读[9],组织学分级:Ⅰ级6例,Ⅱ级48例,Ⅲ级26例;临床分期:Ⅰ期5例,Ⅱ期43例,Ⅲ、Ⅳ期32例;有淋巴结转移46例,无淋巴结转移34例。两种乳腺肿瘤患者年龄与肿瘤直径比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.2 LAD1和P-ERK蛋白在不同乳腺组织中的表达 LAD1蛋白在癌旁正常组织主要表达于细胞膜,见图1A;乳腺导管原位癌、乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1蛋白主要表达于细胞质和细胞膜内,呈棕黄色颗粒,见图1C、E。P-ERK蛋白在癌旁正常组织主要表达于细胞质,见图1B;乳腺导管原位癌、乳腺浸润性导管癌P-ERK蛋白主要表达于细胞质,见图1D、F。乳腺导管原位癌、乳腺浸润性导管癌组织LAD1和P-ERK蛋白表达阳性率均高于癌旁正常组织(字2=3.956、11.634、7.033、20.008,P=0.047、0.001、0.008、0.000);浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK蛋白表达阳性率虽高于导管原位癌,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
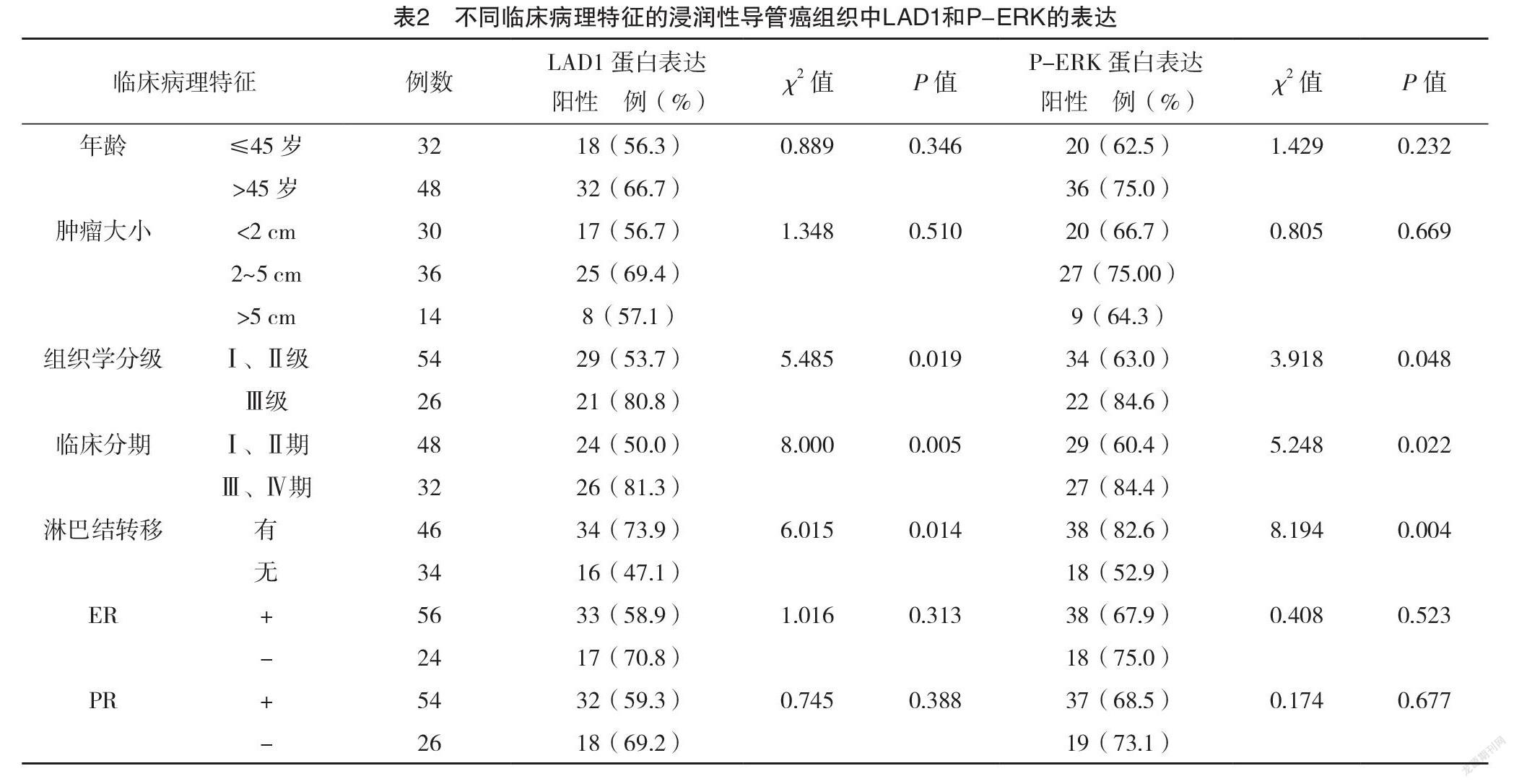
2.3 不同臨床病理特征的浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK的表达 不同组织学分级、临床分期、淋巴结转移情况者LAD1蛋白和P-ERK蛋白表达阳性率比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。不同年龄、肿瘤大小及ER、PR表达情况者LAD1蛋白和P-ERK蛋白表达阳性率比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。
2.4 乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK表达的关系 LAD1和P-ERK表达均为阳性的标本共41例,表达均为阴性的标本共15例,具体表达情况见表3。乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK表达之间呈正相关(r=0.320,P=0.002)。
2.5 不同LAD1和P-ERK表达的乳腺浸润性导管癌患者5年生存率比较 Kaplan-Meier生存分析显示,LAD1表达阳性的患者5年生存率为66.0%低于LAD1阴性患者的90.0%,差异有统计学意义(字2=5.691,P=0.017)。P-ERK表达阳性的患者5年生存率为67.9%低于P-ERK阴性患者的91.7%,差异有统计学意义(字2=4.679,P=0.031)。见图2。
注:A为LAD1在癌旁正常组织中的表达;B为P-ERK在癌旁正常组织中的表达;C为LAD1在导管原位癌组织中的表达;D为P-ERK在导管原位癌组织中的表达;E为LAD1在乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中的表达;F为P-ERK在乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中的表达。
3 讨论
乳腺癌是女性常见的恶性肿瘤,EGFR激活的信号通路能够提高细胞的迁移能力,在肿瘤的进展研究中得到证实[10-11]。因此有研究利用磷酸化蛋白组学技术对接受EGF刺激的乳腺细胞系进行了分析,发现一种名为LAD1的蛋白是媒介EGF激活ERK信号通路的重要因子,在这个过程中LAD1不但蛋白产量升高,还会发生结构修饰,然后和其他重要的细胞骨架蛋白肌动蛋白(actin)等一起参与调节乳腺细胞的增殖和侵袭,在乳腺癌的进展中发挥重要作用[5]。且有基因学研究发现LAD1在基底细胞样和三阴性乳腺癌中表达,提示LAD1与乳腺癌的恶性度相关,其高表达患者可能预后不良[12-13]。在甲状腺癌的研究中发现LAD1基因特异表达于BRAF V600E突变的肿瘤[14]。且有研究报道LAD1在口腔鳞癌、喉癌中高表达,并在肿瘤的转移中发挥作用,提示LAD1与肿瘤的发生发展存在重要作用[15-16]。LAD1的DNA甲基化可作为肾细胞癌预后的标志物[17-18]。但关于其在肿瘤组织中的研究报道较少,在乳腺癌组织中LAD1蛋白存在怎样的表达目前国内还未见相关报道。
MAPK家族成员中的ERK,包括ERK1/2,P-ERK是ERK活化形式,研究已证明活化的ERK在乳腺癌的发生发展中发挥重要作用[19-20]。LAD1能够活化ERK信号转导通路,那么两者是否协同在乳腺癌的进展中发挥作用,LAD1和P-ERK在乳腺癌组织中的表达存在怎样的关联?本研究发现,LAD1和P-ERK在癌旁正常组织中少量表达,在乳腺导管原位癌、乳腺浸润性导管癌中高表达,且呈递增趋势;LAD1和P-ERK的蛋白表达和组织学分级存在相关,且组织学分级越高,蛋白表达阳性率越高;两种蛋白表达和临床分期及淋巴结转移存在相关,Ⅲ、Ⅳ期乳腺浸润性导管癌患者两种蛋白表达阳性率均高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ期患者;有淋巴结转移者两种蛋白表达高于无淋巴结转移者。本研究结果显示,在乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中LAD1和P-ERK表达均为阳性的标本共41例,表达均为阴性的标本共15例,两者表达存在正相关(P<0.05)。提示LAD1在乳腺癌的发展中发挥重要作用,LAD1作为P-ERK的上游因子可能通过调控ERK的表达从而在乳腺癌的发展中发挥作用。生存分析发现,LAD1和P-ERK表达阳性乳腺浸润性导管癌患者的术后5年生存率低于表达阴性者(P<0.05)。
综上所述,LAD1在乳腺浸润性导管癌组织中高表达,与P-ERK的表达存在正相关,两者在乳腺癌的进展中发挥协调作用,并与乳腺癌患者的预后生存期相关,有望成为乳腺癌诊治和预后的生物学标志物。关于LAD1的研究较少,深入研究LAD1及其上下游调控因子可为乳腺癌的靶基因治疗提供新的思路。
参考文献
[1] Klingler-Hoffmann M,Mittal P,Hoffmann P.The Emerging Role of Cytoskeletal Proteins as Reliable Biomarkers[J/OL].Proteomics, 2019,19(21-22):e1800483.
[2] Haider K,Rahaman S,Yar M S,et al.Tubulin inhibitors as novel anticancer agents:an overview on patents (2013-2018)[J].Expert Opin Ther Pat,2019,29(8):623-641.
[3] Motoki K,Megahed M,LaForgia S,et al.Cloning and chromosomal mapping of mouse ladinin,a novel basement membrane zone component[J].Genomics,1997,39(3):323-330.
[4] Santin A D,Zhan F,Bellone S,et al.Gene expression profiles in primary ovarian serous papillary tumors and normal ovarian epithelium:Identification of candidate molecular markers for ovarian cancer diagnosis and therapy[J].Int J Cancer,2004,112(1):14-25.
[5] Roth L,Srivastava S,Lindzen M,et al.SILAC identifies LAD1 as a filamin-binding regulator of actin dynamics in response to EGF and a marker of aggressive breast tumors[J].Sci Signal,2018,11(515):eaan0949.
[6] McCubrey J A,Steelman L S,Chappell W H,et al.Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2007,1773(8):1263-1284.
[7] Liu F,Yang X,Geng M,et al.Targeting ERK, an Achilles’ Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer therapy[J].Acta Pharm Sin B,2018,8(4):552-562.
[8]孟媛,徐斌.CX3CL1与CX3CR1在乳腺非特殊类型浸润性癌中的表达及其临床意义[J].臨床与病理杂志,2019,39(4):752-758.
[9]杨文涛,步宏.第5版WHO乳腺肿瘤分类解读[J].中华病理学杂志,2020,49(5):400-405.
[10] Sigismund S,Avanzato D,Lanzetti L.Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer[J].Mol Oncol,2018,12(1):3-20.
[11] Hsu J L,Hung M C.The role of HER2,EGFR,and other receptor tyrosine kinases in breast cancer[J].Cancer Metastasis Rev,2016,35(4):575-588.
[12] Alexe G,Dalgin G S,Ramaswamy R,et al.Data perturbation independent diagnosis and validation of breast cancer subtypes using clustering and patterns[J].Cancer Inform,2007,2:243-274.
[13] Wang X,Guda C.Integrative exploration of genomic profiles for triple negative breast cancer identifies potential drug targets[J/OL].Medicine(Baltimore),2016,95(30):e4321.
[14] Rusinek D,Swierniak M,Chmielik E,et al.BRAFV600E-associated gene expression profile:Early changes in the transcriptome,based on a transgenic mouse model of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J/OL].PLoS One,2015,10(12):e0143688.
[15] Abé T,Maruyama S,Yamazaki M,et al.Proteomic and histopathological characterization of the interface between oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion fronts and non-cancerous epithelia[J].Exp Mol Pathol,2017,102(2),327-336.
[16] Klobučar M,Sedić M,Gehrig P,et al.Basement membrane protein ladinin-1 and the MIF-CD44-B1 integrin signaling axis are implicated in laryngeal cancer metastasis[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2016,1862(10):1938-1954.
[17] Joosten S C,Deckers I A,Aarts M J,et al.Prognostic DNA methylation markers for renal cell carcinoma:a systematic review[J].Epigenomics,2017,9(9):1243-1257.
[18] van Vlodrop I J H,Joosten S C,De Meyer T,et al.A Four-Gene Promoter Methylation Marker Panel Consisting of GREM1,NEURL,LAD1,and NEFH Predicts Survival of Clear Cell Renal Cell Cancer Patients[J].Clin Cancer Res,2017,23(8):2006-2018.
[19] Li J,Guo Y,Duan L,et al.AKR1B10 promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion via activation of ERK signaling[J].Oncotarget,2017,8(20):33694-33703.
[20]田继华,常思佳,郭海秀,等.ERK抑制剂U0126通过下调cyclin D1与survivin蛋白表达抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖.中国药理学通报,2019,35(8):1061-1066.
(收稿日期:2021-04-20) (本文编辑:田婧)

