Effects of Different Extract of Pseudostellaria Heterophylla on Immunological Function in Mice based on Meta-analysis and Network Meta-analysis
ZHANG Yan-da , PAN Hui-qing *, MA Yu-fang , SHI Shao-hua , ZHAO Qi
1. Municipal Enterprise Technical Center of Fujian Beidi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Ningde 355300, PRC;
2. Fujian Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, PRC;
3. Institute of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Fuzhou 350013, PRC
Abstract To evaluate the effects of different extract of Pseudostellaria heterophylla on immunological function in mice based on Meta-analysis and Network meta-analysis, the article retrieved domestic and foreign databases according to the "PICO" retrieval strategy, and used Stata and ADDIS software for Meta analysis. A total of 6 reports, 10 randomised controlled trials (RCTs) were eventually involved. Meta analysis results showed that: compared with the control group, the experimental group of polysaccharide, saponin and crude extract were better than that of the control (P<0.05), which significantly improved the immunological function in mice. Network meta-analysis results showed that the saponin had the best effect on the increase of phagocytic index and the differences were statistically significant [MD=1.50, 95% CI(0.71, 2.28), P<0.05]; The polysaccharide and saponin had better effect on the increase of spleen index than the control and crude extract, and the differences were statistically significant [MD=0.77, 95% CI (0.27, 1.31), P<0.05], [MD=0.71, 95% CI (0.01, 1.50), P<0.05]; the polysaccharide had the best effect on the increase of thymus index and the differences were statistically significant [MD=0.70, 95% CI (0.11, 1.34), P<0.05]. The rank probability showed that the saponin of Pseudostellaria heterophylla had the maximum probability to increase phagocytic index of mice; the probability for the components of Pseudostellaria heterophylla increasing spleen index of mice was in the order of crude extract>polysaccharide>saponin; the probability for the components of Pseudostellaria heterophylla increasing thymus index of mice was in the order of saponin>polysaccharide>crude extract. Based on the available evidence, the extract of Pseudostellaria heterophylla could improve the immunity of mice, and the clinical effect of polysaccharide and saponin was the best, which provided a more valuable scientific reference for evidencing that the polysaccharide and saponin of Pseudostellaria heterophylla was the effective components for improving immunological function, and also was conducive to the proper further development of Pseudostellaria heterophylla resources.
Key words Pseudostellaria heterophylla; Extraction; Mice; Immunological function; Network meta-analysis
1. Introduction
Pseudostellaria heterophylla
is dry root in Caryophyllaceae family andPseudostellaria
genus, which was first recorded in theNew Compilation
ofMateria medica
in the Qing Dynasty. It is mainly produced in Fujian, Guizhouetc
. andPseudostellaria heterophylla
of Zherong had better quality.Pseudostellaria heterophylla
belong to a tonic Chinese medicine, which has both medicinal and nutritional effects, and is rich in polysaccharides, saponins, cyclic peptides and other components. Clinical trials ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
indicated that it has the effects of invigorating the spleen and benefiting the lung, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, probiotic strains and strengthening the immunitywhich has become one of the research hot spot.It was found that the polysaccharides, saponins and crude extracts were the main research components inPseudostellaria heterophylla
to improve immunologi- cal function of mice by retrieving literature. However, the research on the effects of different components inPseudostellaria heterophylla
on the immunological function of mice was isolated and dispersive. Few studies have been done on the comparison of the effects of different components on the immune indices, as well as the comparison of the polysaccharides, saponins and crude extracts inPseudostellaria heterophylla
. It can be seen from the literature reviewed that the sample size of experiment is less, and the experiment indices are single. And so far there has not been a randomized controlled trial (RCT) with a large amount of samples. In this study, Network meta-analysiswas used to evaluate the effects of different extract inPseudostellaria heterophylla
on immunological function in mice and accurately analyze multiple immunological intervention trials treated with different components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
with phagocytic index, thymus index and spleen index as indices, so as to provide references for determining the effective components that can improve immunological function and further developingPseudostellaria heterophylla
resources accurately.2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrieval strategy
Literatures collected from domestic database including CNKI, Wanfang and VIP, and foreign database including Web of Science, PubMed, Elsevier and Research Gateetc
., which ranging from the day establishing the database to June 1, 2021. According to the "PICO" retrieval strategy, Chinese search words were “太子参”, “孩儿参”, “童参”, “提取物”, “多糖”, “皂苷”, “免疫”, “胸腺”, “脾脏”; English search words were “Taizishen”, “Pseudos- tellaria
heterophylla
”, “Tongshen”, “extract”, “polysaccharide”, “saponin”, “immune”. All literatures were retrieved with a combination of subject retrieval and free retrieval, and collected manually. For unpublished or doubtful data, the author have consulted the corresponding author.2.2. Literature screening and data extraction
Literature screening and data extraction methods refered to literature. The literatures collected by retrieving should be screened primarily and secondly. Only the literatures using mice as test animals were included. Literature extraction table was designed to fill in the basic information of the literatures included. A third researcher would intervene to discuss when there was disagreement in literature re-screening.
2.3. Literature inclusion and exclusion standard
2.3.1. Literatures inclusion standard
1) The original material was the published literature about the randomized controlled trial (RCTs) or non-randomized controlled clinical trials (CCT) ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
components intervening mice immunity;2) Whether or not randomized grouping or blindness was used in study;
3) The control was set and mice number was taken asn
value;4) Only polysaccharides, saponins and crude extract ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
were involved in the paper;5) The literature must contain at least one indicator that was consistent with the topic of the study;
6) In the literature, the index value was expressed as "mean ± standard deviation".
But, unfortunately, while I was still with her she became seriously ill, and though she presently recovered, her beauty is entirely11 gone, so that she hates the very sight of herself, and is in despair
2.3.2. Literature exclusion standard
1) The research object was not mice;
2) The content of the literature was not fully explained and there was no control experiment;
3) Duplicate literatures or suspected plagiarism would be excluded;
4) Research data were indicated only as averages or direct readings;
5) In this study, experimental group was treated withPseudostellaria heterophylla
components and other agents;6) The subject indicators of this study was not involved in the literatures.
2.4. Statistic analysis
Stata 12 software was used to draw the network plot for the effects of different extracts ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on the immunology function in mice. ADDIS 1.16.6 software was used for Meta analysis and Network meta-analysis. In the Meta-analysis, mean difference (MD) was used as the statistical data, and each effect size was represented by 95%CI. The consistency model with system default parameters were used for Network meta-analysis. The potential scale reduction parameter (PSRF) was used to evaluate the convergence of the model results. If 1.00≤PSRF≤1.05, the convergence of the model was satisfactory, and the results obtained high reliability. For "closed loop" in the network plot, Nod-split model was used to determine whether there was local inconsistency among each node. IfP
>0.05, it indicated that there was no obvious inconsistency. Then, a Rank Probability was made to evaluate the probability for the effects of different extract inPseudostellaria heterophylla
on immunological function in mice.3. Meta analysis results
3.1. Literature retrieve and screening results
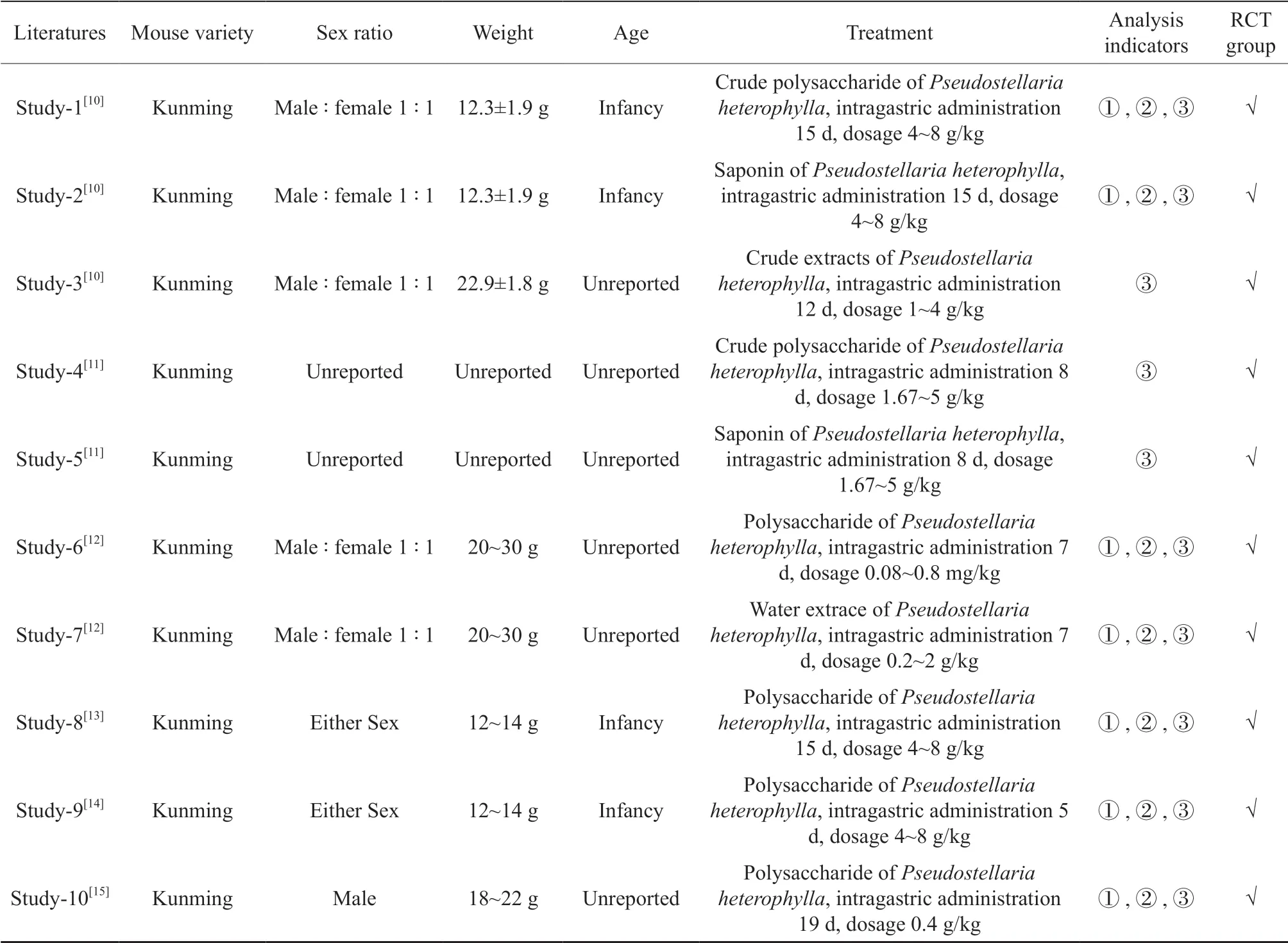
Table 1 Basic information of the included studies
3.2. Meta analysis results for the effects of different extract of Pseudostellaria heterophylla on immunological function in mice
There were 6 literaturesand 10 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reported the study on the effects of different components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on immunological function in mice and different components included crude extract, polysaccharides, saponins, respectively. As shown in Fig. 1-A-1, 1-A-2 and 1-A-3, the Meta analysis results for the effect of polysaccharides ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on the phagocytic index, spleen index and thymus index were [MD=0.63, 95%CI (0.25, 1.02),P
<0.05], [MD=0.78, 95% CI (0.37, 1.19),P
<0.05] and [MD=1.02, 95%CI (0.46, 1.58),P
<0.05], respectively. In the experiment group treated with polysaccharide, the confidence intervals of each indicator fell to the right of the invalid line and did not intersect with the invalid line. Compared with the control, the effect size of the experimental group was large, and the difference was statistically significant, indicating that the polysaccharide ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
could improve the immunological function in mice. As shown in Fig. 1-B-1, 1-B-2 and 1-B-3, the Meta analysis results for the effect of saponin ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on the phagocytic index, spleen index and thymus index were [MD=1.49, 95%CI (0.96, 2.02),P
<0.05], [MD=0.67, 95%CI (0.21, 1.13),P
<0.05] and [MD=0.83, 95%CI (0.58, 1.07),P
<0.05], respectively. In the experiment group treated with saponin, the confidence intervals of each indicator fell to the right of the invalid line and didnot intersect with the invalid line. Compared with the control, the effect size of the experimental group was large, and the difference was statistically significant, indicating that the saponin ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
could improve the immunological function in mice. As shown in Fig. 1-C-1, 1-C-2 and 1-C-3, the Meta analysis results for the effect of crude extract ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on the phagocytic index, spleen index and thymus index were [MD=1.36, 95%CI (0.22, 2.49),P
<0.05], [MD=0.98, 95%CI (0.45, 1.51),P
<0.05] and [MD=0.45, 95%CI (-0.06, 1.06),P
<0.05], respectively. In the experiment group treated with crude extract, the confidence intervals of phagocytic index and spleen index fell to the right of the invalid line and did not intersect with the invalid line. Compared with the control, the effect size of the experimental group was large, and the difference was statistically significant, indicating that the crude extract ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
could improve the level of some immunity indexes in mice. Therefore, different components ofPseudos- tellaria heterophylla
could improve the immunity of mice, and there were differences between different components.3.3. Network meta analysis results for the effect of different extract of Pseudostellaria heterophylla on immunological function in mice
3.3.1. Network relationship and model selection in Network meta analysis
A total of 6 literaturesand 10 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included for Network meta analysis. Intervention components were crude extract, polysaccharides, saponins respectively, with phagocytic index, spleen index and thymus index as evaluation indicator. The network plot of each outcome variable was shown in Fig. 2. In which, each circular node represented an intervention component, the larger the node, the more literatures involving the component. The line between the nodes represented the direct comparison between the two components, and the thickness of the line indicated the number of studies between the two components. Meanwhile, it can be seen from Fig. 2, there was a "closed-loop" study in the network relationship. Node-split model was used to obtain theP
value range between two components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
, which was 0.23~0.92,P
>0.05. It indicated that there was no obvious local inconsistency between the nodes and consistency model was suitable for Network meta analysis. ADDIS 1.16.6 software was used to obtain PSRF value, which was 1.00~1.02, indicating that the convergence of the consistency model was satisfactory and the results were reliable.3.3.2. Network meta analysis results
As can be seen from Fig. 1, the crude extract, polysaccharides and saponins ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
could improve immunological function in mice and there were difference between components. In order to expand the experimental samples and develop a multicenter randomized controlled trial (RCT), a Network meta-analysis was conducted to compare the effects of the three components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on the immunology function in mice. As shown in Table 2, the saponin had the best effect on the increase of phagocytic index and the differences were statistically significant [MD=1.50, 95%CI (0.71, 2.28),P
<0.05]; the polysaccharide and saponin had better effect on the increase of spleen index than the control and crude extract, and the differences were statistically significant [MD=0.77, 95%CI (0.27, 1.31),P
<0.05], [MD=0.71, 95%CI (0.01, 1.50),P
<0.05] respectively; the polysaccharide had the best effect on the increase of thymus index and the differences were statistically significant [MD=0.70, 95%CI (0.11, 1.34),P
<0.05]. It can be seen from Fig. 3, the saponin ofPseudos- tellaria heterophylla
had the maximum probability to increase phagocytic index of mice. The probability for the components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
increasing spleen index of mice was in the order of crude extract>polysaccharide>saponin. The probability for the components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
increasing thymus index of mice was in the order of saponin>polysaccharide>crude extract. The comprehensive analysis showed that the polysac- charide and saponin ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
were the effective components to improve immuno- logy function in mice, and had good effect.
Fig. 1 Meta-analysis for the effects of different extract of Pseudostellaria heterophylla on immunological function in mice

Fig. 2 Network plot of different outcome variables for Network meta-analysis
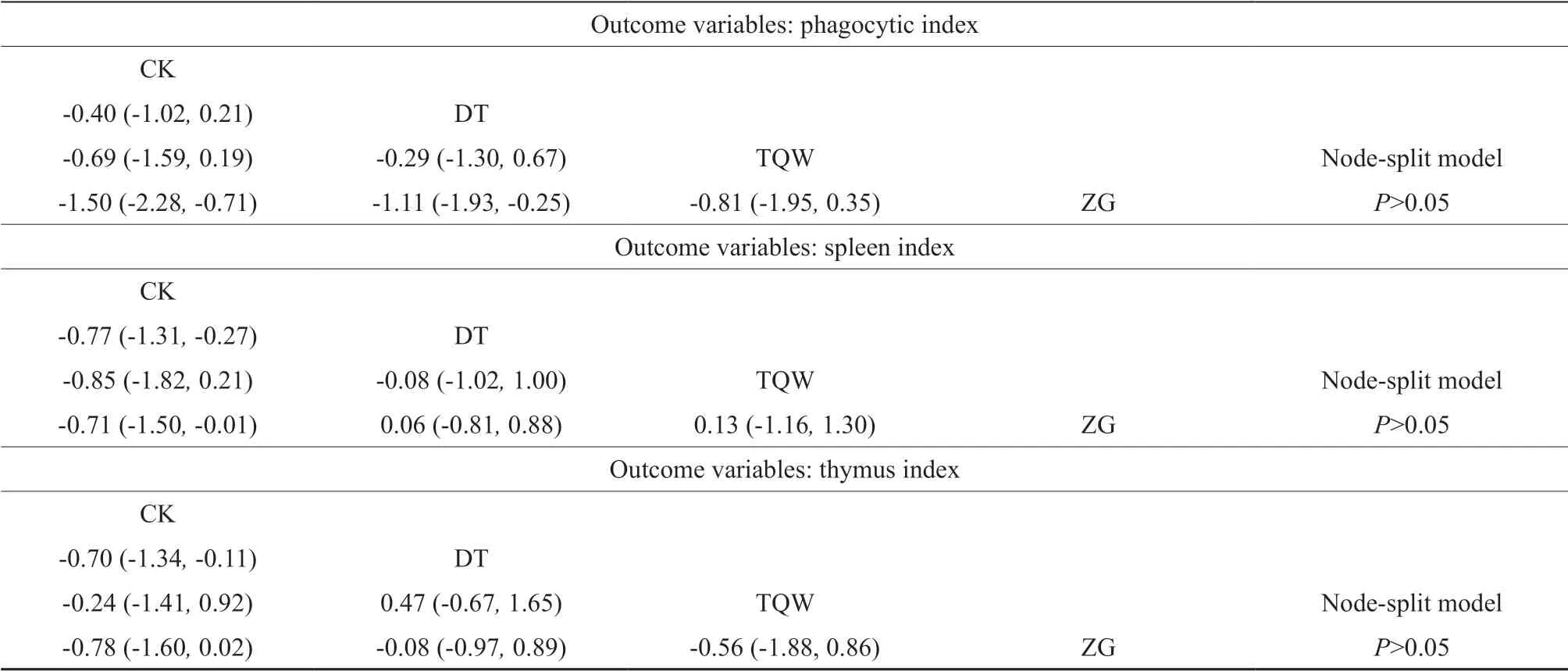
Table 2 Results of bayesian Network meta-analysis for different outcome variables

Fig. 3 The rank probability of the effect of different extract of Pseudostellaria heterophylla on immunological function in mice
4. Discussion
In this study, Network meta analysis was used to evaluate the effects of different extract ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on immunological function in mice with phagocytic index, thymus index and spleen index as indicators. In clinical, the clearance rate of charcoal particles was often used to determine phagocytic index, which can reflect the phagocytic ability of animal body. Thymus and spleen are important immune organs in animal body and the index of immune organs directly reflects the immune function of animal body. In this study, the results showed that the crude extract, polysaccharides and saponins ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
all could improve immunological function in mice compared with the control and there were differences between components, which was concluded from macro level. While, WANG J Ket al
. proved from the molecular level thatPseudostellaria heterophylla
could increase the contents of DNA in spleen and DNA and RNA in thymus of mice, and could promote the synthesis of nucleic acid in immune organs. The concentration of different components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
included in the Network meta-analysis in this study was significantly different, and it was difficult to evaluate the optimal clinical efficacy concentration of different components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
to improve the immunology function in mice from the existing research literature. Meanwhile, most of the age of mice included in this study were not reported or labeled. Therefore, bias was easy to occur in the Network meta-analysis, which was not conducive to the accuracy or stability of the analysis results.Meta-analysis and Network meta-analysis were conducted to analyze the results of multiple independent studies systematically, quantificationally and objectively based on statistical methods, and evaluate effect indicators accurately and scientifically, so as to provide a strong basis for clinical decision.In this study, only polysaccharides, saponins and crude extracts ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
were included and analyzed, and no other components were involved, which may result in research bias and reduce the reliability of the research results. Therefore, follow-up studies still need to expand the sample size, standardize clinical research methods and include high-quality literature.In this study, Network meta analysis showed that the different components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
can improve the immunology function in mice, and the comprehensive results suggested that polysaccharides and saponins were the effective components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
to improve the immune function of mice. Polysaccharide and saponins ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
had positive immune regulation effects, which indicated the tonic effect ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
. This study not only analyzed the immune effect ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
, but also compared the effects of different components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on each immune index, which was beneficial to the development ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
resources, and also beneficial to the research and application of new products ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
components.5. Conclusion
In this study, a total of 6 reports, 10 randomised controlled trials (RCTs) were included to evaluate the effects of different components ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
on the immunology function in mice based on Meta analysis and Network meta analysis. The results showed that the polysaccharides, saponins and crude extract all could improve immnunology function in mice; the saponin had the best effect on the increase of phagocytic index and the differences were statistically significant; the polysaccharide and saponin had better effects on the increase of spleen index, and the differences were statistically significant; the polysaccharide had the best effect on the increase of thymus index and the differences were statistically significant. Based on the existing literature, the polysaccharide and saponin ofPseudostellaria heterophylla
were the effective components for improving immunological function in mice and their immune effects were significant. Agricultural Science & Technology2021年2期
Agricultural Science & Technology2021年2期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Different Soil Preparation and Fertilizer Application Methods on the Growth and Yield of the Rice-Crayfish Rotation Direct Seeding Rice Nongxiang 32
- Influence of Seedling Age and Seeding Rate on Grain Yield in Double Cropping Rice with Machine Transplantation
- Genotype Analysis of Yuzhenxiang, a Long Grain, High Quality Aromatic Rice Cultivar
- Effects of Dust on Male and Female Floral Organs and the Pollination of the Walnut
- Comparision of the Leaf Morphology of Two Phoebe bournei Varieties
- Effects of Biochar on Physiological Characteristics of Lonicera Japonica and Accumulation of Cd and Pb in Cd and Pb Contaminated Soil
