BL Lac天体ON 231的光变周期研究*
徐云冰,张 雄,李孝攀,董富通
(1.云南师范大学物理与电子信息学院,昆明 650092;2.中国科学院国家天文台,北京 100012)
ON 231是活动激烈的BL Lac天体,天体的周期性光变现象可以给出天体内部的一些参数,进而可以研究其内部物理机制[1]。因此,人们对ON 231周期性的研究具有浓厚兴趣,很多人已经对其光变周期进行了研究并取得了很多成果。1987年,Xie等人发现了约6天的周期[2],这一结果与OJ 287不存在几天短时标光变的结果不一致[3];1988年,Barbieri等人用Deeming(1975)使用的功率谱分析方法没有发现ON 231有明显的周期[4-5];1995年,Liu F K等人找到了ON 231有(0.981±0.005)年、(13.6±1.3)年的周期[3];1998年,Zhang等人找到了(13.6±1.3)年、(26.6±0.8)年的周期[1]。但是,由于ON 231内部结构复杂且活动剧烈,其光变曲线也很复杂,另外,由于观测手段和天气等因素的限制,目前还没有很完备的长期样本数据库,因此,对ON 231周期性的明确认证总体来说还比较困难,其长周期光变有可能大于现有的观测历史,有待于进一步监测认证[1]。
本文主要利用Jurkevich方法[6]和小波分析法[7-8]研究了ON 231的历史光变资料中可能存在的周期。
1 ON 231的光变周期性分析
1.1 ON 231的光变曲线
ON 231的测光资料来源于文献[4,9-29],共收集了1374个B波段观测数据,获得了其天平均历史光变曲线如图1。从光变曲线可以看出天体活动十分剧烈,在1998年最亮时达mB=13.1mag,1984年最暗时达mB=17.80mag,在近110多年的观测中出现过多次大的爆发,从天平均的历史光变曲线很难看出明显的周期变化。
1.2 ON 231周期性分析
ON 231的观测资料表明它内部确实存在剧烈变化。它的长期光变周期一直没有最后确认,观测已经发现了很多次大的爆发结果。从这些结果可以看出,它有可能存在光变的周期性,有许多人用多种方法研究周期性,但由于计算方法的缺陷和观测数据的连续性差,确定的周期均未被观测验证,选用小波分析法研究其周期性,用Jurkevich方法进行比较,获得了较好的结果。当然,它的实际周期也有可能大于现有的观测资料[1]。
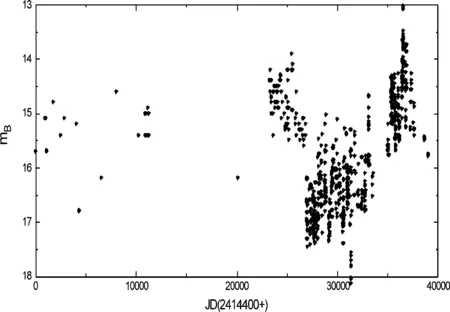
图1 ON 231 1898~2005年天平均的历史光变曲线
1.2.1 Jurkevich方法

如果f≥0.5,则表明样本数据有很强的周期性;如果f<0.25,则表明样本数据可能有弱的周期性;如果f=0,则表明样本数据没有周期性。


图2 用图1中的数据由Jurkevich方法寻找ON 231周期结果
1.2.2 小波分析法
小波分析法[7-8]是为了克服Fourier分析的不足而发展起来的,Fourier分析反映的是信号的整体特征,但不能刻画信号的局部特性。小波分析法是一种时频分析方法[31],既能在时域很好地刻画信号的局部性,同时也能在频域反映信号的局部性。它的基本思想是通过小波变换对信号进行多尺度分析,从而突出信号的局部特征。该方法已广泛应用于地震勘探、气象学等方面的周期性研究。
选用Morlet小波:ψ(t)=e-t2/2eiωt,容许性条件要求ω≥5。根据Morlet小波尺度因子a与周期T之间的关系[32]:
取ω=6.2,则周期T≈a。利用离散小波变换求出小波系数,然后给出小波系数的实部等值线图,等值线的变化即可反映出所分析数据在小波域中的波动情况。对时间域上的尺度因子a积分得到小波方差,再画出小波方差图。通过该图可以对一些复杂的非线性过程进行解释,从而确定其中的主要周期。
ON 231 1962年以前的数据点很少,只取了1962年以后的数据进行分析。为了平滑观测误差,对该时间段中的数据进行30天平均,再利用线性插值的方法对不等间隔的数据进行填充[8],以消除边界效应。图3给出了ON 231 1962~2005年B波段数据小波变换系数实部等值线图。图中显示星等值在小波域中高低起伏的变换情况,即反映了ON 231在时间域上的总体光变过程。
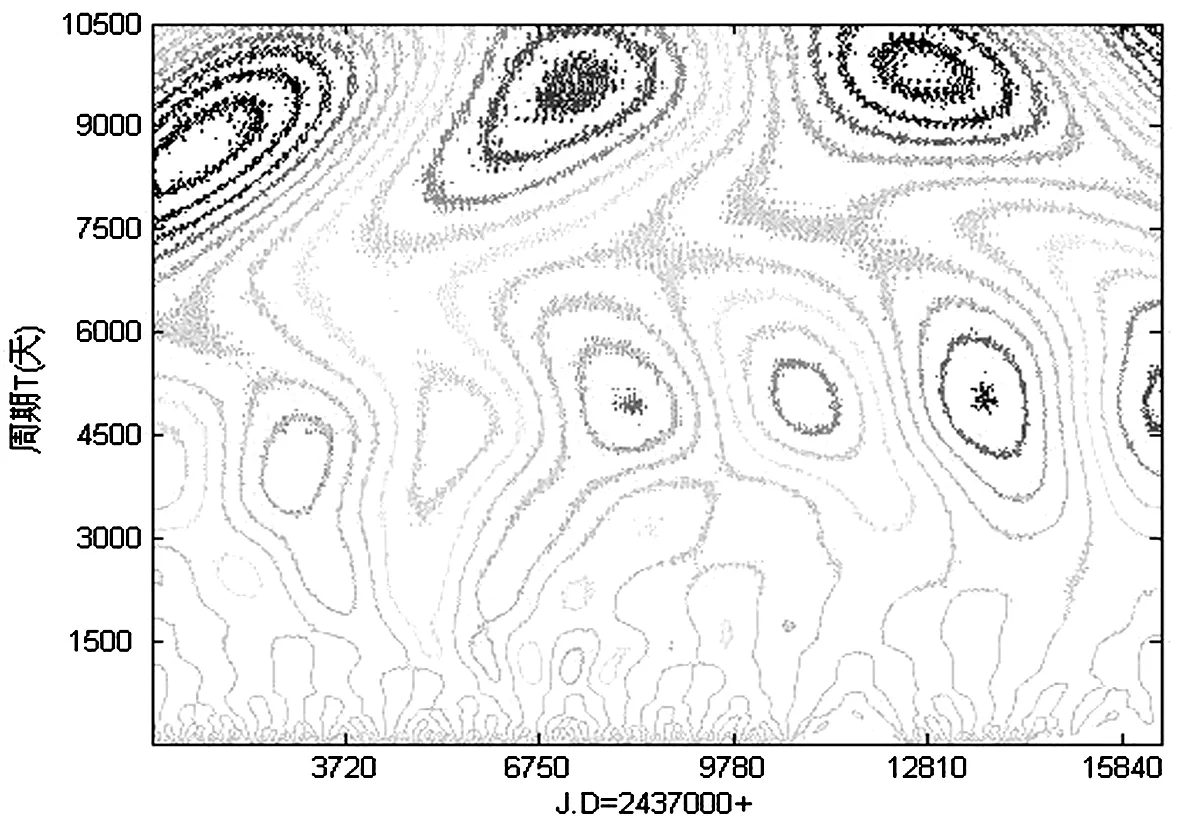
图3 ON 231 B波段数据小波变换系数实部等值线图
从图中等值线的变化可以看出在周期尺度T=4000~6000天之间和T=7500~10500天之间存在明显的周期性。为了确定其中的主要周期,作出其变换系数的小波方差图如图4。

图4 变换系数的小波方差图
从图4可以看出,在T=4940天和T=9520天处达到极大值,说明这两个值就是分析信号中含有的周期。T=4940天(13.5年),T=9520天(26.1年)与Liu F K等人[3]、Zhang等人[1]26.6±0.8年的结果基本一致。
1.3 中心黑洞质量估计
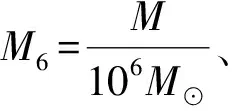


2 讨 论

作者认为,时标为几年的光变特性可能是由于通常在活动星系核中心区黑洞周围的吸积盘不稳定所致,特别是薄盘的热不稳定性可能导致爆发式振荡[36];双黑洞模型不是解释BL Lac天体长周期光变最理想的模型,长周期爆发不可能完全起源于双黑洞[1]。
3 结 论
综上所述,ON 231具有0.978年、4940天(13.5年)和9520天(26.1年)的周期。其中T=0.978年与Liu F K等人[3]的0.981±0.005年一致;T=13.5年和T=26.1年,与Liu F K等人[3]、Zhang等人[1]的13.6±1.3年和26.6±0.8年的结果一致。
[1] 张雄,谢光中,白金明.用Jurkevich方法计算BL Lac天体的光变周期[J].天体物理学报,1998,18(3):260-268.
Zhang Xiong,Xie Guangzhong,Bai Jinming.Computing the Period of Light Variability in BL Lac Objects Using the Jurkevich Method[J].Acta Astrophysica Sinica,1998,18(3):260-268.
[2] Xie G Z,Li K H,Bao M X,et al.The optical variability of seven BL Lacertae objects[J].A &AS,1987,67:17-24.
[3] Liu F K,Xie G Z,Bai J M.An historical light curve of ON 231 and its periodic analysis[J].A&A,1995,295:1-10.
[4] Barbieri C,Cappellaro E,Romano G,et al.Optical variability of 16 quasi stellar objects[J].A&AS,1988,76:477-487.
[5] Deeming T J.Fourier analysis with unequally-spaced data[J].APSS,1975,36(1):137-158.
[6] Jurkevich I N.A method of computing periods of cyclic phenomena[J].APSS,1971,13(1):154-167.
[7] Christopher Torrence,Gilbert P Compo.A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,1998,79(1):61-78.
[8] 董富通,张雄.类星体3C345的光变周期特性[J].物理学报,2009,58(11):8116-8122.
Dong Fu-Tong,Zhang Xiong.Analysis of the variability periodicities of quasar 3C345[J].Acta physica sinica,2009,58(11):8116-8122.
[9] Craine E R,Warner J W.Optical variations of OJ 287,ON 231,and OQ 208[J].ApJ,1973,179:L53-L56.
[10] Wing R F.UBV sequences in the fields of radio sources[J].AJ,1973,(78):684-686.
[11] Pollock J T,Hall D J,Ambruster C,et al. A Sustained Pulse from ON 231[J].A&A,1974,30:41-43.
[12] McGimsey B Q,Smith A G,Scott R L,et al.Optical behavior of 20 violently variable extragalactic radio sources[J].AJ,1975,80:895-922.
[13] V’eron P,V’eron M P.Photographic Photometry of Five BL Lacertae-type Objects[J].A&A,1975,39:281-288.
[14] Tapia S,Craine E R,Jahnson K.Four-point optical energy distributions for faint BL lacertae objects[J].ApJ,1976,203:291-296.
[15] Pollock J T,Pica A J,Smith A G,et al. Long-term optical variations of 20 violently variable extragalactic radio sources[J].AJ,1979,84:1658-1676.
[16] Barbieri C,Romano G.Survey of the optical variability of compact extragalactic objects.IV.Objects from 12#to 16#[J].A&AS,1981,44:159-162.
[17] Schaefer B E.A search for rapid variability in eight quasars and BL Lacertae objects[J].PASP,1980,92:255-258.
[18] Zekl H,Klare G,Appenzeller I.Optical Brightness Variations of BL Lac Objects[J].A&A,1981,103:342-348.
[19] Gruze-Gonzalez I,Huchra J P.Continuum distributions of an x-ray observed sample of BL Lac objects[J].AJ,1984,89:441-465.
[20] Webb J R,Smith A G,Leacock R J,et al.Optical observations of 22 violently variable extragalactic sources:1968-1986[J].AJ,1988,95:374-397.
[21] Xie G Z,Li K H, Bao M X,et al.The optical variability of seven BL Lacertae objects[J].A&AS,1987,67:17-24.
[22] Xie G Z,Li K H,Zhou Y,et al. The optical variability of two x-ray-selected and nine radio-selected BL Lac objects[J].AJ,1988,96:24-29.
[23] Xie G Z,Li K H,Cheng F Z,et al.Search for short variability time-scales of BL Lacertae objects[J].A&A,1990,229(2):329-339.
[24] Xie G Z,Li K H,Cheng F Z,et al.CCD photometry of 10 BL Lacertae objects[J].A&AS,1991,87(3):461-469.
[25] Xie G Z,Li K H,Liu F K,et al.CCD photometry of 14 BL Lacertae objects and theoretical model[J].ApJ S,1992,80(2):683-699.
[26] Tosti G,Fiorucci M,Luciani M,et al.BVRcIcmonitoring of ON 231 during the great outburst in 1994-1997[J].A&AS,1998,130:109-115.
[27] Fan J H,Lin R G.Optical variability and periodicity analysis for blazars I Light curves for radio-selected BL Lacertae objects[J].ApJ,2000,537:101-122.
[28] Tosti G,Massaro E,Nesci R, et al. The optical behaviour of ON 231(W Comae)during and after the great outburst of spring 1998[J].A&A,2002,395(1):11-15.
[29] Babadzhanyants M K,Belokon’ E T.Optical monitoring of the BL Lac object ON 231 in 1972-1990[J].ARep,2002,46(8):609-625.
[30] Kidger M,Takalo L,Sillanpaa A.A new analysis of the 11-year period in OJ287:Confirmation of its existence[J].A&A,1992,264(1):32-36.
[31] 彭玉华.小波变换与工程应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2002.
[32] Meyers S D,Kelly B G,O’Brien J J.An Introduction to Wavelet Analysis in Oceanography and Meteorology:With Application to the Dispersion of Yanai Waves[J].Mon Wen Rev,1993,121(10):2858-2866.
[33] Wallinder F H,Abramowicz M A,Kato S.Variability of the central region in active galactic nuclei[J].A&AR,1992,4(2):79-122.
[34] Honma F,Kato S,Matsunioto R.Nonlinear oscillations of thermally unstable slim accretion disks around a neutron star or a black hole[J].PASJ,1991,43(1):147-168.
[35] Horiuch T,Kato S.A model of hydromagnetic turbulent viscosity in radiation-pressure-dominated disks[J].PASJ,1990,42(5):661-674.
[36] 樊军辉,G E Romero,林瑞光.3C273的光学光变周期[J].天文学报,2001,42(1):9-15.
Fan Junhui,G E Romero,Lin Ruiguang.The Optical Variability Periodicity Analysis of 3C273[J].ACTA Astronomica Sinica,2001,42(1):9-15.

