弹性髓内针治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折的临床应用研究
李兵 张军 张亚军
弹性髓内针治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折的临床应用研究
李兵 张军 张亚军
目的探讨弹性髓内针治疗桡骨颈骨折疗效。方法我院于2006年5月至2009年9月应用弹性髓内针治疗23例桡骨颈骨折患者,其中男性17例,女性6例,年龄6~13岁,平均9.3岁。摔伤21例,绞伤2例。按Judet分型,其中Ⅱ型3例、Ⅲ型16例、Ⅳ型4例。合并肘关节其他部位损伤3例,其中肘关节内侧副韧带损伤2例,肱骨内上髁骨折1例。结果术后随访6~38个月,平均17.5个月。根据Métaizeau术后X线片评价标准,优18例、良3例、中2例,优良率达91%。功能评价采用Métaizeau功能评价标准,优16例、良6例、一般1例,优良率达96%。其中2例桡骨头骺变形膨大,1例出现关节周围异常钙化。结论弹性髓内针治疗桡骨颈骨折操作简便,效果满意。
弹性髓内针;骨折,桡骨颈
桡骨颈骨折在肘关节骨折中约占5%~10%[1-2],多数为无移位或轻微移位骨折,保守治疗效果满意,而对于严重移位的桡骨颈骨折,临床上对于其治疗方法的选择及疗效存在争议。目前文献报道的治疗方法及疗效不一,而诸如桡骨头坏死、肘关节功能障碍等并发症也困扰着临床医生。为探讨桡骨颈骨折的治疗方法,为临床诊治积累经验,我院于2006年5月至2009年9月应用弹性髓内针治疗23例桡骨颈骨折患者,疗效满意,现总结报道如下。
材料和方法
一、一般资料
自2006年5月至2009年9月,我院共收治桡骨颈骨折患者23例。其中男性17例,女性6例,年龄6~13岁,平均9.3岁。致伤原因:摔伤21例、机器绞伤2例;右侧20例、左侧3例;手术距受伤时间1~5d,平均2.3d。合并肘关节其他部位损伤3例,其中肘关节内侧副韧带损伤2例、肱骨内上髁骨折1例。所有患者入院后给予X线和CT检查,并根据桡骨颈成角移位的严重程度,按Judet分型:其中Ⅱ型3例、Ⅲ型16例、Ⅳ型4例。
二、治疗方法
1.闭合复位弹性髓内针内固定:患者取仰卧位,麻醉满意后,患肢外展,放于侧台上,C臂X线透视下,在桡骨远端桡侧骺板近端1~2cm处切口,保护桡神经浅支及周围肌腱,以尖锥在桡骨远端桡侧垂直骨皮质开髓,待尖椎头进入髓腔后,改变尖椎角度,使之与桡骨干交角约为45°,继续向桡骨近端刺入,将尖端预弯好AO弹性髓内针插入髓腔内,针的直径以桡骨干最小横径的1/2~2/3为宜[3],将针体向近端旋转推进直至桡骨头,牵引前臂,并将肘关节内翻以扩大肱桡关节间隙,按压移位的桡骨头,矫正成角移位,同时将弹性髓内针尖端推至并顶住桡骨头,进一步矫正成角畸形,使用T柄旋转髓内针纠正桡骨头侧方移位。C臂X线透视复位满意后,轻轻击打弹性髓内针尾端,使其进一步稳定固定折端,剪断髓内针尾,使之有0.5cm长度留置于桡骨远端骨皮质外,方便取出。术后患肢屈肘90°中立位石膏固定。
2.克氏针经皮撬拨弹性髓内针内固定:对于桡骨头倾斜角度较大的患者,由于桡骨颈外侧缘常有不同程度嵌插和压缩,关节周围的关节囊被撕裂破坏,闭合复位桡骨头可能较为困难,此时需要经皮辅助克氏针复位骨折端。一位助手牵引患者上臂,另一位助手牵引前臂做对抗,将肘关节内翻以扩大肱桡关节间隙,维持肘关节半屈曲位。术者右手持1枚克氏针,于肘外下方视桡骨头移位情况选择进针点,在C臂X线透视下,将克氏针进至骨折端,利用远折面作支点,桡骨小头外侧皮质为受力点,抬高针尾,通过克氏针尖端撬拨桡骨小头,同时左手拇指逆骨折移位方向推挤桡骨小头使其复位。之后打入弹性髓内针,进一步辅助骨折端复位和固定。
3.切开复位弹性髓内针内固定:对于骨折端移位较大,闭合复位及辅助克氏针复位后仍不能复位的患者,为防止进一步闭合复位导致的软组织损伤,可行切开复位。术中要注意防止损伤桡神经深支,显露桡骨头后将其复位,在C臂X线透视下,打入弹性髓内针,维持骨折端复位。
三、合并损伤治疗
本组合并肘关节其他部位损伤3例,其中肘关节内侧副韧带损伤2例,肱骨内上髁骨折1例。对于2例肘关节内侧副韧带损伤的患者未行特殊治疗。1例肱骨内上髁骨折患者,在治疗桡骨颈骨折同时,肘关节内侧切口,行肱骨内上髁切开复位内固定。
四、术后处理
术后所有患者给予常规抗炎治疗3d,患肢屈肘90°,中立位,石膏固定3~4周,拆除石膏,指导患者以健侧肢体辅助患侧肘关节自行进行主动屈伸及前臂旋前、旋后功能锻炼,尽可能减少被动功能锻炼,以防止出现过度疼痛及异位骨化。分别于术后6周、12周、6、12、24、36个月进行随访,随访内容包括:摄X线片,了解骨折愈合情况和桡骨头变化,了解肘关节功能恢复情况及是否存在并发症。
结 果
一、疗效评定标准
按照Métaizeau术后X线片评定标准评定[4]:解剖复位为优;倾斜成角<20°为良;20°~40°为中等;>40°为差。后期则按照Métaizeau功能评定标准[4]:肘关节及前臂活动无受限为优;肘关节屈伸或前臂旋前、旋后受限活动度之和<20°为良;肘关节屈伸或前臂旋前、旋后受限活动度之和介于20°~40°为一般;>40°为差。
本组全部患者中,有2例切开复位,6例克氏针经皮撬拨辅助复位,其余15例均为单纯闭合复位,弹性髓内针固定。手术时间20~50min,平均36.4min。术中出血5~20ml,平均8.3ml。术后石膏固定3~4周,平均3.7周。术后骨折愈合时间3~4周,平均3.7周。去除内固定时间为术后3~12个月,平均4.7个月。术后随访6~38个月,平均17.5个月。术后X线片评定:优18例、良3例、中2例,优良率达91%。功能评价:优16例、良6例、一般1例,优良率达96%。无感染、骨折不愈合、迟延愈合病例。2例桡骨头骺变形膨大,1例出现关节周围异常钙化(表1)。

表1 桡骨颈骨折患者分型、复位方式与术后X线片评定、功能评定结果统计
二、典型病例
患者肖某,男性,10岁,因摔伤致肘部肿痛、活动受限,于伤后1d就诊于我院,摄X线片,诊断为桡骨颈骨折(图1)。完善化验后,于伤后2d在臂丛麻醉下,行左桡骨颈骨折闭合复位,弹性髓内针内固定术,术后骨折复位及内固定物位置良好(图2),常规抗炎换药,屈肘90°中立位石膏固定3周,去除石膏,指导患肘关节进行主动屈伸及前臂旋前、旋后功能锻炼,术后4周骨折愈合。术后9个月摄X线片显示骨折愈合良好,未见明显骨骺膨大及桡骨头坏死征象(图3)。查体显示,患侧旋转功能较健侧完全恢复(图4,5)。

图1 术前X线片示桡骨颈骨折 图2 术后X线片示骨折复位、内固定物位置良好 图3 术后9个月X线片示骨折愈合良好,未见明显骨骺膨大及桡骨头坏死征象
讨 论
一、桡骨颈骨折的特点
桡骨颈骨折多发于儿童,主要原因是儿童跌倒时,前臂旋前肘关节伸直位,应力延前臂桡侧向上传递,肘关节易受到垂直及外翻应力作用,而儿童在骨发育成熟前,韧带连接强度是骨与软骨连接强度的2~5倍,骺板及干骺端成为生物力上的薄弱区,同时由于桡骨颈的生理结构的特点,即桡骨颈与骨干约呈平均12.5°外倾和3.5°前倾,从而导致桡骨颈骨折,并出现成角移位,如应力进一步传递,还可以导致肘关节内侧附韧带、肱骨内上髁、尺骨鹰嘴等合并损伤。损伤应力越大,桡骨颈移位越严重,合并的损伤越多。

图4 术后9个月外旋功能恢复情况
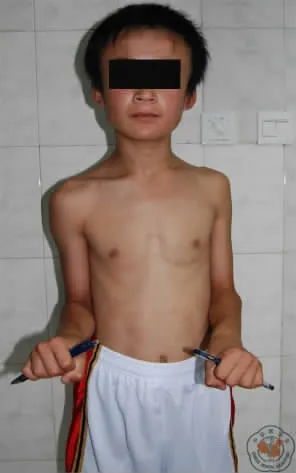
图5 术后9个月内旋功能恢复情况
二、诊断要点
通过查体和标准的肘关节正侧位X线片,桡骨颈骨折的诊断并不困难。但对无明显移位的青枝骨折或嵌插骨折,应该引起注意,故对于症状重、体征明显而X线片无明显骨折的患者,应详细查体,拍健侧X线片对照,必要时行CT检查。对于骨折移位严重的患者,应该重点检查肘关节的稳定性,防止漏诊肘关节合并损伤。本组合并肘关节其他部位损伤3例,其中肘关节内侧副韧带损伤2例、肱骨内上髁骨折1例,均为JudetⅣ型患者。近年来有双侧桡骨颈骨折的报道[5-6],故对于双手同时着地的患者,要详细询问受伤史,对双上肢伤情进行物理和影像学检查,防止漏诊。
三、治疗
由于桡骨颈骨折多为SalterHarrisⅠ、Ⅱ型损伤或干骺端骨折,因此尽可能要求解剖复位。对于JudetⅠ型和多数Ⅱ型骨折通过保守治疗即可。但是对于移位较大的不稳定骨折或对肘关节功能要求高,难以配合长时间肘关节制动Ⅱ型患者需通过手术来治疗。本组3例Ⅱ型骨折患者,均难以配合长时间石膏固定,故均采用手术治疗。对于桡骨颈骨折手术的方法选择,临床上一直存在争议。一些学者认为单纯闭合复位或经皮克氏针撬拨复位及石膏外固定[3,7-8],复位效果及骨折端的稳定性均无法确切维持,可能发生继发性移位。切开复位曾是一些学者的选择,但是由于切开复位可能使受损的桡骨头血运进一步损伤,有可能导致桡骨头坏死、异位骨化等并发症,有学者报道[9]切开复位并发症的发生率超过50%。对于内固定物的选择,有学者认为可以在骨折复位后,通过桡骨头外侧斜行向桡骨远段内侧固定克氏针,但是该方法操作较为困难,有损伤桡神经的可能,在患者功能锻炼时,由于克氏针影响肌肉滑动,可能引起不适感。另外,有学者建议通过肱骨小头与桡骨头贯穿克氏针固定[6],但是进一步损伤了肱桡关节,可能引起肘关节后期的功能障碍。此外,较细的克氏针通过桡骨头、桡骨颈后进入桡骨髓腔,无法确切稳定骨折端,而较粗的克氏针,又会导致骨骺的损伤,因此该方法并非首选。
1980年,法国Métaizeau报道通过髓内针治疗桡骨颈骨折取得良好疗效,之后在此基础上,众多学者进行了临床研究[10-12]。对于移位较大的桡骨颈骨折,保护骨折端的血运的同时尽可能稳定骨折端。近来有文章报道,对于复位困难的骨折,可以采用将克氏针打入桡骨头,通过控制克氏针尾复位成功的技术[13],但本组患者除2例患者闭合复位不成功后改用切开复位,其余均采用闭合复位或经皮撬拨复位成功,而弹性髓内针的使用,兼有复位和固定骨折端的作用。术中入髓内针前,一定要通过C臂X线透视,避开桡骨远端骨骺。插入弹性髓内针后,争取一次复位成功,不要反复通过髓内针复位,否则会引起骨折端骨道扩大,导致复位困难及固定效果差。留置于桡骨远端的针尾不宜过长,以0.5cm为宜,防止出现局部假性囊肿,引起不适。术后尽早去除石膏外固定,指导患者进行功能锻炼。本文中多数患者取得良好疗效,1例切开复位的患者,术后关节外可见异位骨化,关节功能受限,因患者无进一步功能要求,未做处理。另外2例患者桡骨头骺变形膨大,考虑与骨折及治疗中的进一步骨骺损伤有关,但是对于肘关节功能影响不大,故未做处理。该结果与文献的报道一致[3,8,14-15]。
本组患者治疗效果满意,并发症较少,分析可能有以下原因:(1)本组患者多数为JudetⅢ型患者,损伤相对较轻,肘关节合并损伤较少;(2)本组患者年龄均较小,肘关节代偿塑形能力较强[16];(3)手术损伤较小,术后早期功能锻炼。不过本组患者随访时间较短,平均17.5个月,对于远期效果还不明确。总之,弹性髓内针是一种具有微创、出血少、不干扰骨折端愈合、并发症低,并兼有复位和固定作用的一种治疗桡骨颈骨折的方法,值得在临床上推广。
[1]Fowles JV,Kassab MT.Observations concerning radial neck fractures in children[J].J Pediatr Orthop,1986,6(1):51-57.
[2]Radomisli TE,Rosen AL.Controversies regarding radial neck fractures in children[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1998(353):30-39.
[3]钱驭涛,王玉琨,张建立,等.弹性髓内针治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(24):1867-1870.
[4]Metaizeau JP,Lascombes P,Lemelle JL,et al.Reduction and fixation of displaced radial neck fractures by closed intramedullary pinning[J].J Pediatr Orthop,1993,13(3):355-360.
[5]K se O,Demiralp B,K mürcü M.Bilateral radial neck fractures in a child:report of a case[J].Pediatr Emerg Care,2008,24(7):464-465.
[6]李俊龙,刘志松,祁振良.双侧桡骨颈骨折一例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(8):683.
[7]Prathapkumar KR,Garg NK,Bruce CE.Elastic stable intramedullary nail fixation for severely displaced fractures of the neck of the radius in children.J Bone J Surg Br,2006,88(3):358-361.
[8]姜星明,刘文霞,王红建.弹性髓内钉治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2008,14(5):287-288.
[9]Gonzalez Herranz P.Displaced radial neck fractures in children treated by closed intramedullary pinning(Metaizeau technique)[J].J Pediatr Orthop,1997,17:325-331.
[10]孙建华,张新虎,周连军,等.闭合复位弹性髓内钉固定术与切开复位克氏针固定术治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(6):661-665.
[11]Klitscher D,Richter S,Bodenschatz K,et al.Evaluation of severely displaced radial neck fractures in children treated with elastic stable intramedullary nailing[J].J Pediatr Orthop,2010,29(7):698-703.
[12]姚陆丰,叶招明,李朝旭,等.弹性髓内针治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(12):1028-1031.
[13]Yarar S,Sommerfeldt DW,Gehrmann S,et al.Severely displaced radial neck fractures after minimally invasive joystick reduction and Prévot nailing:long-term course in childhood[J].Unfallchirurg,2007,110(5):460-466.
[14]Ursei M,Sales De Gauzy J,Knorr J,et al.Surgical treatment of radial neck fractures in children by intramedullary pinning[J].Acta Orthop Belg,2006,72(2):131-137.
[15]Métaizeau JP.Reduction and osteosynthesis of radial neck fractures in children by centromedullary pinning[J].Injury,2005,36(Suppl 1):A75-A77.
[16]米琨,钟远鸣,周宾宾,等.儿童桡骨颈骨折的治疗及远期疗效评估[J].医学文选,2003,22(1):27-29.
Clinical application of elastic stable intramedullary nail in treatment of radial neck fractures
LiBing,ZhangJun,ZhangYajun.DepartmentofTraumaandOrthopaedic,TheSecondWujingHospital,Beijing100037,China
:ZhangYajun,Email:zhangyajun@vip.sina.com
BackgroundRadial neck fractures account for 5%-10%in elbow joint fractures and most of them are slightly displaced or non-displaced types.Satisfactory therapeutic results can be achieved by conservative treatment.As to severe displaced radial neck fractures,it is controversial in selection of therapeutic methods and curative effect clinically.To explore clinical therapeutic effect of radial neck fractures with elastic intramedullary nail and accumulate experience for diagnosis and treatment,23cases of radial neck fracture were treated with elastic intramedullary nail from May 2006 to September 2009in our hospital.MethodsFrom May 2006to September 2009,23cases of radial neck fracture were admitted into our hospital and treated with elastic intramedullary nail,including 17 male and 6female,aged from 6to 13,and the average age was 9.3years.Traumatic mechanisms were classified as fallen injuries with 21cases and wringer injuries with 2cases.Twenty cases were in right elbow and 3cases were in left elbow.Operation time from injury ranged from 1to 5days,and averaged in 2.3days.There were 3cases of associated injuries on other parts of the elbow joint,including 2cases of medial collateral ligament injury and 1case of fracture of medial epicondyle of humerus.All patients were given X-ray and CT examinations after hospitalization.According to the severity of radial neck angular displacement and Judet classification system,3patients were classified into type II,16patients into typeⅢ,and 4patients into type IV.Close reduction and elastic intramedullary nail fixation:After successful anesthesia,the patient was in spine position with the affected limb abducted.The nail would be inserted from distal to proximal.The insertion site was just 1to 2cm proximal to the distal radial epiphyseal plate level.A small incision was made.The underlying tendons and superficial branch of radial nerve were well protected.An awl was used perpendicular to the lateral radius to open the cortex.And then proceeded the awl 45°to radial shaft into bone canal.An AO elastic intramedullary nail was pre-bended on its tip and inserted into radius retrorward.The optimal diameter of the nail was 1/2-2/3of the minimum transverse diameter of the radial shaft.Proximally rotated,the nail body is pushedto the radial head with traction of the forearm,and the space of humeroradial joint is broadened by varus of the elbow.The displaced radial head was pressed from outside by doctor’s finger to correct angular deformity.Then the elastic intramedullary nail was further introduced into the radial head to achieve further angular correction.The nail was then rotated by its T handle to correct lateral displacement of the radial head.After successful reduction under Carm fluoroscopy,gently hammer at the nail tail for further stability of fracture end.Cut off the nail tail with 0.5cm left out of cortical bone in the distal radius,which will make it convenient for extraction.After the operation,the elbow joint is fixed with plaster in 90°flexion of neutral position.Percutaneous poking reduction by Kirschner wire and elastic intramedullary nail fixation:For patient with large tilted angle of radial head,the lateral borders of the radial neck have impacted or compression fracture of various levels and the periarticular joint capsule is lacerated or interrupted,resulting in difficulties of closed reduction for radial head,hence,percutaneous reduction of fracture end with Kirschner wire assisted is essential.With the traction of forearm by one assistant and the countertraction of upper limb by the other,the space of humeroradial joint is enlarged by the varus of elbow maintained in semiflexion.The selection of entry point depends on the situation of fracture displacement in the lower outer bottom of the elbow.Kirschner wire in the right hand,the operator put it into the fracture end under the C arm fluoroscopy.Through the use of distal fracture end as fulcrum and lateral bone cortex of radial head as pressure point,the reduction is gained by elevating the nail tail,poking the radial head with the tip of Kirschner wire,and in the meanwhile pushing it in the reverse direction of fracture shift via the left thumb.After that,the intramedullary nail is inserted to further assist the reduction and fixation of fracture end.Open reduction and elastic stable intramedullary nail fixation:For patient with large fracture displacement and inefficiency of closed or Kirschner wire assisted reduction,it is feasible to perform open reduction in order to prevent soft tissue damage caused by further closed reduction.Intraoperative attention should be paid to prevent damage to the deep branch of radial nerve,then expose and reduce the radial head under the fluoroscopy of C arm,and insert the elastic intramedullary nail to maintain the reduction of fracture ends.Treatment of combined injury:There are 3patients with injuries on other parts of the elbow joint in this group,including 2cases of medial collateral ligament injury and 1case of humeral medial epicondyle fracture.No special treatment was given to the 2patients with medial collateral ligament injury.Open reduction and internal fixation via medial incision of elbow joint as well as treatment of radial neck fracture were conducted at the same time in treatment of humeral medial epicondyle fracture.Postoperative management:All patients were given regular anti-inflammation therapy within 3days after operation.The affected limb was externally fixed with plaster in 90°flexion of the elbow joint for 3or 4weeks.After removal of the plaster,the patients were instructed to take functional exercises of forearm pronation and supination as well as elbow flexion and extension.Follow- ups were conducted in the 6thweek,12thweek 6thmonth,1styear,2ndyear,and the 3rdyear,including taking X-ray films,understanding the state of fracture healing and change of radial head,and as well understanding the state of functional recovery of elbow joint and whether complications did exist.ResultsEvaluative criteria of curative effect:In accordance with Métaizeau postoperative X-ray assessment standards:Anatomic reduction is excellent;tilted angle<20°is good;tilted angle ranging from 20°to 40°is medium;tilted angle>40°is poor.In accordance with Métaizeau functional evaluative standards in the later stage:No limitation of elbow and forearm activity is excellent;The sum of the limited elbow flexion and extension activity,or the limited forearm pronation and supination activity<20°is good;The sum of the limited elbow flexion and extension activity,or the limited forearm pronation and supination activity ranging from 20°to 40°is good,and>40°is poor.2All patients of this group include 2cases of open reduction,6cases of percutaneous poking assisted reduction by Kirschner wire,and the remaining 15cases of simple closed reduction and elastic intramedullary nail fixation.The operative time ranged from 20to 50minutes,and the mean time is 36.4minutes.Intraoperative bleeding was from 5to 20ml with the average of 8.3ml.The duration of external fixation with plaster was 3to 12months and the average period was 3.7months.Fracture healing time after operationranged from 3to 4months,and the mean time was 3.7months.The time of removing internal fixator was 3to 12months with an average of 4.7months.Postoperative follow-ups last 6to 38months and the average is 17.5months.Postoperative X-ray assessment:18cases were excellent,3cases were good,1case was normal,and the assessment was good and excellent in 91%.Functional assessment was conducted by on the basis of Métaizeau functional evaluative standards:16cases were excellent,6 cases were good,1case was normal,and the assessment was good and excellent in 96%.Among the patients were 2cases of enlargement deformation of the radial head epiphysis and 1case of periarticular abnormal calcification.No case of infection,nonunion and delayed union was detected.ConclusionsElastic intramedullary nailing for radial neck fracture is a treatment method with minimal invasiveness,less bleeding,less interference with fracture healing,low complication rate,and the act of both reduction and fixation.It is simply operated in treatment of radial neck fracture with satisfactory effects,and worth of promoting in clinical practice.
Elastic stable intramedullary nail;Fractures,radial neck
2014-03-10)
(本文编辑:李静)
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2014.02.006
100037 武警北京总队第二医院骨科
张亚军,Email:zhangyajun@vip.sina.com
李兵,张军,张亚军.弹性髓内针治疗儿童桡骨颈骨折的临床应用研究[J/CD].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2014,2(2):97-102.

