ELISA Detection of Antibody against Canine Distemper Virus in Fox
Yanying ZHANG,Huipeng LU,Xiaoshan WANG,Yangliu GUO,Nan WU,Yanyun LI,Qiumei SHI,Chao GAO
Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hebei Province,Hebei Normal University of Science&Technology,Changli 066600,China
ELISA Detection of Antibody against Canine Distemper Virus in Fox
Yanying ZHANG,Huipeng LU,Xiaoshan WANG,Yangliu GUO,Nan WU,Yanyun LI,Qiumei SHI*,Chao GAO
Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hebei Province,Hebei Normal University of Science&Technology,Changli 066600,China
Canine distemper is one of the most important common viral epidemics in farmed foxes.In this study,the whole blood samples of foxes that had been immunized with canine distemper vaccine were collected from a farming area in Changli County.The antibody against canine distemper virus in the 85 prepared serum samples were detected with a double-antibody sandwich ELISA method.The results showed among the 85 samples from the 4 farms,81 samples were antibody-positive,and only 4 samples had no antibody against canine distemper.The overall antibody level was higher in that farming area.It is indicated canine distemper vaccination and vaccination program have gotten attention from most of the local farmers,and the immune effect of canine distemper vaccine is better.
Canine distemper in fox;Antibody;ELISA
C anine distemper(CD)is caused by canine distemper virus,which is a kind of acute infectious RNA virus that can infect more than 40 kinds of rare wildlife, economic animals and domestic pets. Canine distemper can occur throughout the year,but winter and spring are the high seasons.Foxes of all ages are susceptible to canine distemper. However,2.5-5 month-old foxes are most sensitive,and they are most vulnerable to infection of canine distemper virus[1].The incubation period of canine distemper is usually 3-7 d. Once infected,foxes willhave a continuously-increased body temperature (up to 40-41℃),severe depression, dry rhinariums,less or even rejected feed intake,yellow oliguria and dry stool[2].The body temperature willfirst rise continuously for 2-3 d and then declines to normal level.After 2-3 d, the body temperature will rise again, and then the symptoms will be worsened.Conjunctivitis,conjunctival flushing,photophobia and tearing will occur.Serous,sticky and purulent secretion willbe heaped around the corners of eyes.Rhinariums willbe drier, and sticky and purulent snot willeven flow out.In terms of respiratory system,cough and dyspnea will be shown.Constipation will first occur, and it is followed by diarrhea.There is often intestinal mucosal shedding in the feces.In the facial and foot skin, blisters will be emerged.The blisters willbe festered,ulcerated and scarred then.The footpads will be first inflamed and then hardened.In addition, the neurological symptoms,such as excitement,muscle tremors and circling will also be shown in foxes[3-5]. Canine distemper is one of the most important common epidemics in farmed foxes.Itnotonly brings serious economic losses to the farms(households)butalso affects and restricts seriously the rapid development of the whole industry.
In recent years,canine distemperin foxes has been better prevented and controlled through vaccine inoculation.However,due to various reasons,canine distemper still outbreaks in foxes every year[6].In order to effectively and fully prevent and controlcanine distemper in foxes,rapid,specialized,accurate and simplified diagnosis and timely understanding of occurrence and spreading of epidemics are required.Changli is an important fur producer in Hebei Province and even in China.However,canine distemper seriously threatens the safe production.It is one ofthe mostsevere epidemics in fur-bearing animals.To better control canine distemper and reduce economic losses of farmers, whole blood samples of foxes thathad received canine distemper vaccination were collected from a farming area in Changli County,and then the canine distemper virus antibody titer in the prepared serum samples was determined.This study aimed to understand the immune effect of canine distemper vaccine in farmed foxes,thereby providing a theoretical basis for reducing the occurrence of canine distemper in farmed foxes.
Materialand Methods
Material
Whole blood samples
The 85 whole blood samples of foxes thathad been immunized with canine distemper vaccine were collected randomly from the 4 farms of a farming area in ChangliCounty.There were 15,14,30 and 26 samples collected from the 4 farms respectively(Table 1).Each whole blood sample had a volume of 2 ml.
Main reagents
The sodium chloride, potassium chloride,disodium hydrogen phosphate,potassium dihydrogen phosphate were all purchased from the Sinopharm ChemicalReagent Co., Ltd.
The formula of0.01 M PBS(1 L) was as follows:NaCl18 g,KCl0.2 g, Na2HPO41.44 g,KH2PO40.24 g, ddH2O 800 ml,pH 7.2(regulated with 1 M HClor 1 M NaOH).The prepared0.01 M PBS was sterilized in an autoclave and then preserved atroom temperature.
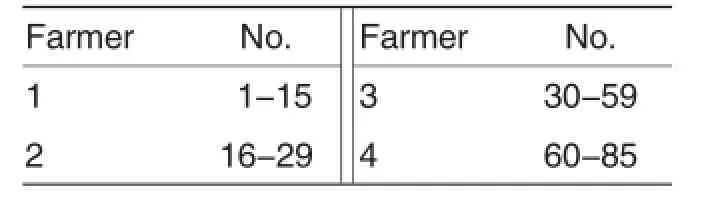
Table 1 Numbering of samples
The CDV-Ab ELISA kit was purchased from the Beinuo(Shanghai) Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.
Main equipment
The main equipment(instruments)used in this study included different specifications of pipettes and corresponding pipette tips,microplate reader(Thermo Group (Finland)),centrifuge(An Ke TCL-16G, Shanghai Anting Scientific Instrument Factory)and water-jacket incubator (ShanghaiYiheng Technologies Ltd.).
Methods
Preparation of serum samples
The whole blood samples were first placed at room temperature for 2 h and then centrifuged at 3 000 r/min for 10 min. The supernatants were transferred and stored at-20℃.
Operating procedure of ELISA
Numbering of standards and samples and dilution of standard
From the 2ndwellof the antigen-coated plate on(upper-left corner,in horizontal),10 continuous wells were used to dilute the standard.A certain amount of standard(100μl)was added to the 2ndand 3rdwells,respectively.Subsequently,a certain amount of standard dilution(50μl)was added.Then a certain amount of the solution in each of the 2ndand 3rdwells was transferred to each of the 4th(100μl)and 5th(100μl) wells respectively.In the 4thand 5thwells,certain amounts(50μl)ofstandard dilution were added respectively. The solutions in the 4thand 5thcells were mixed.After then,50μl of solution from each of the 2 wells was discarded.Then a certain amount of the solution in each of the 4th and 5th wells was transferred to each of the 6th(50μl)and 7th(50μl)wells respectively.Certain amounts(50μl)of standard dilution were added to the 2 wells then.The solutions in the 6thand 7thwells were mixed.After then,50μl of solution from each of the 2 wells was transferred to each of the 8thand 9thwells respectively.Certain amounts (50μl)ofstandard dilution were added to the 2 cells.Then a certain amountof solution in each of the 2 wells was added to each of the 10thand 11thwells respectively.At final,50μl of solution in each of the 10thand 11thwells was discarded respectively.
Adding samples
The 1stwell was treated as control(added without samples or reagents).The 12th-96thwells were used to determine the antibody levels in the samples.The well No.was consistent with sample No. Certain amounts(40μl)of sample dilution were first added to the cells,and then 10μlof each of the samples was added respectively.The solutions in the wells were mixed gently.The added samples were located at the bottom ofthe wells.
Incubation
The plate was sealed with plate film,and then placed at 37℃for 10 min.The 30 time concentrated wash solution was diluted with distilled water by 30 times.
Washing
The plate film was uncovered carefully.The solutions in the wells were discarded.After dried,the wells were filled with wash solution and stood for 30 s.Then the wash solution was discarded.The wells were washed 5 times.After then,the wells were dried.
Adding enzyme
A certain amount (50μl)of enzyme was added to each of the wells(except the 1stwell)respectively.The plate was then bathed in warm water.After a certain time,the wells were washed.
Coloring
A certain amount(50μl)of color reagent A was first added and then a certain amount(50μl)of color reagent B was added to each of the cells respectively.The plate was shocked gently and then placed in dark at37℃for 15 min.
Termination
A certain amount(50 μl)of termination solution was added to each of the wells respectively.At that time,the blue color was changed into yellow.
Determination
The control was used to calibrate the spectrophotometer.The absorbances of samples at 450 nm were determined.
Results evaluation
If the absorbance of a sample was≥the threshold,the sample was considered to be canine distemper antibody-positive.Itnot,the sample was considered to be antibody-negative.
Threshold=average OD of negative wells+0.15.
Preparation of standard curve
The standard curve was drawn with ODvalue as the horizontal axis and concentration of standard as vertical axis. Thus the antibody concentration in the diluted sample can be referred according to the absorbance of the sample. Finally,the actual concentration in the sample can be obtained.The linear regression equation of the standard curve(concentration vs.OD)can be calculated.Thus the antibody concentration in diluted sample can be directly calculated by taking the OD value of the diluted sample into the equation.At final,the actual concentration in the sample can be obtained.Only when the average OD of positive control was≥1.00 and the average OD of negative control was≤0.15 was the testconsidered to be valid.
Results and Analysis
The determined OD value ofnegative controlwas<0.055,and the determined OD value of negative control was>1.16.The calculated threshold was 0.205(0.055+0.15).If the OD value of a sample was below 0.205, the sample was considered to be antibody-negative,and if the OD value of a sample was above 0.205,the sample was considered to be antibodypositive.The drawn standard curve was shown in Fig.1.The obtained linearregression equation was as follows:
The actualantibody concentration in a sample was 5y.
As shown in Table 2,the 15 samples from the 1st farmer were allantibody-positive with qualified rate of 100%(Fig.2).Among the 14 serum samples from the 2ndfarmer,13 samples had canine distemper antibody. So the qualified rate was 93%(Fig.3). The 30 serum samples from the 3rdfarmer were all antibody-positive with qualified rate of 100%(Fig.4).Among the 26 serum samples collected from the 4thfarmer,3 samples were antibody-negative,and 23 samples were antibody-positive.Thus the qualified rate was 88%(Fig.5).
The 4 absorbance curves showed the physique of most of the foxes was equivalent,and only few foxes had a stronger or weaker physique.Among the 85 serum samples,4 samples were CDV antibody-negative,and 81 samples were CDV antibody-positive. The qualified rate was 95%.Among the samples from the 4 farmers,there were only 4 samples that are from the 4thfarmer had no CDV antibody. This may be caused by individual difference.It is indicated the immunization should be strengthened for some foxes.
The determination results showed the qualified rate of CDV antibody level in immunized foxes is commonly higher,indicating a high immunization quality.In addition,it is also suggested the canine distemper vaccination and vaccination procedure has attracted much attention from mostfarms.
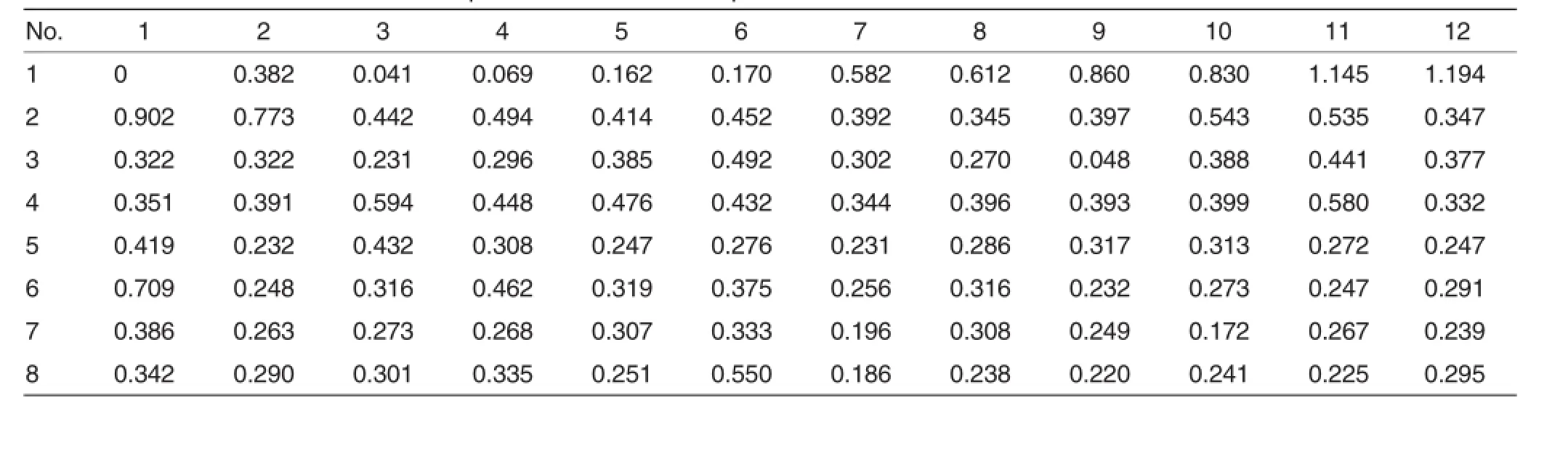
Table 2 OD values of standards and samples on a 96-well ELISA plate
Conclusions and Discussion
Principle ofdetermining serum antibody levelwith ELISA
The kit adopts the double-antibody sandwich ELISA method to determine the CDV-Ab level in foxes. The plate is coated with solidified purified CDV antigen.When the CDV-Ab was added to the wells,itwillbe bound with the HRP-marked CDV-A,forming antigen-antibody-enzymatic marker complex.After a through wash,the TMB willbe added to color.Under the catalysis of HBR,the color of TMB will be changed into blue and finally changed into yellow due to the presence of acids.In addition,the darkness ofthe color is positively related to the CDV-Ab levelin samples.
Compared with immunofluorescence and radioimmunoassay,the ELISA technique has no special requirements for equipment(ie.fluorescent microscope),is safer(without radiation)and can be completed under ordinary experimental conditions in laboratories[7].The sensitivity and specificity of ELISA technique can catch up with those ofimmunofluorescence,and of some improve ELISA technique can catch up with and even exceed those of radioimmunoassay. ELISA has a broader application range compared to those of immunofluorescence and radioimmunoassay.Therefore,among the immunolabelling techniques,ELISA,an immunoserologicalmethod,has the mostrapid developmentand mostapplication range.
Determination results of CDV antibody level
The canine distemper virus attenuated vaccine is usually used to immunize animals.The vaccine is injected to parentanimals in late December or early January.The first canine distemper vaccination for the young foxes that have eaten the colostrum is performed half a month after they are separated,and the second vaccination is performed 2 weeks later.The immunization program is reasonable and can achieve a good immune effect.
The canine distemper virus antibody titer is>1∶100 in most animals.If the antibody titer is lower than 1∶100, the animalwillbe susceptible to canine distemper[8].The canine distemper protective antibody is mainly composed of neutralizing antibody,which is also an important index in immunodetection.In general,77%ofthe antibody in maternal serum can be transferred to the young through placenta and colostrum.The half-life of maternalantibody is 8.4 d.When the neutralizing antibody titer declines to 1∶20, the young will be susceptible to CDV infection.It can be presumed that the 40-50 d-old(around the weaning) young foxes may be infected with canine distemper.Of course,the antibody level should be determined to make sure the critical period.Thus the optimum vaccination time will be determined.When the antibody level in serum of adult foxes is lowerthan 1∶100,the adult foxes willbe vulnerable to CDV infection[9-10].In this study,the highest antibody concentration reached 1 844.289 ng/L,and the lowest was 108.929 ng/L(Table 3). The qualified rate ofantibody levelwas 95%.
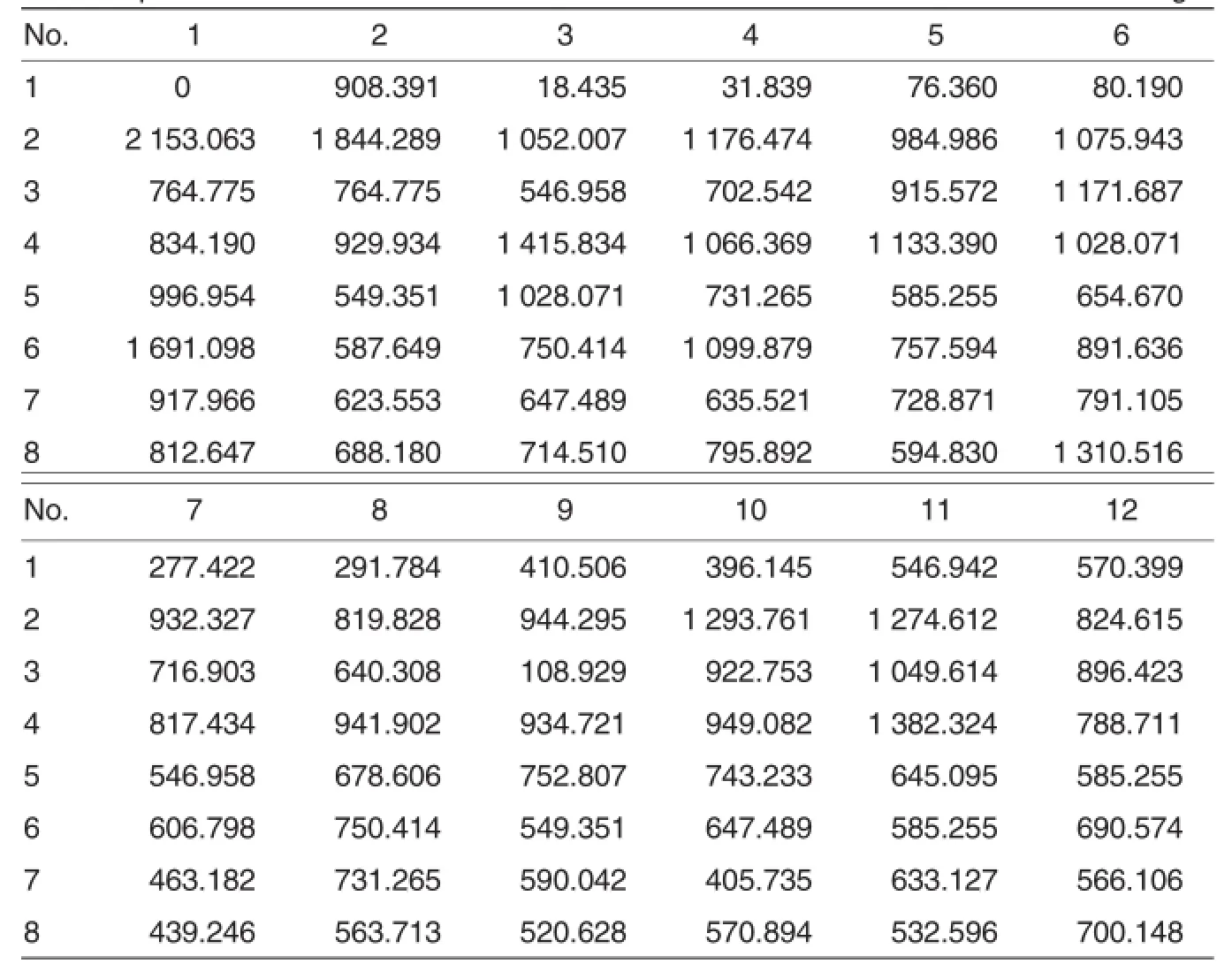
Table 3 Actual concentrations of antibody in standards and samples on a 96-well ELISA plate ng/L
Controlmeasures
In order to increase the antibody level and prolong the protection time, the attenuated virus is usually used to prepare vaccine[11-13],which has a certain degree of risk.There is also difference in antibody level among different animals.Some immunized foxes were still infected with canine distemper virus,and this may be caused by the non-detection of maternal antibody and residualantibody levels before the immunization.So in the routine immunization,the immunization program should be abided strictly,and the immunization time should also be selected appropriately.Thus the stresses to animals,caused by immunization and other factors,will be weakened.If the immunization time is selected inappropriately and the weather changes unexpectedly just after the immunization,immune suppression may occur in foxes.Thus the antigen virus in vaccine may infect foxes,resulting in immunization failure[14],thereby leading to the outbreak of canine distemper in foxes.
[1]BRUGGER M,JUNGITW,ZURBRIGGEN A,et al.Canine distemper virus increases procoagulant activity of macrophages[J].Virology,1992,190: 616-623.
[2]ZHANG LH(张立恒),ZHANG ZM(张智明),TAN TT(谭婷婷),et al.Study on treating canine distemper with self-prepared raccoon-origin antiserum(自制貉源抗血清治疗犬瘟热病的研究)[J].China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine(中国畜牧兽医),2010,37(7): 143-144.
[3]SUN X(孙霞),SHAN QM(单庆美),SUN HY(孙海岩).Diagnosis and prevention of canine distemper in martens and foxes(貂㈦狐狸犬瘟热的诊断及防制)[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science and Technology(中国兽医科技),2004, 3:134-136.
[4]XIANG Q(向前).Disease controlin specialanimals(特种动物疾病防治)[M]. Central-Palin Farmers Press(中原农民出版社),2009:176-180.
[5]ZHAO GR(赵桂容),MA ZS(马自山).Diagnosis and treatment ofcanine distemper in foxes(狐狸犬瘟热的诊疗体会)[J]. Clinical Veterinary(兽医临床),2001,5: 76-78.
[6]WANGJW(王君玮).Study on isolation, identification and molecular biological characteristics of canine distemper virus in foxes,martens and raccoon dogs(狐、貂、貉源犬瘟热病毒分离鉴定㈦分子生物学特性研究)[D].Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University(南京:南京农业大学),2008.
[7]SONG WJ(宋文剑).Pathogen Biology and Immunology(病原生物学㈦免疫学) [M].Changsha:Hunan Science and Technology Press(长沙:湖南省科技出版社),2010.
[8]LU Y(鲁岩),ZHANG ZZ(张志洲),JIN L (金立).Diagnosis and treatment ofcanine distemper in foxes and raccoon dogs(狐、貉犬瘟热病的诊断㈦防治)[J]. Jilin Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine(吉林畜牧兽医),2011,9:122-124.
[9]GAO JH(高计会),JING S(景松),ZHAIL (翟兰).Diagnosis and prevention of canine distemper in foxes(狐狸犬瘟热诊断㈦防治)[J].Contemporary Animal Husbandry(当代畜牧),2007,8:143-146.
[10]LU P(吕品).Diagnosis and prevention ofcanine distemper in foxes(狐狸犬瘟热的诊断㈦防治)[J].Guangdong Journalof Animal and Veterinary Science (广东畜牧兽医科技),2006,6:67-69.
[11]DONG SW(董书伟),YAN ZT(严作廷), LIX(荔霞),etal.Diagnosis and treatment of a fox canine distemper case caused by immunization failure(免疫失败诱发一起狐狸犬瘟热的诊治)[J]. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine(中国畜牧兽医),2012,5: 56-58.
[12]QIN Y(秦艳).Diagnosis and treatment ofa fox canine distemper case(一起狐狸犬瘟热的诊治)[J].Shandong Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine(山东畜牧兽医),2012,8:36-38.
[13]HUA Y(华育),WANG P(王平).Diagnose of canine distemper in several fur-bearing animals in autumn and winter of 2002(2002年秋冬若干毛皮动物饲养场爆发狐狸犬瘟热的诊断) [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University(东北林业大学学报),2004,34 (6):124-126.
[14]WANG YL(王Ⅰ龙).Detection ofpathogenic nucleic acids and serum antibodies ofseveralviralepidemics in furbearing animals(几种毛皮动物病毒性传染病病原核酸及血清抗体的检测) [D].Harbin:NortheastForestry University(哈尔滨:东北林业大学),2004.
Responsible editor:Tingting XU
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
狐狸犬瘟热抗体的ELISA检测
张艳英,卢会鹏,王晓姗,郭杨柳,吴 楠,李艳云,史秋梅*,高 超
(河北科技师范学院,河北省预防兽医学重点实验室,河北昌黎066600)
从昌黎县某养殖小区中,采集经犬瘟热疫苗免疫接种后的狐狸全血,制备血清后,应⒚双夹心ELISA法对狐狸免疫接种犬瘟热病毒后85份样品进行抗体检测。结果显示,该养殖小区4个养殖户的85份样品有81例呈阳性,4例呈阴性,抗体水平较高,说明该地区犬瘟热的免疫和免疫程序得到大部分养殖户的重视,免疫保护效果较好。
狐狸犬瘟热;抗体;ELISA
河北省科技支撑计划(10960408D;14826613D);河北省石家庄市科技局研究㈦发展计划(09150923A);河北省教育厅项目(Z2007212);秦皇岛市农科院项目(2014-04)。
张艳英(1974-),女,河北安新人,硕士,副教授,主要从事动物疫病防控技术研究,E-mail:yanyzha@163.com。*通讯作者,教授,主要从事动物疫病防控技术研究,E-mail:shiqiumei@126.com。
2014-10-24
Supported by Hebei Science and Technology Support Program(10960408D; 14826613D);Research and Development Plan of Shijiazhuang Municipal Science and Technology Bureau(09150923A);Hebei Province Department of Education Fund (Z2007212);Qinhuangdao Academy of AgriculturalSciences Fund(2014-04).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:shiqiumei@126.com
Received:October24,2014 Accepted:January 3,2015
修回日期2015-01-03
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年1期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年1期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Technology Research of Plantlets Rooting and Transplanting on Tissue Culture of Ilex centrochinensis
- Establishmentand Comparison of Two TaqMan Real-time PCR Methods for PCV2
- Analysis on Expression Patterns of NAC1 Gene in Tomato Induced by Low Temperature
- Changes of Protective Enzyme Activity and MDA Contentin Leaves of Agropyron cristatum Under Grazing Stress
- Characteristics and High-yielding Cultivation Technology of HuaimaiNo.29
- Study on Sensitivities of16 Rice Varieties to Acetochlor
