微型锁定钢板治疗肱骨大结节骨折
马骏 付强 叶添文 陈爱民
微型锁定钢板治疗肱骨大结节骨折
马骏 付强 叶添文 陈爱民
目的 评价微型锁定钢板治疗肱骨大结节骨折的临床疗效。方法 回顾性分析上海长征医院应用微型锁定钢板治疗6例肱骨大结节骨折患者,其中男性3例、女性3例;左侧3例、右侧3例;患者骨折AO分型:A1-2型。采用Neer评分标准评价肩关节功能, X线片观察骨折愈合情况。结果 6例患者平均手术时间66 min(50~85 min),术中平均出血量87 ml(60~110 ml)。手术切口均为I期愈合,未见感染、内固定断裂或松动、骨折块移位、肩峰撞击综合征等并发症。患者获得11~36个月的随访,平均随访19.8个月。X线片复查示骨折愈合时间为9~14周,平均11.3周。最后一次随访时,患者未出现肩关节疼痛,肩关节上举、外展无明显受限。Neer评分为89~95分,平均91.2分。结论 微型锁定钢板是治疗肱骨大结节骨折的一种理想选择。
肱骨大结节骨折;微型锁定钢板;手术治疗
肱骨近端骨折临床上较常见,其中累及大结节的骨折占13%~33%,多为高能量伤引起[1]。肱骨大结节骨折是关节周围骨折,离断大结节受肌腱牵拉容易移位,治疗不当可引起肩功能障碍[2]。当大结节移位>5 mm或成角>45°时,须行手术复位内固定治疗[3]。当前对于此类骨折内固定方法多采用肱骨近端锁定钢板固定、空心拉力螺钉固定或经骨缝合技术等。2010年9月至2014年1月,我院对6例肱骨大结节骨折患者行大结节复位微型锁定钢板内固定,取得满意效果。
资 料 与 方 法
一、一般资料
本组6例患者,其中男性3例,女性3例,年龄50~63岁,平均57.0岁,均为步行摔伤,肩部着地。左侧3例,右侧3例。均为新鲜闭合骨折(受伤距手术时间<6 d),X线片显示均为单纯性大结节骨折,骨折移位>5 mm,不伴肩关节脱位,无腋神经损伤。
二、手术方法
患者均行切开复位微型钢板内固定术。全身麻醉下,患者取仰卧位,患肩垫高,采用三角肌纵行劈开入路,长约4~5 cm。避免损伤关节囊、韧带等软组织,暴露肱骨近端骨折处,直视下复位,必要时使用克氏针临时固定骨折块,术中可根据骨折具体情况对微型钢板塑形及剪切,使之充分附贴,塑形后将钢板覆盖在撕脱大结节上,骨折近、远端分别予以锁定固定。术中探查肩袖是否撕裂损伤,必要时对肩袖损伤进行缝合修补,活动肩关节,C臂机透视复位满意后关闭切口。
三、术后康复
术后肩肘吊带制动6周。术后1 d行患侧肘腕关节被动活动;术后2周行肩外旋、内旋主动活动;术后3周行肩前屈、后伸主动活动;术后6周增大肩关节活动范围和上肢力量。术后4周门诊复查X线,观察内固定位置及骨痂生长情况,术后12周正常负重。
四、术后评价
通过门诊影像学结合查体,采用Neer评分标准评价治疗效果,包括疼痛35分,功能30分,运动限制25分,解剖复位10分,术后总评分在>90分为优,80~89为良,70~79为可,<70分为差。
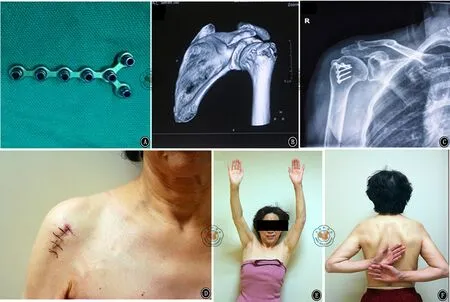
图1 患者女性,63岁,右肱骨大结节骨折。A.微型锁定钢板(邦美.美国);B.63岁老年女性,步行摔倒至右肱骨大结节骨折,术前CT三维重建;C.术后4周X线片,未见骨折端移位及内固定松动; D.手术切口;E、F.术后12个月后肩关节功能(E外展接近180°,F内旋超过90°)
结 果
患者均顺利完成手术,手术平均时间66 min(50~85 min),术中平均出血87 ml(60~110 ml),切口均为I期愈合,未见感染、内固定断裂或松动、骨折块移位、肩峰撞击综合征等并发症。患者获得11~36个月的随访,平均随访时间19.8个月。X线复查示骨折愈合时间为9~14周,平均11.3周。最后一次随访时,患者未出现肩关节疼痛,肩关节上举,外展无明显受限(图1)。最后一次随访后肩关节Neer评分为89~95分,优5例,良1例,平均91.2分。
讨 论
肱骨大结节作为冈上肌、冈下肌和小圆肌的止点,对维持肩功能活动意义重大,骨折后由于各方肌肉牵拉作用不均,易发生移位,这种分离可以造成大结节骨不连,影响肩袖和肱盂关节的活动。对于骨折移位>5 mm应该采取手术治疗[3],Park等[4]认为对于需要手臂过头的重体力劳动者和运动员即使移位3 mm也应被矫正。
临床上,此类骨折较为常见的手术方法是切开复位锁定钢板内固定、空心拉力螺钉固定以及经骨缝合技术等。这些手术方式存在一些问题,Lill等[5]认为,传统肱骨近端钢板与骨质接触多,影响骨膜血供,不利于骨折愈合。植入钢板越大,越容易导致继发性肩峰撞击综合征[6-7],钢板还可能影响肱二头肌肌腱解剖床,持续摩擦造成肱二头肌的损伤甚至断裂。Braunstein等[8]报道空心拉力螺钉的固定强度及加压力量有限,易松动。加之肱骨大结节处多为松质骨,若合并老年患者骨质疏松,术后骨折块因为肌肉牵拉易发生再移位。螺空心拉力钉钉孔较粗,钻孔及拧螺钉时易造成骨质二次损伤,且拉力螺钉的垫圈易造成继发性肩峰撞击征[9]。经骨缝合技术临床中也在广泛应用,其固定肌腱-骨界面,可避免患者对于内置物的过敏反应, 也无需再取出内置物。长期的随访研究证明此方法能获得满意预后[9],但如果大结节的骨折块非常碎小,缝合线将难以将碎骨片稳定缝压在骨折端,缝合时可能进一步损伤周围的软组织,不利于碎骨片的固定[3]。
微型锁定钢板最初被应用在指骨等细小长骨骨折的内固定中,其具有创伤小、复位精确、固定牢固等特点。我们将这种微型钢板应用于治疗单纯肱骨大结节骨折,手术采用三角肌纵行劈开入路,此种入路成熟,切口小,软组织剥离损伤少,最大程度的保护骨膜和血供,微型锁定钢板可充分覆盖骨折块,锁定螺钉成角固定在骨质疏松和粉碎骨折中具有良好的抗拉力和锚合力,能确保对骨折块的固定强度,不易移位。钢板具有体内塑形及剪切功能,有助于最大程度地贴合复杂的骨表面。钢板上多个钻孔,可以将压力分散在各个钉孔,且钉孔小,可最大程度的避免钻孔时对正常骨质的二次损伤及对碎骨块周围血供的破坏。因为钢板小,可减少内植物对肱二头肌肌腱和结节间沟的干扰,不易造成肩峰撞击及肩袖损伤,患者可早起行肩关节外展、前屈、后伸等功能锻炼。
综上所述,微型锁定接骨板是一种理想的治疗肱骨大结节骨折的内固定植入物,其具有创伤小、复位精确、固定牢固等优点。本研究也存在一些缺点和不足,如病例少、随访时间短、无对照研究。对于该种钢板固定肱骨大结节骨折的生物力学的研究及大宗病例远期结果还需进一步研究。
[1] Kim E, Shin HK, Kim CH. Characteristics of an isolated greater tuberosity fracture of the humerus[J]. J Orthop Sci, 2005, 10(5): 441-444.
[2] Platzer P, Kutscha-Lissberg F, Lehr S, et al. The influence of displacement on shoulder function in patients with minimally displaced fractures of the greater tuberosity[J]. Injury, 2005, 36(10): 1185-1189.
[3] Gruson KI, Ruchelsman DE, Tejwani NC. Isolated tuberosity fractures of the proximal humeral: current concepts[J].Injury,2008,39(3):284-298.
[4] Park TS, Choi IY, Kim YH, et al. A new suggestion for the treatment of minimally displaced fractures of the greater tuberosity of the proximal humerus[J]. Bull Hosp Joint Dis, 1997, 56(3): 171-176.
[5] Lill H, Lange K, Prasse-Badde J, et al. T-plate osteosynthesis in dislocated proximal humerus fractures[J]. Unfallchirurgie, 1997, 23(5): 183-190; discussion 191-192.
[6] Clavert P, Adam P, Bevort A, et al. Pitfalls and complications with locking plate for proximal humerus fracture[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2010,19(4):489-494.
[7] Niall DM, O′Mahony J, McElwain JP .Plating of humeral shaft fractures--has the pendulum swung back? [J]. Injury,2004,35(6):580-586.
[8] Braunstein V, Wiedemann E, Plitz W, et al. Operative treatment of greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus--a biomechanical analysis[J]. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon), 2007, 22(6): 652-657.
[9] Scheibel M, Lichtenberg S, Habermeyer P . Reversed arthroscopic subacromial decompression for massive rotator cuv tears[J]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2004,13(3):272-278.
(本文编辑:李静)
马骏,付强,叶添文,等.微型锁定钢板治疗肱骨大结节骨折[J/CD]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2015,3(3):156-159.
Treatment of humeral greater tuberosity fracture with micro locking plates
MaJun,FuQiang,YeTianwen,ChenAimin.
DepartmentofOrthopaedicTraumaSurgery,OrthopaedicInstituteofPLA,ShanghaiChangzhengHospital,SecondMilitaryMedicalUniversity,Shanghai200000,China
ChenAimin,Email:Aiminchen@aliyun.com
Background Proximal humerus fracture is a rather common fracture clinically. And the greater tuberosity fractures occupy 13%-33%, most of which are caused by high energy injury. Humerus fracture of greater tuberosity is a peri-articular fracture which is easily towed to be displaced by the greater tuberosity tendon. Improper treatment of humerus fracture of greater tuberosity may led to shoulder dysfunction. When the displacement of the greater tuberosity is greater than 5 mm or the angle is greater than 45°, reduction internal fixation operation is a necessary for treatment. Currently, the means for this fracture internal fixation are varies. Means of fixation can be adopting the proximal humerus locking plate, or two parallel annulated compression screws, or the bone suture. From September 2010 to January 2014, the internal fixation operation with restoration micro locking plate was performed in 6 cases of humerus fracture of greater tuberosity in our hospital and achieved satisfactory effects.Methods General data: 3 males and 3 females aging from 50 to 63 years old with an average age of 57.0 years old were selected to be the study subjects. They were all injured because of falling over with their shoulder strike against the floor. 3 of them injured the left shoulder and 3 of them injured the right shoulder, and all of them were fresh closed fracture (the time after injury was less than 6 days to the operation time). The X-ray picture indicated them to be exclusive humerus fracture of greater tuberosity and the displacement was more than 5 mm, without shoulder dislocation nor injury of axillary nerve.Operation methods: Open reduction micro plate internal fixation was carried out on all patients. General anesthesia and the patients lay down in supine position with their shoulders supported up. The operators adopted the incision of 4-5 mm from deltoid in lengthways. The operation should be performed cautiously to avoid damaging the joint capsule tissues, ligament tissues or other tissues. Revealed the proximal humerus fracture and restored under direct vision. Kirschner pins were necessary for temporary fixation of the fracture. The operators should shape the micro plate to fully match the fracture. After shaping, the plate was covered on the avulsion of greater tuberosity and then fixed the remote and proximal points of the fracture. The operator should check out whether the rotator cuffs were avulsion injury and suture was necessary when the rotator cuffs were injured. Move the shoulder joints properly and the incision can be closed if the perspective restoration was satisfactory through C-arm X-ray indication.Post-operation rehabilitation: After operation, the elbow should be belt immobilized for six weeks. The lateral elbow wrist joints passive movements should be started the first day after the operation. Shoulder extorsion and internal rotation active movements should be started two weeks after operation. Shoulder forward bends and rear protraction active movements should be started three weeks after operation. Six weeks after operation, the shoulder joints movement range should be enlarged and the upper body strength should be increased. Four weeks after operation, the patients should re-examination the X-ray in the outpatient department for further knowing the internal fixation location as well as the callus growing conditions. Twelve weeks after operation, the shoulder can bear burden normally.Post-operation evaluation: The curative effects were evaluated by physical examination through outpatient imaging, and adopting Neer standard for evaluation. The evaluation scores included pain 35 points, function 30 points, limitation of movement 25 points, anatomical reduction 10 points. The total post-operation evaluation points more than 90 points can be marked as excellent, 80-89 points as good, 70-79 points as ok, below 70 points as poor.Results All patients had successful operation with an average operation time of 66min (50-85 min). During the operation, the average bleeding volume was 87ml (60-110 ml). All the incisions were I phase union without any infections, internal fixation breakage, looseness, fracture dislocation, shoulder peak impingement syndrome nor other complications. The patients were followed up for 11-36 months and the average follow-up visit time was 19.8 months. The X-ray re-examination indicated that the fracture union time was 9-14 weeks, the average time was 11.3 weeks. In the last follow-up visit, the patients never complained any shoulder joints pain, and the shoulder joints lifting and outstretch were not limited. The Neer score of the last follow-up visit was 89-95, with 5 cases excellent, 1 case good, and the average points was 91.2 points.Conclusion Micro locking plate for internal fixation of the humerus fracture of greater tuberosity posses the advantages of minimal trauma, accurate restoration, firm consolidation and so on. Micro locking plate is a perfect choice for treating the humerus fracture of greater tuberosity.
Humeral greater tuberosity fracture;Locking plates;Treatment;
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2015.03.006
长征医院青年启动基金 (2012CQN09)
200000上海,第二军医大学附属长征医院骨科研究所 骨科创伤外科
陈爱民,Email:Aiminchen@aliyun.com
2014-12-26)

