MicroRNA与NF-κB调控的细胞凋亡
齐仁立 黄金秀 龙定彪 黄萍
(重庆市畜牧科学院 农业部养猪科学重点实验室 养猪科学重庆市市级重点实验室,荣昌 402460)
MicroRNA与NF-κB调控的细胞凋亡
齐仁立 黄金秀 龙定彪 黄萍
(重庆市畜牧科学院农业部养猪科学重点实验室养猪科学重庆市市级重点实验室,荣昌402460)
NF-κB是一种非常重要的核转录调控因子,激活后的NF-κB通过调节靶基因的转录表达参与细胞的各项生命活动,特别是炎症、免疫和凋亡。NF-κB在不同类型的细胞凋亡中可能发挥不同的调控作用。而microRNA这类非编码的RNA对于NF-κB的表达和功能又能够产生系统性或者特异性的调节。综述分析NF-κB对细胞凋亡的调控作用,并探讨microRNA在此过程中的作用。
NF-κB;microRNA;细胞凋亡
1 NF-κB及其作用机制
早在1986年,Sen和他的同事们通过试验在B淋巴细胞的核提取物中发现了一种能与免疫球蛋白κ轻链基因特异结合的蛋白因子,并将其命名为核因子κB(Nuclear factor Kappa B,NF-κB)[1]。NF-κB广泛存在于多种细胞中,当细胞受到外部刺激(药物、辐射、缺氧等)或者细胞因子、病毒感染、脂多糖等刺激时,NF-κB被激活并与相应的病毒、细胞因子、受体蛋白等所调节的基因增强子区结合,启动基因转录[2-5]。随着时间的推移,研究逐渐证明NF-κB是一种细胞核内极为重要的转录调节因子,对于细胞的增殖和分化、衰老和死亡、黏附和迁移都具有重要的调节作用[3,6]。
NF-κB是由NF-κB/Rel蛋白家族成员NF-κB1(p50/前体为P105)、NF-κB2(p52/前体为P100)、Rel(p65)、RelB和C-Rel以同源或异源二聚体的形式组成。虽然有多个不同的二聚体组合,但p50和p65组成的二聚体最早被发现,并且其分布和作用也最为广泛,是通常所说的NF-κB。在细胞静息状态下,NF-κB以无活性状态存在于细胞浆中,并与抑制因子IκBs(包括IκBα、IκBβ,IκBγ、IκBε、IκBζ、IκBS和Bcl-3等)一起组成了异源多聚体P50/P60/ IκBs。在这个多聚体中,IκBs能阻碍P50和P65的二聚体化,使NF-κB以无活性的形式存在。当细胞受到肿瘤坏死因子α(Tumor necrosis factor α,TNFα)、白介素或者其他药物的刺激时,IκBs的激酶IκK会被磷酸化激活,并作用于P50/P60/IκBs三聚体中的IκBs,使其从三聚体中脱离并被泛素化降解,暴露出P50亚基上的移位信号和P65亚基上的DNA结合位点,从而使P50/P65二聚体表现出NF-κB活性,并从细胞浆移位到细胞核中,然后与靶基因的κB基序结合,发挥转录调控作用。除了上述的典型激活方式,NF-κB的激活还存在其他非典型的方式[2](图1)。在非经典激活途径中,P100和RelB的二聚体被激活,这种激活主要存在于B细胞和T细胞发育过程中。接收到特定的受体信号后(例如淋巴毒素B和B细胞活化因子)在NF-κB诱导激酶(NIK)的作用下,IκKa复合体被磷酸化进而引起p100的磷酸化,经蛋白激酶作用诱导产生p52-RelB异源二聚体,并使其进入细胞核参与核转录活动。

图1 NF-κB典型和非典型激活方式[2]
2 NF-κB对细胞凋亡的调控作用
细胞凋亡是多细胞生物一种正常的生命现象,在受到外部或者内部的刺激以后,细胞为了维护内环境的稳态,出现由多种基因控制的细胞程序性的主动死亡。细胞凋亡对于维持细胞正常生长和代谢稳定具有十分重要的意义,而细胞凋亡的异常与各种肿瘤的产生密切相关[7]。
活化的NF-κB与细胞凋亡紧密相关,但是NF-κB对于细胞凋亡产生和发展的影响还存在很多谜团。在不同的细胞中,不同的诱导刺激下,NF-κB似乎扮演了不同的角色。多数研究认为NF-κB具有凋亡抑制作用[3,8-11],因为NF-κB 对于许多抗凋亡基因都有特异性调控作用,包括TRAF1、TRAF2、c-IAP1、c-IAP2、IEX-1L、Bcl-xL和Bfl-1/A1等[12-17]。典型的功能缺失试验可以清楚地说明NF-κB抗凋亡作用。体外培养的胚胎成纤维细胞在剔除RelA时对于TNFα引起的凋亡更为敏感,而在个体试验上,TNFα能够促使RelA-/-小鼠出现肝细胞大量的凋亡,并最终导致小鼠的死亡[18,19]。
但是,另一方面,NF-κB的促凋亡作用也同样明显,Stefan等[20]报道了撤去培养基中的血清会造成293细胞的大量凋亡并伴随着NF-κB的显著激活。肿瘤抑制因子P53能够改变细胞周期,诱发多种细胞凋亡,而NF-κB在其中起到了明显的促凋亡作用。Ryan等[21]研究表明P53能够以与TNFa不同的方式激活NF-κB,并且诱导细胞走向凋亡,而抑制或者减少NF-κB的活性,则会阻断P53引起的凋亡。为了检测NF-κB的促凋亡和抗凋亡作用,Kaltschmidt[22]和他的同事们通过遗传学和药理学方法阻止HeLa细胞中的NF-κB被激活,结果发现虽然细胞对于TNFα诱导的凋亡更为敏感,但是却能够完全阻止H2O2和pervanadate诱导的凋亡。他们认为不同的凋亡诱导物引发的分子信号不同,决定了NF-κB在细胞凋亡产生和发展中的作用也不相同。
此外,似乎不同的NF-κB激活方式在细胞凋亡中也有不同的调控作用。与TNFα类似,FAS能够激活死亡受体FASL诱发细胞凋亡。典型激活的NF-κB能直接与FAS基因启动子结合,抑制NF-κB的典型激活能够降低FAS表达,而抑制非典型形式激活NF-κB则能够增加FAS的表达[23]。
这些试验结果提示,NF-κB在细胞凋亡中的调控作用十分复杂,受到激活方式、存在形式、细胞种类等多种因素的影响,在不同的细胞中可能分别或者同时具有抑制细胞凋亡和促进细胞凋亡的作用。
3 MicroRNA参与NF-KB对细胞凋亡的调控
MicroRNA是一种广泛存在于动物、植物、细菌和病毒体内的非编码RNA(non-coding RNA),通过序列互补的方式引导沉默复合体降解靶mRNA或者抑制翻译[24-26]。一个microRNA可以调控多个甚至影响数百个靶基因,而一个基因也可能同时受到多个microRNA的调节[27]。通过对靶基因的特异性/系统性调控,microRNA广泛参与并调控了细胞增殖、分化、代谢、衰老和凋亡的各种转录激活和信号传导[28]。反之,一些转录因子(如NF-κB)的激活和表达的改变又影响了microRNA的转录、加工和功能[29]。
目前已有一些研究探寻microRNA和NF-κB之间的相互作用关系,并且发现NF-κB的活化和功能的施展需要一些特定microRNA的参与[30,31](图2)。此外,激活的NF-κB对于特定microRNA的调控机能也是必不可少的。最早被确认参与调节NF-κB信号的是miR-146,它被认为是Toll-like 受体介导的NF-κB激活的抑制者。Taganov等[32]研究发现miR-146是一个NF-κB依赖型基因,并能够通过负反馈调节IL-1受体相关激酶1和TNFα受体相关蛋白6的表达参与到机体的免疫应答反应。Paik等[33]的试验结果显示,miR-146a在NKTL细胞系中的过表达能够明显抑制NF-κB的活性,阻滞细胞分化,诱导细胞凋亡。还有试验发现miR-125家族能够靶向NF-κB的抑制因子TNFα 诱导蛋白3(TNFAIP3)从而促进NF-κB激活[34]。miR-21能够通过PTEN/AKT通路促进MCF-10A细胞中NF-κB信号,但是却抑制了HEK293细胞中脂多糖LPS介导的NF-κB激活[35]。George等[30]分别于TNFα存在和不存在的情况下使用高通量library扫描NF-κB稳转报告细胞系中miRNA表达变化,并最终确认miR-517a/c可以诱导细胞内源性NF-κB的表达,并促进P65的核移位和IκB的降解。
在已经确认的参与NF-κB网络的microRNA中,有许多都能够直接参与细胞凋亡调控,如miR-21[36,37]、miR-29[38,39]和let-7[40]等。以miR-21为例,在许多实质癌细胞中miR-21都有异常高表达,它能够靶向抑制细胞死亡因子PDCD4基因,并且影响细胞凋亡抑制基因BCL2,阻断凋亡进程,促进癌细胞的生成[36]。miR-21还能够通过降低靶基因PTEN的表达,进而影响AKT的磷酸化并导致NF-κB的激活[36]。反之,miR-21的转录也受到NF-κB的调控,P65亚基的缺失会抑制LPS诱导的miR-21表达[37],所以NF-κB的活性对于miR-21的调控功能是必不可少的。
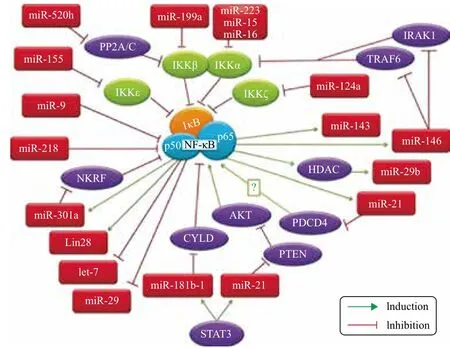
图2 参与NF-κB调控分子网络的microRNA[31]
基于上述研究可以确认一些microRNA能够直接或者间接地参与NF-κB的表达和激活,或者是受到NF-κB的调控而影响下游靶基因,对细胞凋亡的启动和发展起到重要的调节作用。但是这些不同的分子之间如何“交流”在很大程度上还充满了悬念。此外,随着高通量和新一代测序技术的迅速普及,将会有更多参与NF-κB分子网络的microRNA被发现和确认。
4 展望
细胞凋亡有助于清除受损细胞,减少应激损伤,维持机体稳态。凭借其重要的调控作用和在分子网络中的核心地位,NF-κB在细胞凋亡的产生和发展过程中扮演了重要的角色,它可能成为包括癌症、心血管疾病、肥胖及代谢症在内的多种疾病诊疗的靶位点。未来的工作中,我们将更加清楚NF-κB在不同类型的细胞凋亡中的差异调控机制。生物体内大量存在的microRNA对各种生命活动发挥着复杂而精巧的调控作用。迄今为止,只有极少数的microRNA被研究和确认参与了NF-κB的激活和调控。但随着新一代高通量测序和基因芯片技术的快速普及,将会有更多microRNA被发掘,有望在较短的时间内了解更多影响和参与NF-κB分子调节的microRNA,并逐渐掌握它们之间的“对话机制”,一个完整系统的调控网络图谱将会逐渐清晰。
[1] Sen R, Baltimore D. lnducibility of κ immunoglobulin enhancerbinding protein NF-κB by a post translational mechanism[J]. Cell, 1986, 46:705-716.
[2] Gilmore TD. Introduction to NF-κB:players, pathways, perspectives[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25:6680-6684.
[3] Beg AA, Baltimore D. An essential role for NF-B in preventing TNFα induced cell death[J]. Science, 1996, 274:782-784.
[4] O’Neilla LAJ, Kaltschmidtb C. NF-kB:a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function[J]. Trends in Neurosciences, 1997, 20(6):252-258.
[5] Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-KappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity[J]. Trends Immunol,2004, 25:280-288.
[6] Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappa B in cancer development and progression[J]. Nature, 2006, 441(7092):431-436.
[7]Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. “Chapter 18 Apoptosis:programmed cell death eliminates unwanted cells”[C]//Molecular Biology of the Cell(textbook). 5th ed. New York:Garland Science, 2008:1115.
[8] Mitchell TC, Hildeman D, Kedl RM, et al. Immunological adjuvants promote activated T cell survival via induction of Bcl-3[J]. Nat Immunol, 2001, 2:397-402.
[9] Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, et al. Suppression of TNFα induced apoptosis by NF-κB[J]. Science, 1996, 274:787-789.
[10]Wang CY, Mayo W, Baldwin AS. TNFα and cancer therapyinduced apoptosis potentiation by inhibition of NF-κB[J]. Science, 1996,274:784-787.
[11]Alcamo E, Mizgerd JP, Horwitz BH, et al. Targeted mutation of TNF receptor I rescues the RelA-deficient mouse and reveals a critical role for NF-kB in leukocyte recruitment[J]. J Immunol, 2001,167:1592-1600.
[12]Baichwal VR, Baeuerle PA. Apoptosis:Activate NF-kB or die?[J]. Curr Biol, 1997, 7(2):94-96.
[13]Zong WX, Edelstein LC, Chen C, et al. The prosurvival Bcl-2 homolog Bfl-1/A1 is a direct transcriptional target of NF-κB that blocks TNFα induced apoptosis[J]. Genes Dev, 1999, 13:382-387.
[14]Khoshnan AC, Tindell I, Laux D, et al. The NF-κB cascade is important in Bcl-xL expression and for the antiapoptotic effects of the CD28 receptor in primary human CD4 lymphocytes[J]. J Immunol, 2000, 165:1743-1754.
[15]Grumont RJ, Rourke IJ, Gerondakis S. Rel-dependent induction of A1 transcription is required to protect B cells from antigen receptor ligation-induced apoptosis[J]. Genes Dev, 1999, 13:400-411.
[17]Wu MX, Ao Z, Prasad KVS, et al. IEX-1L, an apoptosis inhibitor involved in NF-κB-mediated cell survival[J]. Science, 1998,281:998-1001.
[17]Wang CY, Mayo W, Korneluk RG, et al. NF-κB anti-apoptosis:induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation[J]. Science, 1998, 281:1680-1683.
[18]Beg A, Sha W, Bronson R, et al. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-κB[J]. Nature, 1995, 376:167-170.
[19]Doi TS, Marino MW, Takahashi T, et al. Absence of tumor necrosis factor rescues RelA-deficient mice from embryonic lethality[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96:2994-2999.
[20]Stefan G, Bauer MKA, Patrick A, et al. Bcl-2 Down-regulates the activity of transcription factor NF-κB induced upon apoptosis[J]. The Journal of Cell Biology, 1996, 134(1):13-23.
[21]Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR, et al. Role of NF-k B in p53-mediated programmed cell death[J]. Nature, 2000, 404(20):892-897.
[22]Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Hofmann TG. The pro-or antiapoptotic function of NF-kappa B is determined by the nature of the apoptotic stimulus[J]. Eur J Biochem, 2000, 267(12):3828-3835.
[23]Liu FY, Bardhan KK, Yang DF, et al. NF-қB directly regulates Fas transcription to modulate Fas-mediated apoptosis and tumor suppression[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(30):25530-25540.
[24]Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14[J]. Cell, 1993, 75(5):843-854.
[25]Corce CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2009, 10(10):704-714.
[26]Zeng Y, Yi R, Cullen BR. MicroRNAs and small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar mechanisms[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100:9779-9784.
[27]Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, et al. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs[J]. Genome Res, 2009, 19(1):92-105.
[28]Angelats MG, Cidlowski JA. Cell volume control and signal transduction in apoptosis[J]. Toxicologic Pathology, 2002, 30(5):541-551.
[29]Zeng Y. Principles of micro-RNA production and maturation[J]. Oncoqene, 2006, 25(46):6156-6162.
[30]George AO, Anton L, Hwang YC, et al. A functional genomics screen for microRNA regulators of NF-kappaB signaling[J]. BMC Biology, 2013, 11:19.
[31]Ma XD, Buscaglia LEB, Barker JR, et al. MicroRNAs in NF-kB signaling[J]. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, 2011, 3:159-166.
[32]Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, et al. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(33):12481-12486.
[33]Paik JH, Jang JY, Jeon YK. MicroRNA-146a downregulates NF-κB activity via targeting TRAF6 and functions as a tumor suppressor having strong prognostic implications in NK/T cell lymphoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2011, 17(14):1-11.
[34]Kim SW, Ramasamy K, Bouamar H, et al. MicroRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b constitutively activate the NF-κB pathway by targeting the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3(TNFAIP3, A20)[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109:7865-7870.
[35]Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, et al. STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 39:493-506.
[36]Lindesy EB, Yong L. Apoptosis and the targets genes of miR-21[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer, 2011, 30(6):371-380.
[37]Shin VY, Jin H, Ng EK. NF-κB targets miR-16and miR-21in gastric cancer:involvement of prostaglandin E receptors[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2011, 32:240-245.
[38]Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, Gores GJ. mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis[J]. Oncogene, 2007, 26:6133-6140.
[39]Xiong YJ, Fang JH, Yun JP, et al. Effects of microRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(3):836-845.
[40]Satoshi S, Tetsuo T, Hayato H, et al. The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human[J]. Journal of Hepatology, 2010, 52(5):698-704.
(责任编辑 狄艳红)
The Role of MicroRNA in the Cell Apoptosis Mediated by NF-κB
Qi Renli Huang Jinxiu Long Dingbiao Huang Ping
(Key Laboratory of Pig Industry Sciences,Ministry of Agriculture,Chongqing Key Laboratory of Pig Industry Sciences,Chongqing Academy of Animal Sciences,Rongchang402460)
As a key regulatory factor in cell, activated NF-κB induces the transcription of target genes involved in many cell activities,especially the inflammation, immunity and apoptosis. Previous studies proved that NF-κB plays various roles in different type of apoptosis. Moreover, expression and function of NF-κB could be systematically or specifically regulated by microRNA of non-encoding RNAS. The mediating effects of NF-κB on apoptosis were summarized, and the role of microRNA in the mediating process were further discussed .
NF-κB;microRNA;Apoptosis
10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2015.05.005
2014-08-01
国家自然科学基金项目(31470117,31302055),重庆市农发资金项目(13412),重庆市自然科学基金重点项目(2011BA1033)
齐仁立,男,博士,助理研究员,研究方向:脂肪细胞凋亡的分子机制;E-mail:qirenli1982@163.com
黄萍,女,高级畜牧师,研究方向:猪肉品质的营养调控;E-mail:505254858@qq.com

