MSCT用于他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效评估的可行性研究
曹中华,高锋,高毅,康陈波,刘岩
(河南省濮阳市安阳地区医院放射科,河南安阳455000)
MSCT用于他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效评估的可行性研究
曹中华,高锋,高毅,康陈波,刘岩
(河南省濮阳市安阳地区医院放射科,河南安阳455000)
目的:探讨MSCT用于他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效评估的可行性。方法:选取确诊的冠状动脉非钙化斑块患者60例,给予单一的他汀类药物治疗,在治疗前、治疗1年时行选择性冠状动脉造影检查(SCA)及MSCT检查,评价动脉血管狭窄情况。MSCT检查同时评价斑块所在位置管腔狭窄度(SE)及截面积(S)、斑块性质及面积、斑块CT密度值变化,检测治疗前后血清总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、低密度脂蛋白(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白(HDL-C)变化。结果:患者治疗后TC、TG、LDL-C较治疗前明显下降,HDL-C较治疗前明显升高(均P<0.05)。以SCA为金标准,冠状动脉狭窄节段治疗前SCA检出114个,诊断符合率89.76%(114/127);治疗1年后MSCT检出93个,诊断符合率91.18%(93/102)。SCA检查冠状动脉狭窄节段的诊断符合率治疗前后比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。MSCT显示治疗前114个非钙化斑块,治疗1年后斑块数下降至93个,下降率为22.84%,治疗后冠状动脉管腔SE、S、斑块面积均较治疗前明显下降(P<0.05),斑块密度值较治疗前升高(P<0.05)。结论:他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效肯定。MSCT可清晰显示斑块治疗前后变化,同时可进行准确的量化评估,是一种可行的监测方法。
体层摄影术,X线计算机;他汀类;冠状动脉疾病;斑块,动脉粥样硬化性;治疗结果
冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病是全球常见病,病理基础是冠状动脉粥样硬化性改变,可表现为稳定性斑块及不稳定性斑块,钙化斑块相对稳定,未钙化斑块稳定性较差,易脱落形成血栓,导致脑中风。目前他汀类药物是冠状动脉粥样硬化常用治疗药物,对改善预后疗效明确[1-4]。本研究对MSCT用于他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效评估的可行性进行了研究,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料选取2015年1—6月我院确诊的冠状动脉非钙化斑块患者60例,其中男32例,女28例;年龄43~78岁,平均(48.16±5.77)岁。非钙化斑块共127个,其中96个位于左侧冠状动脉,31个位于右侧冠状动脉;88个所在动脉管腔轻度狭窄,39个所在动脉管腔中度狭窄;其中脂质斑块(CT值<50 HU)35个、纤维斑块(CT值50~130 HU)92个。纳入标准:①病情确诊。②无介入手术治疗适应证。③自愿配合治疗,有良好的治疗依从性,对本研究知情同意。排除标准:①合并肝肾脑等其他重要脏器功能障碍性疾病。②治疗依从性不佳,可能存在治疗中断。③妊娠期及哺乳期妇女。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 治疗方法患者给予单一的他汀类药物口服治疗,剂量:辛伐他丁40mg/L、氟伐他汀40mg/L、阿托伐他汀20mg/d,疗程1年,其中4例服用辛伐他汀,11例服用氟伐他汀,45例服用阿托伐他汀。治疗期间不服用其他抗血栓、降血脂等可影响血脂及动脉斑块性质的药物。
1.2.2 MSCT检查患者在治疗前、治疗1年时由同一医师行MSCT检查动脉斑块变化。使用GE Lightspeed 16层螺旋CT,扫描范围上至气管分叉、下至心脏膈面下2 cm,检查时患者取仰卧位,足先进,经肘静脉注入70~80mL对比剂(碘比醇,350mgI/mL)行造影。扫描参数:螺距0.25、准直器宽度0.75mm、旋转1周0.42s,扫描时需憋气以减少呼吸的影响。检查结果在CT机自带计算机系统中行三维重建,评价管腔狭窄度(SE)及截面积(S)、斑块性质及面积、斑块CT值。
1.2.3 冠状动脉造影(SCA)检查患者在治疗前、治疗1年时行SCA检查。采用Seldinger经股动脉穿刺,钢丝导引下送入7F动脉套管鞘,肝素抗凝,钢丝直至冠状动脉。采用目测直径法进行动脉狭窄的评价,与CTA检查时间间隔不超过2周。
1.2.4 血脂检测在患者治疗前、治疗1年时抽取外周空腹静脉血以酶法测定总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、低密度脂蛋白(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白(HDL-C)。
1.3 统计学方法采用SPSS 19.0统计软件,计量资料采用t检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 治疗前后血脂比较(表1)患者治疗后TC、TG、LDL-C较治疗前明显下降,HDL-C较治疗前明显升高(均P<0.05)。
表1 患者治疗前后血脂比较(mmol/L,±s)
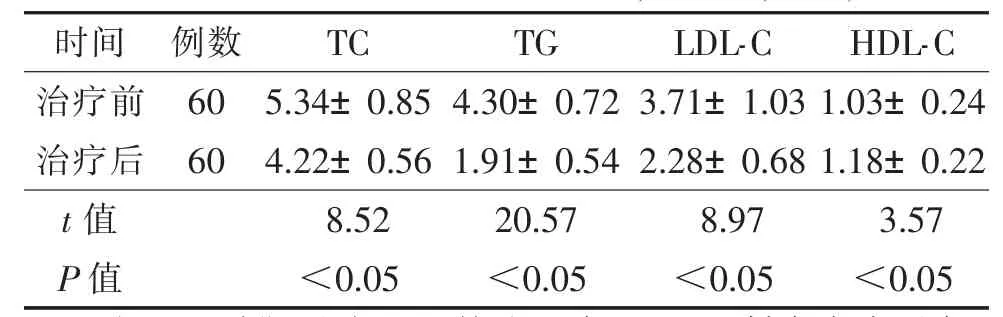
表1 患者治疗前后血脂比较(mmol/L,±s)
注:TC,总胆固醇;TG,甘油三酯;LDL-C,低密度脂蛋白;HDL-C,高密度脂蛋白。
时间例数TC TG LDL-C HDL-C治疗前60 5.34±0.85 4.30±0.72 3.71±1.03 1.03±0.24治疗后60 4.22±0.56 1.91±0.54 2.28±0.68 1.18±0.22 t值8.52 20.57 8.97 3.57 P值<0.05<0.05<0.05<0.05
2.2 治疗前后2种检查方法对冠状动脉狭窄节段检查结果比较以SCA为金标准,冠状动脉狭窄节段治疗前SCA检出127个,MSCT检出114个,诊断符合率为89.76%;治疗1年后SCA检出102个,MSCT检出93个,诊断符合率91.18%;治疗前后SCA诊断符合率比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.01,P>0.05)。
2.3 治疗前后MSCT对SE及S、斑块面积、斑块CT值显示情况比较(表2)MSCT在治疗前检出114个非钙化斑块,治疗1年后斑块数降至93个。患者治疗后冠状动脉管腔SE、S、斑块面积均较治疗前明显下降,斑块CT值较治疗前升高(均P<0.05)。
表2 MSCT检查治疗前后冠状动脉SE及S、斑块面积、斑块CT值比较(±s)
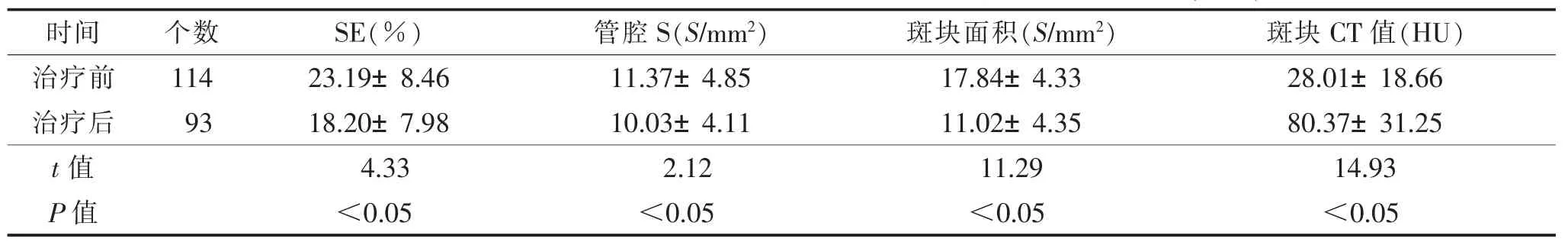
表2 MSCT检查治疗前后冠状动脉SE及S、斑块面积、斑块CT值比较(±s)
注:SE,管腔狭窄度;S,截面积。
?
3 讨论
临床大量研究[5-7]显示,冠状动脉非钙化斑块及血管狭窄与急性心血管事件关系极为密切,非钙化斑块纤维帽相对钙化斑块薄,同时有大量的巨噬细胞浸润,富含有脂质,因此斑块附着的血管内皮易被侵蚀,引起斑块破裂及脱落,导致心血管事件的发生。
冠状动脉非钙化斑块多数并不符合介入治疗指征,行长期内科药物治疗即可,如降血脂、抗血小板聚集、抗缺血等治疗。他汀类药物是临床最常见的降血脂药物,属于HMG-COA还原酶抑制剂,可通过降低HMG-COA的活性及其向甲基戊酸盐转化而起到降血脂作用,临床显示他汀类药物降血脂同时可改善血管内皮一氧化氮水平,起到抗感染及稳定斑块、抗血小板及抑制血栓的作用,可通过抑制HMG-COA竞争酶的活性部位来抑制HMG-COA还原酶作用,阻碍胆固醇的合成,降低血脂水平,还有利于脂质斑块内脂质成分的改变[1-4],因此用于治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效肯定。临床常用血脂等变化判定他汀类药物疗效,目前临床研究更多兴趣在于对斑块大小、范围等进行评价。SCA一直被认为是判定冠状动脉狭窄的金标准[8-9],能准确了解管腔的狭窄程度及血流情况,但无法对斑块的面积及性质进行判定。血管内超声检查是另一血管检查金标准,可清晰显示血管管腔及管壁,也能评估斑块的性质及稳定性[10-13],但其为有创伤性,同时对血管管径也有严格要求,如血管有明显扭曲或狭窄严重时则无法完成检查。本研究对MSCT用于他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效评估的可行性进行了研究,同时以SCA为金标准进行判断,结果显示,治疗前MSCT对冠状动脉狭窄节段诊断符合率为89.76%,治疗1年后诊断符合率为91.18%,差异无统计学意义,说明CTA判断冠状动脉狭窄是可行的。由于SCA无法对斑块性质及面积进行判定,因此对斑块变化进行评估时采用MSCT检查,治疗后非钙化斑块较治疗前有所减少,同时治疗后冠状动脉管腔SE、S、斑块面积均较治疗前明显下降。本研究中斑块CT值较治疗前升高,提示部分非钙化斑块转为纤维斑块或混合斑块,疗效较肯定。
综上所述,他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效肯定,与临床相关报道[14-16]一致,可清晰显示斑块治疗前后变化,以及进行准确的量化评估,是一种可行的监测他汀类药物治疗冠状动脉非钙化斑块疗效的方法。
[1]Camargo LM,Franca CN,Izar MC,et al.Effects of simvastatin/ezetimibe on microparticles,endothelial progenitor cells and platelet aggregation in subjects with coronary heart disease under antiplatelet therapy[J].Braz JMed Biol Res,2014,47:432-437.
[2]Stegman B,Puri R,Cho L,et al.High-intensity statin therapy alters the natural history of diabetic coronary atherosclerosis:insights from SATURN[J].Diabetes Care,2014,37:3114-3120.
[3]Puri R,Nissen SE,Shao M,et al.Sex-related differences of coronary atherosclerosis regression following maximally intensive statin therapy:insights from SATURN[J].JACC Cardiovasc Imaging,2014,7:1013-1022.
[4]Nozue T,Yamamoto S,Tohyama S,et al.Low serum docosahexaenoic acid is associated with progression of coronary atherosclerosis in statin-treated patients with diabetes mellitus:results of the treatment with statin on atheroma regression evaluated by intravascular ultrasound with virtual histology(TRUTH)study[J].Cardiovasc Diabetol,2014,13:13.
[5]Criqui MH,Denenberg JO,Ix JH,et al.Calcium density of coronary artery plaque and risk of incident cardiovascular events[J].JAMA,2014,311:271-278.
[6]Tzellos T,Kyrgidis A,Zouboulis CC.Re-evaluation of the risk for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients treated with anti-IL-12/23 biological agents for chronic plaque psoriasis:a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J].J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol,2013,27:622-627.
[7]Wannarong T,Parraga G,Buchanan D,et al.Progression of carotid plaque volume predicts cardiovascular events[J].Stroke,2013,44:1859-1865.
[8]Chen ZW,Chen YH,Qian JY,et al.Validation of a novel clinical prediction score for severe coronary artery diseases before elective coronary angiography[J].PLoS One,2014,9:e94493.
[9]赵永,邵广瑞.多层螺旋CT在冠状动脉非钙化斑块内科治疗随访中的应用[J].国际医学放射学杂志,2012,35(2):125-127.
[10]Cheng JM,Garcia-Garcia HM,de Boer SP,et al.In vivo detection of high-risk coronary plaques by radiofrequency intravascular ultrasound and cardiovascular outcome:results of the ATHEROREMO-IVUS study[J].Eur Heart J,2014,35:639-647.
[11]Pu J,Mintz GS,Biro S,et al.Insights into echo-attenuated plaques,echolucent plaques,and plaques with spotty calcification:novel findings from comparisons among intravascular ultrasound,near-infrared spectroscopy,and pathological histology in 2,294 human coronary artery segments[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2014,63:2220-2233.
[12]Bezerra HG,Attizzani GF,Sirbu V,et al.Optical coherence tomography versus intravascular ultrasound to evaluate coronary artery disease and percutaneous coronary intervention[J].JACC Cardiovasc Interv,2013,6:228-236.
[13]Chieffo A,Latib A,Caussin C,et al.A prospective,randomized trial of intravascular-ultrasound guided compared to angiography guided stent implantation in complex coronary lesions:the AVIO trial[J].Am Heart J,2013,165:65-72.
[14]Oberoi S,Meinel FG,Schoepf UJ,et al.Reproducibility of noncalcified coronary artery plaque burden quantification from coronary CT angiography across different image analysis platforms[J].AJR Am JRoentgenol,2014,202:W43-W49.
[15]Zeb I,Li D,Nasir K,et al.Effect of statin treatment on coronary plaque progression--a serial coronary CT angiography study[J].Atherosclerosis,2013,231:198-204.
[16]Rajani R,Shmilovich H,Nakazato R,et al.Relationship of epicardial fat volume to coronary plaque,severe coronary stenosis,and high-risk coronary plaque features assessed by coronary CT angiography[J].J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr,2013,7:125-132.
Feasibility study on therapeutic evaluation of non-calcified coronary plaques w ith statins by multi-slice spiral com puted tomography
CAO Zhonghua,GAO Feng,GAO Yi,KANG Chenbo,LIU Yan.Department of Radiology,Anyang District Hospital,Anyang,455000,China.
Objective:To discuss the feasibility on therapeutic evaluation of non-calcified coronary plaques with statins by multi-slice spiral computed tomography(MSCT).M ethods:Select 60 cases of confirmed non-calcified coronary plaque,treated with single statin.Selective coronary angiography(SCA)and MSCT examination performed before treatment and 1 year after treatment to evaluate arterial stenosis,MSCT examination evaluated the luminal stenosis(SE)and the cross-sectional area(S),nature and patch area,patch CT density values change in the location of plaques.Detected the serum total cholesterol(TC),triglyceride(TG),low density lipoprotein(LDL-C),high density lipoprotein(HDL-C).Results:TC、TG、LDL-C of post treatment were less than prior treatment(P<0.05),HDL-C of post treatment was higher than prior treatment(P<0.05).Coronary artery stenosis segment had 127 with SCA inspection of prior treatment,114 with MSCT inspection of prior treatment,the diagnosis coincidence rate were 93.70%,102 with SCA inspection of after treatment,93 with MSCT inspection of after treatment,the diagnosis coincidence rate were 91.18%,the difference was not statistically significant(P>0.05).Coronary artery plaque had 114 with MSCT inspection of prior treatment,93 with MSCT inspection of prior treatment,the drop rate were 22.84%.SE,S,nature and patch area of post treatment were less than prior treatment(P<0.05),patch CT density values of after treatment was higher than prior treatment(P<0.05).Conclusion:Statins have definice efficacy in the treatment of non-calcified plaques of the coronary arteries.MSCT can assess the changes of non-calcified coronary plaques after statins therapy quantitatively,effective monitoring method is feasible.
Tomography,X-ray computed;Statins;Coronary artery;Plaques,atherosclerotic;treatment outcome
2016-10-23)
10.3969/j.issn.1672-0512.2017.04.009
曹中华,E-mail:anyangzhonghua@sohu.com。

