花卉穴盘苗取栽一体式自动移栽机构设计与试验
周梅芳,徐建军,童俊华,俞高红,赵 雄,解 杰
花卉穴盘苗取栽一体式自动移栽机构设计与试验
周梅芳1,徐建军1,童俊华2,俞高红2※,赵 雄2,解 杰2
(1.金华职业技术学院,金华 321017; 2.浙江理工大学浙江省种植装备技术重点实验室,杭州 310018)
为得到一种高效简便、通用性好的花卉自动移栽机械,设计了一种取苗和栽苗一体式花卉自动移栽机构,通过夹苗针相对移栽臂的运动规律设计,实现“双尖嘴”工作轨迹,建立了该机构运动学模型,并应用自主开发的计算机分析和优化软件,分析了机构参数变化对“双尖嘴”轨迹和姿态的影响,优选出符合取栽一体式移栽要求的机构参数,并通过模型仿真和样机试验相结合的方法,对该机构进行了验证分析,结果表明:仿真轨迹、样机测试轨迹与理论轨迹三者基本一致,验证了该取栽一体式移栽机构设计的正确性和可行性。试验选用“万寿菊”花卉穴盘苗,苗龄35 d,平均苗高约10 cm,试验设定机构转速为35 r/min(移栽速度70株/min)时,平均取苗成功率为97.27%,平均栽苗成功率为77.62%,表明该取栽一体式移栽机构具有较好的实用性。该研究可为自动化移栽关键技术的研究提供参考。
农业机械;移栽;设计;花卉;取栽一体
0 引 言
花卉是园林植物中最主要的部分之一,盆栽花卉因其具有良好的观赏效果和生态价值,广泛用于环境美化和家庭装饰。花卉移栽技术可以缩短生长周期,保持品质统一,已成为现代温室盆栽花卉生产中主要的种植措施[1-3]。然而目前中国规模化花卉移栽仍然采用穴盘工厂育苗、手工移栽至塑料盘的方式,移栽作业强度大、效率低[4]。国外虽然研制了机器人技术为主体的全自动移栽机,并实现产业化,这但类移栽机取苗时苗爪垂直插入穴盘抓苗,对于叶面展幅宽的花卉移栽有较大的局限性[5-7],且整套装备复杂、价格昂贵,一次性投入大,中小型花卉企业难以承受。
鉴于国内花卉穴盘苗自动移栽机的需求以及购买国外机器成本高、通用性差的现状,近年国内一些科研院校对穴盘苗移栽机进行了探索性研究,提出多种设计方案并进行相关试验。田素博等[8-10]研制了温室瓜果或蔬菜穴盘苗移栽机,但因花卉与蔬菜移栽农艺要求不同,技术无法通用。冯青春等[11-12]针对花卉穴盘苗到花盆移栽作业环节,设计了花卉幼苗智能移栽机,集成幼苗质量识别、穴盘(花盆)传输以及幼苗夹取和移栽等功能,但取苗机构的核心部件及机理未取得技术性突破,只有在效率较低时才能保证移栽成功率,无法取得市场认可。胡海军等[13-15]研究人手从穴盘中将苗取出时的轨迹及姿态要求,提出了由5个全等的椭圆齿轮组成的行星轮系取苗机构,与国内现有的移栽机构相比,较大幅度缩小了机构尺寸,移栽效率在不增加转速情况下比前述移栽机增倍,移栽效率可达80株/min,但由于移栽臂只需完成推苗动作,对移栽最低段轨迹形态要求不高[16-17]。本文基于该类传动机构,以花卉取栽一体化移栽为设计目标,通过设计夹苗针相对移栽臂的运动规律和机构参数优化获得“双尖嘴”形工作轨迹,在优化得到机构参数基础上试制了机构样机并通过试验验证所提出取栽一体化方案的有效性。
1 移栽机构组成与原理
1.1 花卉穴盘苗取栽一体式自动移栽机构设计要求
花卉移栽机构在一个周期内需要完成取苗、送苗、栽苗和回程4个连续的动作,工作要求能模拟人工动作从穴盘中取苗,并能将苗运送到机构的最低位置后直接将钵苗插入花盆基质,达到取栽一体式的效果。综合多种移栽轨迹的优缺点和试验结果[18-20],提出移栽机构夹苗针尖点运动轨迹如图1所示,机构按照逆时针方向转动一周时,依次经过以下4个轨迹段,对应的夹苗针工作状态及轨迹要求如下。
1)01取苗轨迹段。夹苗针从0点开始向穴盘移动,接近穴盘时夹苗针伸出,在苗爪的限制下,接近1点时迅速收紧,在穴口底部1点时完全夹紧,整个夹苗过程要避免夹苗针与穴盘发生干涉,则夹苗针进入穴盘前要形成内凹的轨迹段(501);
夹苗针要近似垂直于穴盘将花卉钵苗夹紧取出,且整个取苗过程要求搅动较小,则夹苗针取苗轨迹段(012)为“尖嘴”形状,且“尖嘴”宽度尽量小,避免伤及花卉钵苗;
2)1234为持苗轨迹段:花卉钵苗被夹紧并退出穴盘往外运动;
3)45栽苗轨迹段:夹苗针到达轨迹最低点4点,其推苗角度(轨迹45)要求接近垂直,轨迹形成第二个“尖嘴”,夹苗针借助弹簧的推力迅速往上弹起,与钵苗脱离,花卉钵苗能以较好的姿态竖直栽入到花盆中。
4)50回程轨迹段:移栽臂空运行,夹苗针保持回缩状态,准备下一次移栽。
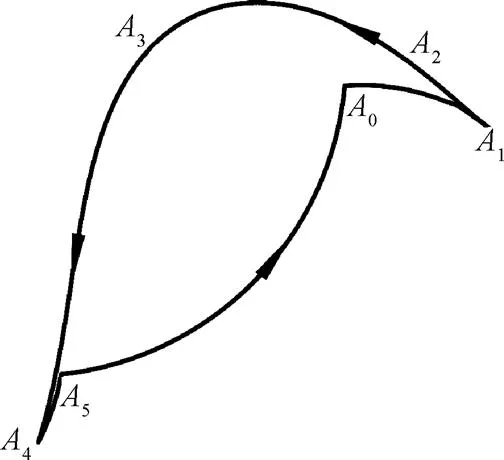
注:A0A1为取苗轨迹段;A1A2A3A4为持苗轨迹段;A4 A5栽苗轨迹段;A5A0回程轨迹段。
本文采用椭圆-非圆齿轮行星轮系机构来实现非匀速传动,利用椭圆齿轮与不完全非圆齿轮在凹凸锁止弧的配合作用下,实现非匀速间歇传动,同时结合可弹出式夹苗装置设计来实现预期的“双尖嘴”形工作轨迹。
1.2 取栽一体式自动移栽机构的组成及原理
移栽机构组成包括齿轮传动部分和2个结构相同的移栽臂,如图2所示。其中,齿轮传动部分由铰接在行星架11上的1个不完全非圆齿轮和4个相同的椭圆齿轮以及凹、凸锁止弧组成,包括固定不动的中心不完全非圆齿轮1(太阳轮)和两侧与之啮合中间椭圆齿轮4、4′(以下简称中间轮),以及与4、4′分别啮合的行星椭圆齿轮5、5′(以下简称行星轮),凸锁止弧2通过销固联在太阳轮1上,凹锁止弧3、3′分别通过销固联在中间轮4、4′上,凸锁止弧2与之凹锁止弧配合和分离,能够实现机构的非匀速间歇运动[17]。
移栽机构以行星架11回转中心为分界点,按空间位置划分,将移栽机构的行星轮5、中间轮4及与之固联的凹锁止弧3、太阳轮1及与之固联的凸锁止弧2、移栽臂6为第一支臂,对称布置的太阳轮1、中间轮4′及与之固联的凹锁止弧3′、行星轮5′以及移栽臂6′为第二支臂,机构工作时,2个支臂所经过的空间位置重合,其运动规律相位差180°,因此可取单个支臂运动进行分析说明。
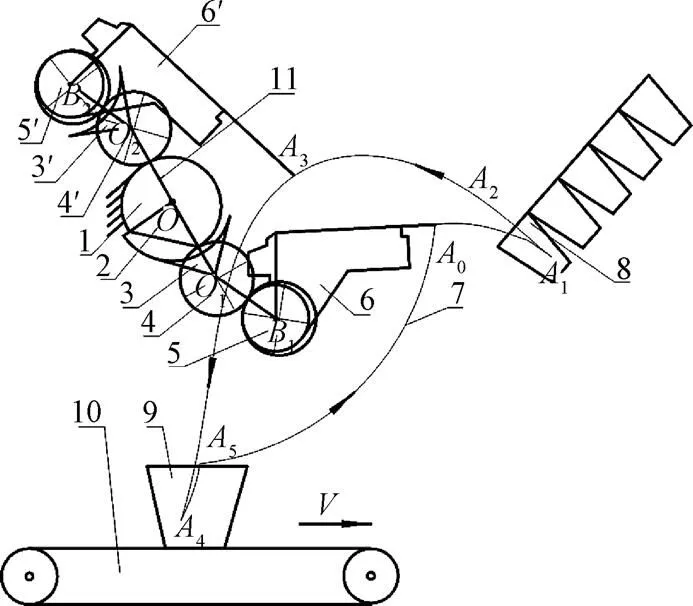
1.太阳轮 2.凸锁止弧 3, 3′.凹锁止弧 4, 4′.中间椭圆齿轮 5, 5′.行星椭圆齿轮 6, 6′.移栽臂 7.移栽轨迹 8.穴盘 9.花盆 10.传送带 11.行星架
1.Sun gear 2. Cam locking arc 3, 3′. Concave locking arc 4,4′. Middleellipse gears 5, 5′.Planetary ellipse gears 6, 6′. Transplanting arm 7. Transplanting trajectory 8. Plug tray 9. Flowerpot 10. Conveyor belt 11. Planetary carrier
注:1为行星椭圆齿轮5′回转中心;1为中间椭圆齿轮4′回转中心;为太阳轮1(不完全非圆齿轮)回转中心;2为中间椭圆齿轮4回转中心;2为行星椭圆齿轮5回转中心。
Note:1is the rotation center of planetary ellipse gear 5′;1is the rotation center of middleellipse gear 4′;is the rotation center of central ellipse gear 1 (incomplete noncircular planetary gear);2is the rotation center of middleellipse gear 4;2is the rotation center of planetary ellipse gear 5.
图2 花卉穴盘苗取栽一体式自动移栽机构示意图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of integrated automatic transplanting mechanism for taking and planting of flower plug seedlings
在机构传动部分中,5个非圆齿轮的旋转中心分别为1、1、、2、2,移栽机构工作时,太阳轮1(中间不完全非圆齿轮)固定不动,铰接于行星架11上的中间轮4和行星轮5在行星架11的旋转带动下,实现行星轮5与中间轮4的非匀速啮合,以及中间轮4与太阳轮1(不完全非圆齿轮)有齿部分的啮合,使得行星轮5的绝对运动是绕中心1的匀速圆周运动(公转)和相对行星架11的非匀速转动(自转)的2个运动的合成,此时凹锁止弧3与凸锁止弧2处于脱离状态,该行星轮5带动与之相对固定的移栽臂6做同样的非匀速转动;当凹锁止弧3与凸锁止2配合时,移栽臂6相对于行星架11静止不动,在这2种运动结合下,移栽臂能按要求的角位移和移栽轨迹运动得到满足取栽一体式花卉自动移栽机构所要求的移栽轨迹012345,如图2中的轨迹曲线。
机构中2个结构相同的移栽臂6、6´分别与该行星齿轮5、5′相对固定安装。移栽臂结构如图3所示,通过移栽臂把行星轮系的旋转运动转化为取苗针的直线来回运动,通过其末端2个夹苗针的张合模拟人工手指抓取和栽插动作。取栽一体式自动移栽机构把取苗和推苗改成花卉穴盘苗取栽一体化,其移栽轨迹以及取苗点和栽苗点的位置都发生了变化,为满足工作需求,论文设计可弹出式夹苗装置,该装置中苗爪通过螺纹孔固定在移栽臂壳体上,夹苗针通过一块专门的连接板固定在推杆上,可以自由伸长和缩短,其设计不仅能增加轨迹的长度,便于实现取栽一体化,而且也不容易与秧箱发生干涉,另一方面有利于取苗和栽苗,取苗时,苗爪移动到穴盘苗附近时以一定的倾角弹出夹苗针插入土坨,可以有效避免伤苗;而栽苗时夹苗针回缩,与夹苗针粘结的土可以通过苗爪刮除。如图4所示为未取苗与夹紧花卉钵苗时的夹苗针的2种状态。

1.凸轮 2.拨叉 3.弹簧座 4.弹簧 5.推杆 6.夹苗针 7.苗爪
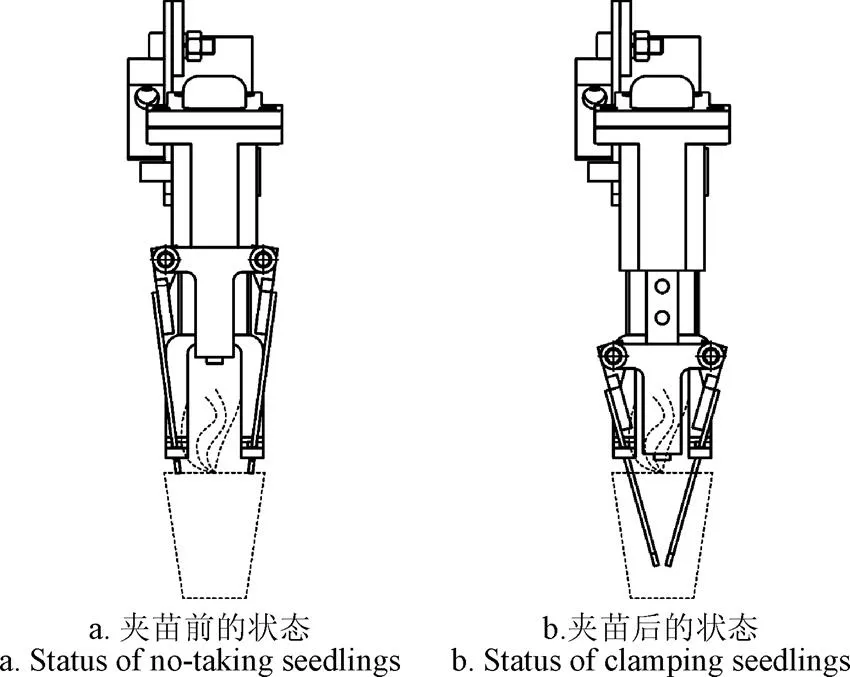
图4 夹苗针的工作状态
2 取栽一体式自动移栽机构运动学模型的建立
取栽一体式自动移栽机构2个移栽臂结构对称,运动规律仅相差180°,故取单臂分析。机构工作过程中的运动关系如图5所示,建立直角坐标系,已知常量、、、0、0、、、、0、,已知变量为1。本文规定所涉及的角度逆时针为正方向。
根据文献[21-24]中的机构分析和建模过程,可得行星椭圆齿轮的旋转中心1的位移方程式(1)。
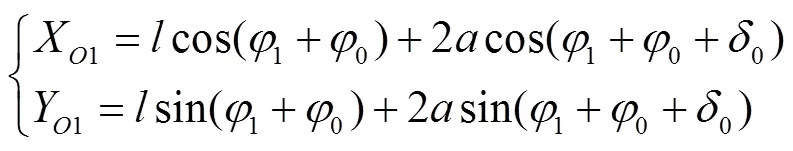
由式(1)对时间求导可得到行星椭圆齿轮的旋转中心1的速度方程式(2)。

夹苗针尖点的运动如图6所示,由图可知取苗前后夹苗针尖点的长度是变化的。

1.移栽臂 2.行星椭圆齿轮 3.中间椭圆齿轮 4.凹锁止弧 5.太阳轮 6.凸锁止弧 7.行星架
1.Transplanting arm 2.Planetary ellipse gear 3.Middleellipse gear 4.Concave locking arc 5.Sun gear 6.Cam locking arc 7.Planetary carrier
注:为行星架7回转中心;为中间椭圆齿轮3回转中心;1为行星椭圆齿轮2回转中心;1为中间椭圆齿轮回转中心从初始位置0转过角位移1后的位置;为太阳轮回转中心与中间椭圆齿轮回转中心的距离,mm;2为中间椭圆齿轮与行星椭圆齿轮中心距, mm;1太阳轮旋转中心到啮合点的距离,mm;2为中间椭圆齿轮旋转中心1到啮合点的距离,mm;′2为中间椭圆齿轮旋转中心1到啮合点的距离,mm;3为行星椭圆齿轮旋转中心1到啮合点的距离,mm;0为行星架(0线)初始角位移,(°);1为行星架从初始位置转过角位移,(°);2为中间椭圆齿轮相对与行星架转过的角位移,(°);3为行星椭圆齿轮相对于行星架转过角位移,(°);30为行星架相对于行星椭圆齿轮的初始角位移,(°);为不完全非圆齿轮有齿部分节曲线所对应的圆心角,0为行星架0与00的夹角,(°);0为夹苗针尖点与行星椭圆齿轮旋转中心0连线与行星椭圆齿轮轴线之间的夹角,(°);为行星架的角速度,rad/s。
Note:is the rotation center of planetary carrier 7;is the rotation center of middle ellipse gears 3;1is the rotation center of planet ellipse gears 2;1is the position of the middleellipse gears rotation center rotate angle1from the initial position;is the distance between the center of rotation of the sun gear and the center of rotation of the middle ellipse gears, mm; 2is center distance of middle ellipse gears and planetary ellipse gears, mm;1is the distance between the center of rotation of the sun gear and meshing point, mm;2is the distance between the center of rotation of the middle ellipse gears and meshing point, mm;′2is the distance between the center of rotation of the middle ellipse gear1and meshing point, mm;3is the distance between the center of rotation of the planetary ellipse gear1and meshing point, mm;0is initial angular displacement of planetary frame (0line), rad;1is angular displacement that is transferred of planetary frame form installation position, rad;2is transferred angular displacement of middleellipse gears relative to planetary frame, rad;3is transferred angular displacement of planetary ellipse gears relative to planetary frame, rad;30is initial angular displacement of planetary ellipse gears relative to planetary frame, rad;is center angle of the incomplete noncircular gear toothed part of section curve corresponding, rad;0is included angle between planetary frame00and0, rad;0is included angle between ligature from taking the tip of clamp needle to center of rotation0of planetary ellipse gears and axis of planetary ellipse gears,rad;angular velocity of planetary frame, rad.
图5 椭圆-不完全非圆齿轮行星轮系运动示意图
Fig.5 Movement diagram of planetary gear train with ellipse-incomplete noncircular gear

注:P为移栽臂上夹苗针尖点。
1)取苗之前与栽苗之后夹苗针尖点的位移方程

2)取苗之后与栽苗之前夹苗针尖点的位移方程
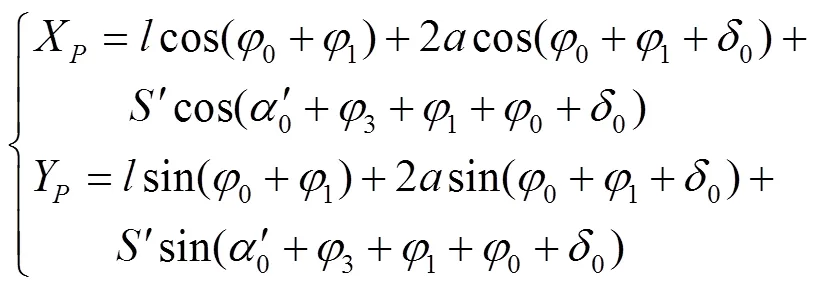
式中为行星轮椭圆齿轮旋转中心到夹苗针(未伸长)尖点的距离,mm;为行星轮椭圆齿轮旋转中心到夹苗针(伸长后)尖点的距离,mm;0为夹苗针(伸长后)尖点与行星椭圆齿轮旋转中心连线与行星椭圆齿轮轴线之间的夹角,(°)。
夹苗针尖点的速度和加速度需根据凸轮与拨叉之间的关系来确定。
3 移栽机构参数优化
3.1 优化目标
基于文献[25-27]对优化目标的研究基础上,分析取栽一体式花卉移栽机构的运动过程和机理,基于花卉钵苗的物理性状、移栽机构的运动干涉、运动轨迹和移栽臂姿态及机构结构要求等确定了以下优化目标和约束条件:1)夹苗针在取苗阶段轨迹与穴盘接近垂直,即夹苗针从开始的取苗角度(01轨迹倾角)逐渐调整取苗姿态到与苗盘成90°(12轨迹)的退出角度,避免移栽臂与穴盘发生干涉;2)移栽轨迹在穴盘内深度达30 mm,才能顺利取出钵苗;3)栽苗角(移栽臂在把花卉钵苗栽入到花盆时,夹苗针与水平面之间的夹角)应在75°~90°之间,能使花卉钵苗能以较好的姿态竖直栽入到花盆中;4)移栽轨迹的高度达到300 mm左右,才能将所取钵苗输送到花盆底部;5)2个移栽臂之间不能发生干涉。
3.2 机构参数对优化目标的影响
根据上述移栽机构运动特性分析和数学建模可知,取栽一体式自动移栽机构的参数优化是一个多参数的复杂优化问题,多个参数对最终的运动轨迹和移栽臂姿态均产生较大影响且各参数之间也会相互影响[28-29]。基于VB可视化设计软件,开发取栽一体式移栽机构辅助分析和优化软件,借助该软件采用控制变量法分析各个参数单独变化时对移栽轨迹的影响,分析可知椭圆长轴半径椭圆短轴与长轴之比移栽臂的初始安装角0取值主要影响着移栽轨迹的长度和形状,而花卉移栽机构的行星架拐角0(图5中行星架111的夹角)、行星架(1线)初始角位移0、行星轮椭圆齿轮旋转中心到夹苗针尖点的距离等参数则主要影响取苗角度、轨迹的圆滑度以及栽苗角度等。
基于上述各参数对移栽轨迹影响分析,通过人机交互方式优化目标,得到一组满足取栽一体式自动移栽轨迹的机构参数:=25.057 6 mm,=0.995,=275(为不完全非圆有齿部分对应的圆心角),0=30°,0=25°,0=−60°,=160 mm,1=276(1为夹苗针回缩的时间)。该组参数对应的夹苗针尖点运动轨迹如图7所示,轨迹形成了“双尖嘴”形状,满足取苗和栽植时夹苗针垂直进出要求;取苗段轨迹与穴盘近似垂直,且在穴盘内长度为33 mm,取苗角度约为33.88°;栽苗角度约为80°;轨迹的总高度为247.88 mm,满足优化目标。通过优化软件的图形显示区观察花卉移栽机构的相对运动模拟如图8所示,显示整个移栽过程2个移栽臂之间、夹苗针与穴盘之间均未发生干涉现象,符合约束条件。
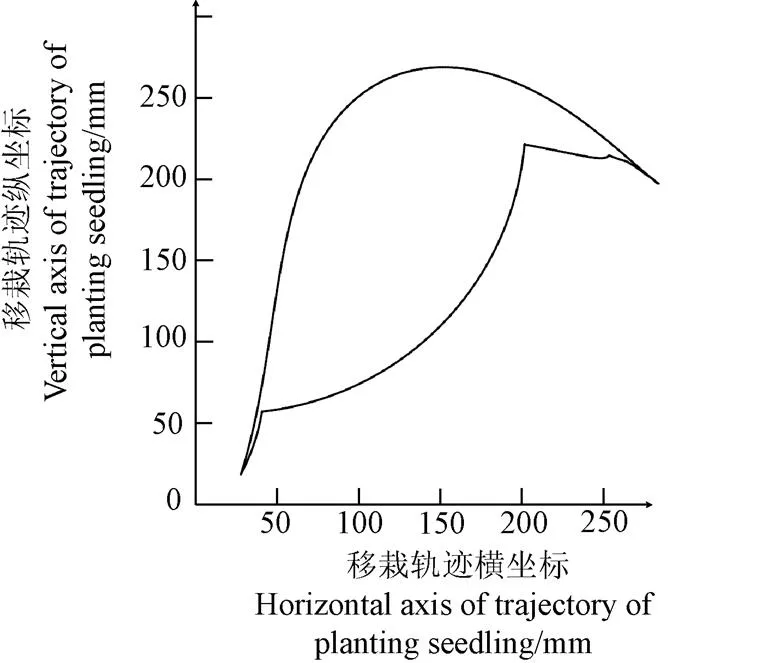
图7 优化后的移栽机构运动轨迹
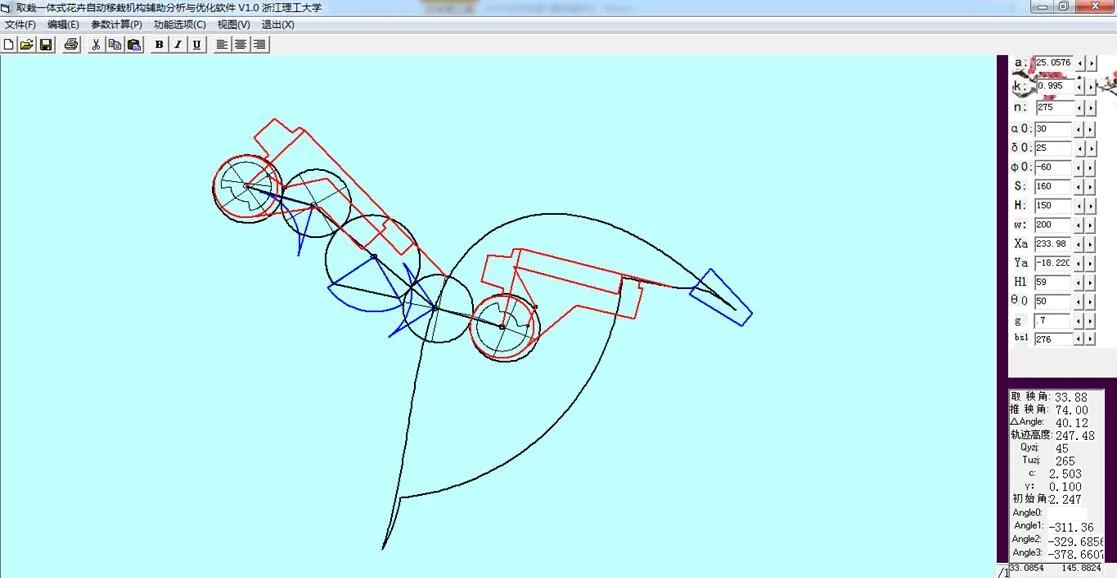
图8 移栽机构相对运动模拟界面
4 机构仿真分析与试验
4.1 移栽机构仿真分析
根据优化后的机构参数,完成移栽机构虚拟装配,对得到的虚拟样机夹苗针尖点轨迹进行分析。将仿真轨迹(图9)与理论轨迹(图7)进行对比,理论轨迹与仿真轨迹取苗段存在着一定的差异,其原因是在取栽一体式自动移栽机构上加装了缓冲装置,以此来减小凹、凸锁止弧脱离时产生的较大冲击;另外仿真轨迹较为圆滑,形成小环扣,更为符合移栽过程取苗和栽苗的要求。轨迹的其余部分都保持一致,验证了理论设计的正确性。
4.2 样机运动轨迹测试
为验证移栽机构夹苗针尖点的实际工作轨迹是否与仿真轨迹一致,将取栽一体式自动移栽机构安装在试验台上进行空转试验。试验方法:1)安装移栽机构,调整机构至运转自如;2)将高速摄像机安装在合适位置,使机构完整显示在屏幕中,调节灯光位置和强度,使机构夹苗片尖点清晰可见;3)调节电机转速为40 r/min,开始空转试验,待运转平稳后采集图像(采集2至3个周期即可);4)利用Bestcam图像分析软件进行描点,得到移栽机构夹苗针尖点的运动轨迹如图10所示。

图9 ADAMS仿真轨迹

图10 样机试验轨迹
结果分析:对比图10和图7轨迹可得:1)两者轨迹基本一致,但理论轨迹尖嘴部分不太平滑,其原因是移栽传动机构中增加了一对缓冲装置,使凹凸锁止弧脱开过程中减少冲击,过渡平顺,因此实际轨迹在尖嘴部分比理论轨迹更圆滑;2)试验证明该机构设计满足移栽轨迹和姿态等农艺要求。
4.3 移栽试验
试验选用万寿菊花卉穴盘苗,穴盘育苗基质采用珍珠岩和泥炭土混合而成,含水率为46%,穴盘规格为8(列)×16(行),穴口长×宽为31 mm×31 mm,深度为43 mm,穴盘数量为10盘,苗龄为35 d,平均苗高约10 cm。移栽机构转速设定为35 r/min(移栽速度70株/min)。进行连续移栽试验如图11所示。
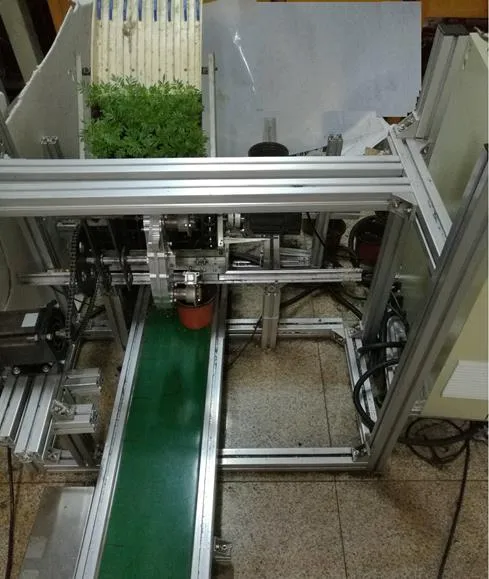

图11 样机移栽试验
移栽试验结果及性能参数如表1所示,去除空穴,共连续取栽1 225株,取出1 192株,栽植961株,平均取出成功率达到97.27%,平均栽植成功率为77.62%,表明该取栽一体式自动移栽机构满足顺利从钵盘取出钵苗的要求,但栽植效果相对偏低,通过试验视频分析发现,主要原因在于选用的花卉苗叶子伸展距离大于苗爪间的距离,在基质不饱满的情况下,钵苗栽入花盆后夹苗针释放钵苗并往上运动时,易把钵苗带出花盆[30],增加移栽失败概率。
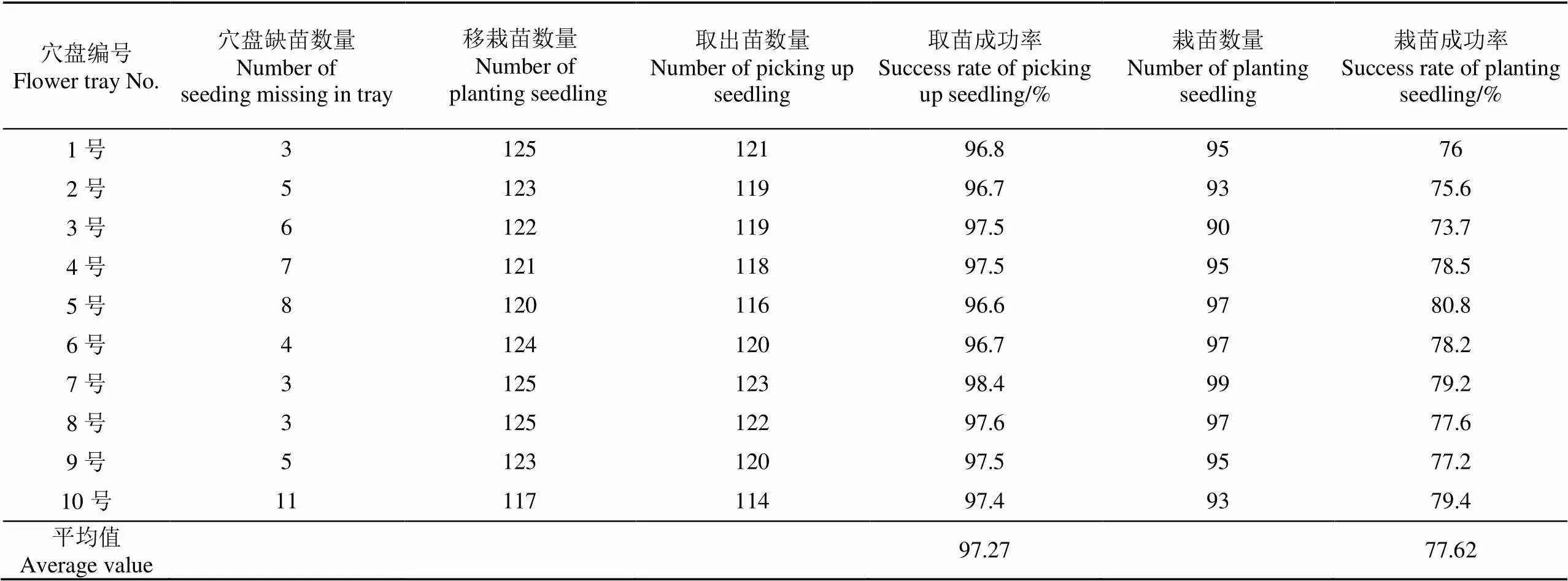
表1 移栽试验参数
5 结论与讨论
1)设计了一种花卉穴盘苗取栽一体式自动移栽机构,分析了该移栽机构的设计要求、工作原理,建立了机构的运动学模型。基于VB可视化平台开发该机构的计算机辅助分析与优化软件,运用软件分析机构参数变化对移栽轨迹和姿态的影响,优选出1组符合取栽一体式自动移栽要求的机构参数,椭圆长半轴为25.057 6 mm,椭圆短轴与长轴之比为0.995,移栽臂的初始安装角为30°,行星架拐角为25°,行星架初始始角位移为−60°,行星齿轮回转中心到夹苗针尖点的距离为160 mm。
2)基于优化得到的参数,在ADAMS中完成了移栽机构的三维设计与仿真分析,并试制样机进行取栽试验,试验结果表明:移栽速度为70株/min时,取苗成功率为97.27%,栽苗成功率为77.62%;验证了取栽一体式自动移栽机构的设计的有效性。
3)运动学仿真与高速摄影移栽试验结果表明:理论轨迹和试验轨迹两者基本一致,该机构设计满足花卉移栽轨迹和姿态等农艺要求;但两者取苗段存在着一定的差异,其原因是在移栽机构上加装了缓冲装置,以此来减小凹、凸锁止弧脱离时产生的较大冲击。
本文研制的花卉穴盘苗取栽一体式自动移栽机构,对于叶面宽且密的花卉钵苗,栽苗后苗爪容易把钵苗带出花盆,使移栽失败。为有效避免上述机构带苗现象发生,后续将从机构运动和结构设计方面进行探索和研究:进一步优化机构尺寸,增加苗爪之间的距离,避免夹苗针蹭刮钵苗叶面;优化栽苗段轨迹,使苗爪能以一定倾角退出花盆,避开叶面;苗针结构优化,减少挂叶现象。
[1] 程堂仁,王佳,张启翔. 发展我国创新型花卉产业的战略思考[J]. 中国园林,2013(2):73-78.
Cheng Tangren, Wang Jia, Zhang Qixiang. Strategic thinking about the development of innovative flower industry in China[J]. Journal of Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2013(2): 73-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 2020年新疆设施农业面积达到200万亩[J]. 农业工程技术:温室园艺,2010(10):76.
The facility agricultural area of XinJiang Will Reach 2 Million Mu in 2020[J]. Agriculture Engineering Technology: Greenhouse & Horticulture, 2010(10):76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 马彩雯,王晓冬,吴乐天,等. 新疆设施农业发展现状分析[J]. 农机化研究,2010,32(10):230-232,236.
Ma Caiwen, Wang Xiaodong, Wu Letian, et al. Analyze of facility agriculture present situation in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(10): 230-232, 236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 王荣华,邱立春,田素博. 我国穴盘苗机械化生产的现状与发展[J]. 农机化研究,2008,30(7):230-231.
Wang Ronghua, Qiu Lichun, Tian Subo. Status and development of mechanized processing of plug seedling in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2008, 30(7): 230-231. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Choi W C, Kim D C, Yu H R. Development of a seedling pick-up device for vegetable transplanting[J]. American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 2002, 45(1): 13-19.
[6] 齐飞,周新群,张跃峰,等. 世界现代化温室装备技术发展及对中国的启示[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(10):279-285.
Qi Fei, Zhou Xinqun, Zhang Yuefeng, et al. Development of world greenhouse equipment and technology and some implications to China[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(10): 279-285. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 辜松,杨艳丽,张跃峰. 荷兰温室盆花自动化生产装备系统的发展现状[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(19):1-8.
Gu Song, Yang Yanli, Zhang Yuefeng. Development status of automated equipment systems for greenhouse potted flowers production in Netherlands[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(19): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 田素博,邱立春,张诗. 基于PLC的穴盘苗移栽机械手控制系统设计[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2007(38):122-124.
Tian Subo, Qiu Lichun, Zhang Shi. Control system of transplanting potted seedlings manipulator based on PLC[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2007(38): 122-124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 韩长杰,徐阳,张静,等. 半自动压缩基质型西瓜钵苗移栽机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(13):54-61.
Han Changjie, Xu Yang, Zhang Jing, et al. Design and experiment of semi-automatic transplanter for watermelon seedlings raised on compression substrate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(13): 54-61. (in Chinese withEnglish abstract)
[10] 孙国祥,汪小旵,何国敏,等. 穴盘苗移栽机末端执行器设计与虚拟样机分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(10):48-53.
Sun Guoxiang, Wang Xiaochan, He Guomin, et al. Design of the end-effector for plug seedlings transplanter and analysis on virtual prototype[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(10): 48-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 冯青春,王秀. 花卉幼苗智能移栽机设计与仿真分析[J].农机化研究,2013,35(12):78-81.
Feng Qingchun, Wang Xiu. Design and simulation of automatic transplanter for flower seedling[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2013, 35(12): 78-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 冯青春,王秀,姜凯,等. 花卉幼苗自动移栽机关键部件设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(6):21-27.
Feng Qingchun, Wang Xiu, Jiang Kai, et al. Design and test of key parts on automatic transplanter for flower seedling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(6): 21-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 胡海军. 椭圆齿轮行星轮系蔬菜钵苗取苗机构的研究与设计[D]. 杭州:浙江理工大学,2014.
Hu Haijun. Study and Design on Vegetable Plug Seedling Pick-up Mechanism of Planetary Gear Train with Planetary Elliptic Gears[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 周梅芳,俞高红,赵匀,等. 椭圆齿轮行轮系蔬菜钵苗取苗机构的参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(18):13-21.
Zhou Meifang, Yu Gaohong, Zhao Yun, et al. Parameters optimization and test on pick-up mechanism of planetary gear train with ellipse gears for vegetable plug seedling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(18): 13-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 吴国环,俞高红,项筱洁,等. 三移栽臂水稻钵苗移栽机构设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(15):15-22.
Wu Guohuan, Yu Gaohong, Xiang Xiaojie, et al. Design and test of rice potted-seedling transplanting mechanism with three transplanting arms[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(15): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 俞腾飞. 非圆-椭圆齿轮行星系取苗机构的参数优化与设计[D]. 杭州:浙江理工大学,2013.
Yu Tengfei. Parameters Optimization and Design of Picking Seeding Mechanism of Planetary Gear Train With Non-Circular and Elliptical Gear[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 祝广辉. 蔬菜钵苗旋转式取苗机构的参数优化与试验研究[D].杭州:浙江理工大学,2015.
Zhu Guanghui. Parameters Optimization and Experimental Research of Rotary Pick-up Mechanism for Vegetable Pot-seedling[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张振国,吕权贵,陈青云,等. 盆栽花卉移栽机取苗机构的现状分析[J]. 江苏大学学报:自然科学版,2016,37(4):409-417.
Zhang Zhenguo, Lü Quangui, Chen Qingyun, et al. Staus analysis of picking seeding transplanting mechanism automatic mechanism for potted flower[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 37(4): 409-417. (in Chinese with Englishabstract)
[19] 吴有特. 蔬菜钵苗取苗机构的优化设计与试验分析[D]. 杭州:浙江理工大学,2016.
Wu Youte. Optimize Design and Test Analysis on Pick-up Mechanism for Vegetable Plug Seedling[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] Jin Xin, Li Daoyi, Ma Hao, et al. Development of single row automatic transplanting device for potted vegetable seedings[J]. Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2018, 11(3): 67-75.
[21] 俞高红,黄小艳,叶秉良. 旋转式水稻钵苗移栽机构的机理分析与参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(3):16-22.
Yu Gaohong, Huang Xiaoyan, Ye Bingliang, et al. Principle analysis and parameters optimization of rotary rice pot seedling transplanting mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(3): 16-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李革,赵匀,俞高红. 椭圆齿轮行星系分插机构的机理分析和计算机优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2000,16(4):78-81.
Li Ge, Zhao Yun, Yu Gaohong. Theoretical analysis and parameters optimizing of separating-planting mechanism with planetary ellipse gears[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2000, 16(4): 78-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 赵匀. 农业机械分析与综合[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2009.
[24] 王永维,何焯亮,王俊,等. 旱地蔬菜钵苗自动移栽机栽植性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(3):19-25.
Wang Yongwei, He Zhuoliang, Wang Jun, et al. Experiment on transplanting performance of automatic vegetable pot seedling transplanter for dry land[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(3): 19-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 俞高红,刘炳华,赵匀,等. 椭圆齿轮行星系蔬菜钵苗自动移栽机构运动机理分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(4):53-57.
Yu Gaohong, Liu Binghua, Zhao Yun, et al. Kinematic principle analysis of transplanting mechanism with planetary elliptic gears in automatic vegetable transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(4): 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 俞亚新,骆春晓,俞高红,等. 椭圆-不完全非圆齿轮行星系取苗机构参数优化[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(6):62-68.
Yu Yaxin, Luo Chunxiao, Yu Gaohong, et al. Parameters optimization of pick-up mechanism of planetary gear train with ellipse gears and incomplete non-circular gear[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(6): 62-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 俞高红,何琰,陈建能,等. 旋转式分插机构运动学多目标非劣解群自动寻求[J]. 农业机械学报,2009,40(6):47-52.
Yu Gaohong, He Yan, Chen Jianneng, et al. Automatic search of pareto solutions of multi-objective for rotary transplanting mechanism kinematics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2009, 40(6): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 裘利钢,俞高红. 蔬菜钵苗自动移栽机送苗装置的设计与试验[J]. 浙江理工大学学报,2012,29(5):683-687.
Qiu Ligang, Yu Gaohong. Design and test of a seedling- delivering device on an automatic transplanter for pots of vegetable seedlings[J]. Journal of ZheJiang Sci-Tech University, 2012, 29(5): 683-687. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 胡建平,靳合琦,常燕超,等. 基于Delta并联机构钵苗移栽机器人尺度综合与轨迹规划[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(5):28-35.
Hu Jianping, Jin Heqi, Chang Yanchao, et al. Dimensional synthesis and trajectory planning of plug seedling transplanting robot based on delta parallel mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(5): 28-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 高国华,马帅. 基于离散单元分析与物场分析的盆花移栽手爪优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(6):35-42.
Gao Guohua, Ma Shuai. Improvement of transplanting manipulator for potted flower based on discrete element analysis and Su-field analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(6): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Design and experiment of integrated automatic transplanting mechanism for taking and planting of flower plug seedlings
Zhou Meifang1, Xu Jianjun1, Tong Junhua2, Yu Gaohong2※, Zhao Xiong2, Xie Jie2
(1.,321017,; 2.,,310018,)
In order to develop a more efficient and universal flower auto-transplantation technique, an auto-transplantation mechanism with the integrated function of seedling pick-up and transplanting has been designed. This mechanism involves gear driving and two transplanting arms of the same structure. The gear driving system is made up of one semi-circle gear, four oval planet gears and concave-convex lock-up arc. It aims to move with the non uniform speed through the operation of planet gears and pulling and imbedding of concave-convex lock-up arc. The auto-transplantation arm includes the transplanting claw, convex gear and removing gear-gap parts. It transfers the whirling operation of planet gear into straight-line operation of pick-up seedling. The manual finger scratching and planting were simulated by two pins at the end of the seedling arm. The auto-transplantation mechanism combines the pick-up and planting. The transplanting trajectory and the location of pick-up and planting were special. Thus, it is essential to design new mechanism accordance with the movement of pick-up clip and achieve “Double beak sharp” trajectory. In this paper, we designed a device of bouncing clip to lengthen the trajectory to realize the function of pick-up and planting, and it could facilitate the integration of the planting. At the same time, when the claw moves nearly to the pot seedling, the seedling needle was inserted into the soil with a certain angle of inclination, which could effectively avoid the injury of the seedlings and the interference with the seedling box. Based on the kinematics characteristics of the mechanism, a corresponding mathematic model was established, and the Visual Basic 6.0 software was used to optimize the mechanism parameters. The program was used to analyze the influence of the parameters of mechanism on the trajectory and attitude of the “Double beak sharp". Finally, the best group of mechanism parameters was selected, and then the 3D design and components assembly were carried out based on SolidWorks 2015 software. Importing the 3D model to Adams, the trajectories of seedling needle could be obtained by the kinematics simulation. Finally, the prototype test was carried out and the test trajectory of the prototype was obtained by the test platform. Through the platform, the operation process was recorded by high-speed camera. Therefore, the trajectories of seedling needle could be tracked through the Bestcam picture analysis software. The results were basically the same among the simulation trajectory, the test trajectory of the prototype and the theoretical trajectory, which verified the correctness and feasibility of the design in this paper. Experimental research was carried out using the prototype, “Marigold chrysanthemum” seedlings were selected in the experiment, the basic composition of the pot seedling combines the pearl cave and peat mud, with the water component of 46%, the seedling tray were eight lines and 16 rows, both the length and width of seedling were 31 mm, and depth was 43 mm, and the test seedlings of marigold were 35 days, with the average height of 10 cm. The rotation speed of the mechanism was set as 35 r/min, its mean efficiency was 70 stems per minute. The obtained seedling success rate was 97.27%, while the transplanting success rate was 77.62%. It reflected the practicality of the integrated transplanting mechanism; the research could provide a reference for the key technology of automatic transplanting.
agricultural machinery; transplants; design; flowers; integration of taking and planting
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.20.006
S223.9
A
1002-6819(2018)-20-0044-08
2018-06-15
2018-08-01
国家自然科学基金项目(51505429,51575495);浙江省科技厅基础公益研究计划项目(LGN18E050003);金华市科学技术农业类重点项目(2014-2-005)
周梅芳,副教授,主要从事农业机械和机电一体化研究。Email:984752073@qq.com
俞高红,教授、博导,主要从事种植机械与机构学研究。Email:yugh@zstu.edu.cn
周梅芳,徐建军,童俊华,俞高红,赵 雄,解 杰. 花卉穴盘苗取栽一体式自动移栽机构设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(20):44-51. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.20.006 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhou Meifang, Xu Jianjun, Tong Junhua, Yu Gaohong, Zhao Xiong, Xie Jie. Design and experiment of integrated automatic transplanting mechanism for taking and planting of flower plug seedlings[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(20): 44-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.20.006 http://www.tcsae.org

