Exosomes derived from stem cells as an emerging therapeutic strategy for intervertebral disc degeneration
Zhi-Lei Hu,Hai-Yin Li,Xian Chang,Yue-Yang Li,Chen-Hao Liu,Xiao-Xin Gao,Yu Zhai,Chang-Qing Li,Department of Orthopedics,Xinqiao Hospital,Army Military Medical University,Chongqing 400037,China
Yu-Xuan Chen,Center of Traumatic Orthopedics,People's Liberation Army 990 Hospital,Xinyang 46400,Henan Province,China
Abstract
Key words:Exosomes;Intervertebral disc degeneration;Stem cells;MicroRNA;Regenerative medicine;Biological characteristic
INTRODUCTION
Low back pain (LBP) is a common spinal health problem worldwide[1].In a global systematic review,the mean prevalence of LBP at a given time in the general population was approximately 18%,and the 1-year prevalence was approximately 38%[2].Therefore,a small reduction in health care or disability rates related to LBP could bring significant social and economic benefits[3,4].
The causes of LBP are complex[5,6],and although there is no direct evidence,IVD degeneration is considered a major cause[5].The cause of intervertebral disc (IVD)degeneration is still not fully understood,but some factors,such as aging,abnormal mechanical stress,trauma,nutritional deficiencies,and heredity,are considered to be involved in this process[7].The pathological process of disc degeneration includes the reduction of nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs)[8,9]and extracellular matrix (due to decreased synthesis and increased degradation),aging of the annulus fibrosus,and calcification of cartilage endplates[10].
Current treatments for LBP caused by IVD degeneration include invasive surgery and conservative treatment[11],which are mainly aimed at relieving symptoms rather than changing pathogenic mechanisms.Therefore,there is an urgent need for new therapies that treat disc degeneration by directly addressing causes and mechanisms to retain and/or restore disc structure and mechanical function.
Recently,an increasing number of studies have focused on degenerated disc regeneration,including studies related to bioactive molecular injection[12,13],cell-based therapies[14-16],tissue engineering[17,18],and gene therapy[19,20].Bioactive molecular injection is a biological therapy utilizing chemical molecules with the effect of recruitment of endogenous stem cells into the IVD or stimulation of their proliferation.Although the short-term effect is acceptable,the long-term maintenance of biological activity has become an unavoidable obstacle for this therapy.Cell-based therapies,as the most attractive method among these studies,involve the injection of extracted cells,such as NPCs or various stem cells,into the discin vivoto restore IVD homeostasis following the proliferation,differentiation,and immune regulation of the transplanted cells[21].Although some progress has been made,the complex environment of the degenerated IVD causes a low survival rate of stem cells and makes it difficult to accurately control cell viability and differentiation.Additionally,the sources and safety issues of stem cells need to be considered.Gene therapy refers to modification of genomes to increase the expression of effector genes and promote the continuous production of one or more biologically active factors in the IVD to promote cell proliferation,extracellular matrix production,and inhibition of apoptosis.
Studies on the mechanism of stem cell therapy have provided increasing evidence that the factors that play an important role in these treatments are the exosomes that are secreted by stem cells[22-24].Exosomes were considered waste products from cells when they were first reported in 1983[25].Currently,this nanoscale cell vesicle is known to be an important substance in intercellular communication that can transfer biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids from parent cells to recipient cells.Their applications in regenerative medicine are also increasing,including in the regeneration of NPCs and the maintenance of disc homeostasis[26-28].This paper reviews the biological characteristics of exosomes and their research status in the field of disc degeneration,and gives outlook on their future applications in this field.
BIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND FUNCTIONS OF EXOSOMES
Exosomes are a type of extracellular vesicle;the other two main types of extracellular vesicles are microvesicles and apoptotic bodies[29,30].The characteristics of the three main extracellular vesicles are shown in Table1.
Exosomes have spheroid membranes of a uniform lipid bilayer with diameters of approximately 30-150 nm[31].They typically can be detected in various body fluids,such as blood[32,33],amniotic fluid[34-36],breast milk[37,38],urine[39,40],synovial fluid[41,42],and saliva[43,44].They can be transported to corresponding target cells through the body fluids to perform a specific function.In vitro,exosomes also have been isolated from cell culture supernatant[45].We now know that the mechanism of exosome formation involves the inward invagination of the endosomal membrane pathway.At the first stage,the inward budding of the plasma membrane with receptors leads to the formation of an endosome.Then,small vesicles can be formed by further inward budding of the limiting membrane to form a multivesicular body (MVB) with intraluminal vesicles.The vesicular contents in MVBs are finally degraded when MVBs fuse with the lysosome or are released into the extracellular space[46].After being released into the extracellular space,exosomes play a biological role when they contact another membrane and are endocytosed into a recipient cell[46,47].
The function of exosomes mainly depends on their contents.Among the components of exosomes,lipids,proteins,and nucleic acids are the three main substances that determine the biological function of exosomes[48,49].Lipids in exosomes are mainly located in the membrane,including cholesterol,phosphatidylserine,sphingomyelin,etc.In addition to maintaining the biological stability of exosomes,lipids are also involved in biological processes such as the formation and release of exosomes[50].Exosomes are also rich in a variety of proteins,including cytoskeleton components,tetraspanins,heat-shock proteins,and other types of proteins[51,52].Among them,ALIX and tetraspanin proteins,such as CD81,CD9,and CD63,are markers of exosomes[51].However,it is difficult to distinguish exosomes from other extracellular vesicles with overlapping size and density based solely on these markers.
Exosomes usually carry nucleic acids,including mRNAs[53],microRNAs(miRNAs)[54,55],and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs)[56].MiRNAs are a class of endogenous noncoding RNAs found in eukaryotes that have a length of approximately 20-25 nucleotides.Mature miRNAs are produced from longer primary transcripts that undergo a series of nuclease-mediated cleavages;then,the miRNAs are assembled into RNA-induced silencing complexes by complementary base pairing to a target mRNA,which guides degradation of targets or suppresses translation of targets,based on the degree of complementarity[57].According to the principle of base complementary pairing,a miRNA usually can target hundreds of corresponding genes,which implies that miRNAs carried in exosomes may play an important role in regulating gene transcription in target cells.LncRNAs are a class of RNA molecules longer than 200 bp that do not encode proteins.They are widely involved in the transcription,translation,and posttranslational regulation of genes.LncRNAs can participate in chromatin modification,transcription activation,and transcription interference in cells,or they can act as "bait molecules" that interact with proteins,DNA,and RNA[58,59].As messengers of intercellular communication,exosomes are secreted by parent cells and taken up by target cells in the following ways:(1)Transmembrane proteins are fused to target cell membranes by binding to receptor proteins;(2) The exosomal membrane fuses directly with the cell membrane,releasing the contents;and (3) Target cells take up exosomes through endocytosis[60,61].
THERAPEUTIC APPLICATION OF STEM CELL-DERIVED EXOSOMES IN VARIOUS TISSUES
Recently,an increasing number of studies have shown that exosomes derived from stem cells play an important role in restoring tissue homeostasis and promoting tissue regeneration.
Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can significantly enhance bone regeneration,promote vascular regeneration,and accelerate fracture healing in a rat femur nonunion model[62].Exosomes from adipose stem cells promote the vascularization of endothelial cells[63].Human umbilical cord MSC exosomes can promote angiogenesis and repair of second-degree burn wounds of the skin[64].Exosomes from human stem cells can promote the repair of jaw joints and the synthesis of extracellular matrix in that tissue[24].Increasing experimental results showthe potential regenerative ability of stem cell-derived exosomes through their promotion of cell proliferation,enhancement of angiogenesis,promotion of extracellular matrix homeostasis recovery,inhibition of inflammation,and other unknown effects.Some of these beneficial mechanisms can also be achieved in the repair of disc degeneration.
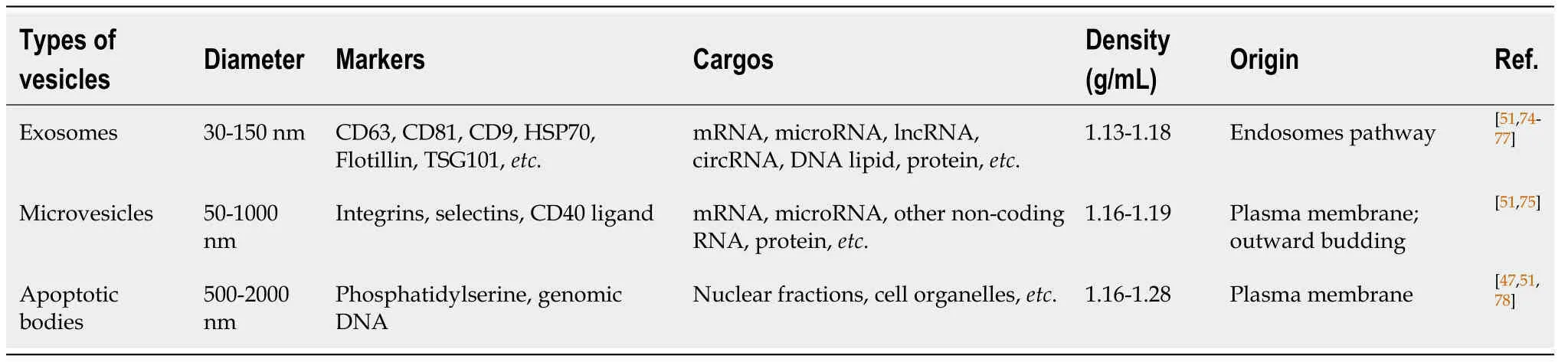
Table1 Characteristics of three main types of extracellular vesicles
THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS OF STEM CELL-DERIVED EXOSOMES ON IVD DEGENERATION
Stem cell transplantation for treatment of IVD degeneration has made great progress.In vitroandin vivostudies have revealed the great advantages of stem cells as seed cells for cell-based therapies.However,because of the complex and harshin vivoenvironment of the IVD,there are obstacles to be overcome by IVD degeneration stem cell therapy approaches[65].With continued research into stem cell therapies,it has been found that the exosomes secreted by stem cells play an important role in their therapeutic effect[26,66].Therefore,exosomes have attracted more and more attention in some preclinical studies of promoting IVD regeneration (Table2).
When exosomes derived from bone marrow MSCs were cocultured with NPCs from degenerated IVDs,cell proliferation was significantly accelerated by extending the incubation time with exosomes.Additionally,the expression of the extracellular matrix synthesis and protection genesACAN,COL2A1,SOX-9,andTIMP-1increased with incubation time,while the degradation-related genesMMP-1andMMP-3were decreased.Therefore,it seems to indicate that MSC-derived exosomes promote the proliferation and extracellular matrix homeostasis of NPCs[26].
Stem cell-derived exosomes not only promote the proliferation of NPCs but also inhibit their apoptosis.In a study by Chenget al[28],human bone marrow MSCs and fibroblast-derived exosomes were used to treat TNF-α-induced apoptotic NPCs.The cells treated with the exosomes derived from the bone marrow MSC group had a significantly lower apoptotic rate than those of the other groups.In vivoexperiments showed that the MSC-derived exosome treatment group had significantly lower Pfirrmann grade,histological grade,and apoptotic rate than the noninjection groups.Anotherin vitrostudy also confirmed the anti-apoptotic effect of stem cell exosomes.Liaoet al[27]co-incubated exosomes from MSCs with advanced glycation end productsinduced NPCs and confirmed that the levels of apoptosis-related markers caspase-3 and caspase-12 decreased significantly.With the increase in exosomal concentration,the declining trend was greater.The above studies confirmed that exosomes have significant anti-apoptotic effects bothin vivoandin vitro.
The accumulation of a large number of inflammatory factors and extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes in the IVD is an important cause of NPC apoptosis and loss of the extracellular matrix[67,68].Xiaet al[69]collected the normal nucleus pulposus from trauma patients and the degenerated nucleus pulposus and then screened 150 proteins by gene ontology and KEGG analysis,of which 69 proteins were downregulated and 81 were upregulated.Most of the proteins were associated with inflammatory responses,showing enhanced inflammatory responses in degenerative discs.By adding MSC-derived exosomes to apoptotic NPCs,the expression of IL-1β,iNOS,COX-2,IL-6,MMP3,MMP13,and other inflammation- and extracellular matrix degradation-related enzymes was significantly reduced.In vivoexperiments also demonstrated that the exosome injection group had significantly lower MMP13 expression at 2,4,and 8 wk than the control group[69].
The decrease of viable cells is a key factor in the process of disc degeneration;conversely,in the process of disc regeneration,the recovery of cell numbers is the most important issue.These studies have confirmed that stem cell-derived exosomes could enhance cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis,especially for stem cells remaining in the disc.Moreover,exosomes could also enhance the expression of the extracellular matrix in NPCs and inhibit the expression of matrix protein degrading enzymes,which is beneficial for maintaining the homeostasis of the extracellular matrix.During IVD degeneration,a large number of cytokines participate in and accelerate the degeneration of the IVD,leading to apoptosis and senescence of NPCs[70].Exosomes have a significant inhibitory effect on inflammation,which induces the restoration of the microenvironment for the surviving cells and reduces the disturbance of the intracellular environment.Therefore,stem cell-derived exosomes have the potential to treat disc degeneration.
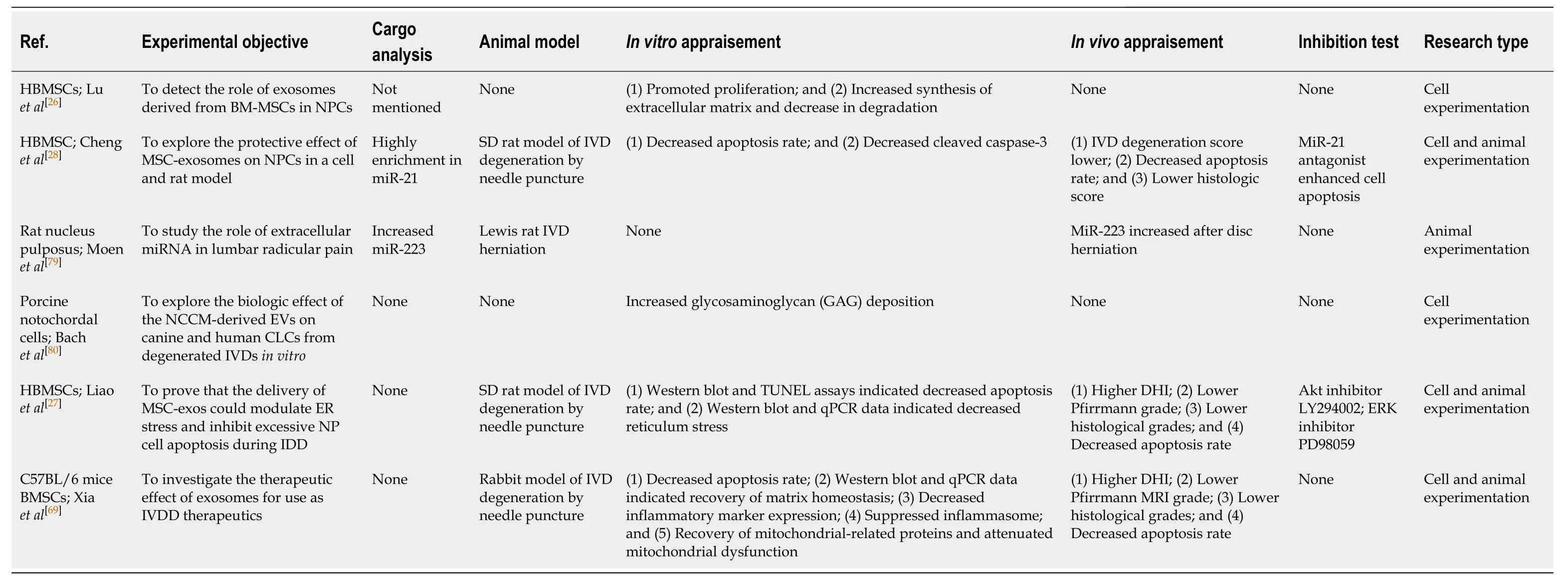
Table2 Studies on exosomes for intervertebral disc degeneration
POTENTIAL MECHANISM OF STEM CELL-DERIVED EXOSOMES FOR IVD DEGENERATION
With an increasing understanding of the mechanisms behind disc degeneration and with in-depth studies of exosomes,the application of exosomes in disc degeneration has achieved some new progress.This progress clearly shows the tremendous potential of exosomes in disc repair.However,the exact mechanism of how exosomes affect disc repair is still unclear.
In a study of Chenget al[28],miRNA array hybridization and data analysis was performed to compare normal NPCs and TNF-induced apoptotic NPCs;five miRNAs(miR-18a,miR-21,miR-106b,miR-217,and miR-26a) were found at significantly lower levels in the TNF-induced NPC group than in the control group.Furthermore,only miR-21 was present in MSC-derived exosomes at higher levels than it was in fibroblast-derived exosomes.MiR-21 also decreased apoptosis and suppressed the expression of PTEN.Based on the above results,the researchers believe that the PTENPI3K-Akt pathway is a potential target of exosomal miR-21-mediated apoptosis protection in NPCs.However,they believe that there are still other extracellular vesicles or other components in exosomes that are involved in this procedure[28].
Liaoet al[27]proposed another possible mechanism.The endoplasmic reticulum stress-related markers GRP78 and CHOP were significantly increased in degenerated discs,and their expression positively correlated with Pfirrmann classification.Then,exosomes were added to induce NPCs,and the expression of endoplasmic reticulumrelated pathways and apoptosis markers was inhibited.This means that exosomes inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis through AKT and ERK signaling pathways by reducing the levels of CHOP,the key molecule of endoplasmic reticulum stress[27].
In addition to the above studies,Xiaet al[69]found that 150 proteins differentially expressed in degenerative discs are closely related to enhanced inflammatory responses.Exosomes can significantly inhibit the inflammatory response of apoptotic NPCs and the formation of inflammatory bodies.The proteins found in bone marrow MSC exosomes mainly recovered the damage to mitochondria in NPCs,restored the normal structure of mitochondria,and reduced oxidative stress in mitochondria.The results indicate that exosomes can play a role in inhibiting disc degeneration by restoring mitochondrial homeostasis and the antioxidative response and inhibiting formation of inflammatory bodies[69].
These potential mechanisms have mainly been studied in terms of promoting extracellular matrix production,inhibiting matrix degradation,promoting an antiinflammatory response,and inhibiting apoptosis and other aspects of exosome-based promotion of IVD repair.Unfortunately,there is no study on how exosomes promote the proliferation mechanism of NPCs.One of the most important reasons for the degeneration of the disc is the decrease in the number of cells,and how to restore the number of cells in the disc is a key question in treatment.Alternatively,in the process of IVD degeneration,the senescence of NPCs is also an important factor.Some molecules have also been found in exosomes that can inhibit the senescence of cells.Previous research has mainly focused on specific miRNAs in exosome-mediated apoptosis,but are there additional miRNAs in exosomes that promote the proliferation and inhibit the aging of NPCs? Furthermore,how do exosomes inhibit inflammation and promote mitochondrial homeostasis,and how are other molecules in exosomes,including lipids,proteins,mRNAs,and lncRNAs,involved?
DISCUSSION
The unique double-layered membrane structure of exosomes makes their contents difficult to degrade by various enzymes in body fluids.The unique shape,size,and density range of exosomes,as well as the special molecular markers on their surface,enable their identification and isolation.Animal experiments have confirmed that exosomes are more efficient at delivering effective content into cells and cause a lower immune response in recipients than other methods.By overexpressing miRNAs targeting specific mRNAs in donor cells,exosomes promote cell proliferation,inhibit apoptosis,and promote the production of the extracellular matrix[28].Engineered exosomes can also be loaded with miRNA synthesizedin vitroby electroporation and can then be injected into tissues to achieve therapeutic goals[71].Exosomes may also be combined with scaffold material to promote IVD regeneration.In a study by Liuet al[72],photoinduced imine crosslinking hydrogel glue combined with stem cellderived exosomes promoted defective cartilage repair and regeneration[72].Therefore,an increasing number of studies have shown that exosomes are a promising method for the treatment of disc degeneration.However,there are still many challenges and disadvantages.
First,the physiological environment of the IVD is complex.As the largest avascular tissue in the body,long-term internal high pressure,high permeability,low pH,low nutrition,and low oxygen make it not suitable for cell proliferation[73].In the degenerated IVD,the complex inflammatory environment,the decrease in the number of cells,and fibrosis may affectin vivoasin vitroresults being the same.Additionally,IVD degeneration is a pathological process involving multiple factors,and the exact mechanism has not yet been determined.Therefore,choosing the appropriate exosomes for specific causes is very important.
Second,the exact mechanism of exosomal biogenesis needs to be further investigated.Exosomes are derived from endosomes after cell endocytosis.After processing,they may join multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and may contain proteins,nucleic acids,lipids,cholesterol,and other biologically active molecules;further,they may be secreted by exocytosis or may be encountered by a lysosome and become degraded[29].This is a complex set of biological process,and more research needs to be done to determine the specific mechanisms.An increasing number of studies have demonstrated that exosome-mediated effects are mainly due to the contents of the exosomes,such as miRNAs,lncRNAs,and other molecules.Understanding how cells assemble these molecules in exosomes will enable additional exosomes to be harvested.The isolation of exosomes also has limitations regardless of the current methods being used,such as ultracentrifugation,ultrafiltration,and chromatography.Therefore,new methods need to be developed to improve the isolation and purity of exosomes.
Moreover,exosomes,as a collection of various biologically active molecules,are also affected by various factors,such as the source of cells,the status of cell growth,the conditions of culture,and even the consistency and reproducibility of their effects.All of those factors need to be considered.As a special carrier in the treatment of diseases,the application of exosomes still faces a series of problems,such as dosage,mode of administration,and evaluation of the efficacy.
CONCLUSION
Exosomes are attracting increasing attention because of their unique structures and diverse properties.Exosomes have shown favorable possibilities during the repair of IVD,since they can promote the proliferation of NPCs,promote the homeostasis of the extracellular matrix,and inhibit cell apoptosis (Figure1).However,the detailed mechanisms behind these activities are still unclear,so further research is needed to explore the complex regulation mechanisms,optimize the culture and transplant conditions,and perform more preclinical trials to verify the safety of exosomes.

Figure1 Exosome-mediated mechanism of stem cells regulating the activities of nucleus pulposus cells.
 World Journal of Stem Cells2020年8期
World Journal of Stem Cells2020年8期
- World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- Hunting down the dominating subclone of cancer stem cells as a potential new therapeutic target in multiple myeloma:An artificial intelligence perspective
- Role of mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles in autoimmunity:A systematic review
- Human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells improved premature ovarian failure
- Assessment of tobacco heating system 2.4 on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and primary human osteoblasts compared to conventional cigarettes
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes:Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine
- Autophagy in fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells and bone remodeling
