A New Species of the Genus Achalinus from Huangshan,Anhui,China (Squamata:Xenodermidae)
Ruyi HUANG,Lifang PENG,Lei YU,Tianqi HUANG,Ke JIANG,Li DING,Jinkang CHANG,Diancheng YANG,Yuhao XU and Song HUANG*
1 Anhui Province Key Laboratory of the Conservation and Exploitation of Biological Resource,College of Life Sciences,Anhui Normal University,Wuhu 241000,Anhui,China
2 Shanghai Jian Qiao University,Shanghai 201306,China
3 Huangshan Noah Biodiversity Institute,Huangshan 245000,Anhui,China
4 Anhui Rare Birds Protection Association,Hefei 230601,Anhui,China
5 Graduate Program in Ecology and Evolution,Department of Ecology,Evolution,and Natural Resources,Rutgers,the State University of New Jersey,New Brunswick,NJ 08901,USA
6 Chengdu Institute of Biology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chengdu 610041,Sichuan,China
7 School of plant protection,Anhui Agricultural University,Hefei 230036,Anhui,China
8 School of Life Sciences,Anhui Agricultural University,Hefei 230036,Anhui,China
Abstract A new species of the genus Achalinus is described based on five specimens collected from the villages of Huangjialing and Fuxi,Huangshan,Anhui,China.It can be morphologically differentiated from all the other species in Achalinus except for A.spinalis and A.werneri by the presence of a dotted black streak in the middle of the subcaudal.It can be distinguished from A.spinalis in that its two anterior temporals are in contact with eye,and A.werneri by its light brown flanks.The phylogenetic relationship of Achalinus was reconstructed using the mitochondrial locus of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (CO1).The five new specimens form a monophyletic clade with strong support.The uncorrected p-distances between the new species and other representatives of Achalinus range from 13.6% to 21.7%.The recognition of the new species increases the number of described Achalinus species to 14.
Keywords Achalinus huangjietangi sp.nov.,Huangjialing Village,morphology,molecular phylogeny,taxonomy
1.Introduction
There are currently 13 described species in the genusAchalinus
Peters,1869 (Serpentes:Xenodermidae):A.ater
,A.emilyae,A.formosanus
,A.hainanus
,A.jinggangensis
,A.juliani,A.meiguensis
,A.niger
,A.rufescens
,A.spinalis
,A.timi,A.werneri
,andA.yunkaiensis
.They are reported from three countries:Vietnam,China,and Japan;there are nine species from China (superscript),with five endemic to China (superscript).We collected five specimens from the villages of Huangjialing (4) and Fuxi (1),Huangshan,Anhui Province,China from 2014 to 2018.The specimens are composed of three adults and two juveniles.They match the generic diagnosis ofAchalinus
(Peters,1869;Zhaoet al
.,1998;Zhao,2006):1) small,nocturnal,subterranean,non-venomous,and not aggressive;2) whole body covered with lanceolate scales with metallic luster under light,which do not overlap one another and lie individual;3) small,oval head indistinct from neck;4) eyes small with round pupils;5) preocular absent,loreal extending from the nasal to the eye;6) postocular absent,temporals contacting orbit;7) supralabials 3-2-1,gradually elongated,the last one almost the sum of the first five in size;8) dorsal scales 23 rows,keeled;9) anal entire;10) subcaudals single.We conducted morphological and DNA comparative analyses.The five specimens were found to be different both morphologically and genetically from all 13 previously described species ofAchalinus
,and therefore represent a new species ofAchalinus
,bringing the total species ofAchalinus
to 14.2.Material and methods
2.1.Sampling
Sampling procedures involving live snakes were in accordance with the Wild Animals Protection Law of China and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee at Anhui Normal University.Five specimens were collected from Huangjialing (4) and Fuxi (1),Huangshan,Anhui Province,China.An adult female (collection and voucher number:HSR18030,ANU20200001) was caught on the stone steps (Figure 1A) in Huangjialing Village,two adult males and one juvenile (HSR18220,SNHM5412;HSR14023,CIB116366;HSR18059,ANU20200002) at the foot (Figure 1B) and on the roads of the mountains about 500-1000 m from Huangjialing Village,and one juvenile (HSR19141,ANU20200003) from the side of a road (Figure 1C) in Fuxi Village.All specimens were fixed in 10% formalin for one day,and then were transferred to 75% ethanol.The specimens were deposited in Anhui Normal University Museum (ANU),Shanghai Natural History Museum (SNHM),and Chengdu Institute of Biology,Chinese Academy of Sciences (CIB,CAS) respectively.
Figure 1 Habitats of Achalinus huangjietangi sp.nov.A:the microhabitat of holotype (HSR18030,ANU20200001) on the stone steps in Huangjialing Village,Qimen Country;B:the holistic habitat of a paratype (HSR14023,CIB116366) on the mountain path at the foot of mountains beside Huangjialing Village;C:the microhabitat of a paratype (HSR19141,ANU20200003) on the side of a road in Fuxi Village.
2.2.Molecular analyses
Muscle tissues were sampled from each specimen and preserved in 95% ethanol at -80°C in the laboratory.Total genomic DNA was extracted using a Qiagin DNEasy blood and tissue extraction kit (Qiagen Inc.,Valencia,CA).The partial mitochondrial DNA gene encoding cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (CO1) was obtained by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and direct sequencing using the primers (Dglco and Dghco) and methods described in Meyeret al
.(2005).All sequences were deposited in GenBank (Accession numbers in Figure 2).The homologous CO1 sequences of 10 other species ofAchalinus
,and ofFimbrios klossi
Smith,1921 andParafimbrios lao
Teynié,David,Lottier,Le,Vidal and Nguyen,2015 were downloaded from GenBank (Accession numbers in Figure 2).We aligned the newly generated CO1 sequences from the new specimens with the sequences retrieved from GenBank using MEGA X (Kumaret al
.,2018).Maximum likelihood (ML) method was used to construct the phylogenetic tree.In order to detect genetic differences,uncorrected pairwise distances (p
-distance) were calculated in MEGA X (Kumaret al
.,2018).
Figure 2 Maximum-likelihood tree inferred from CO1.Numbers indicate bootstrap support for maximum likelihood (1000 replicates) analyses (>50 retained).
2.3.Morphometrics
We examined 28 morphometric characters in the five newAchalinus
specimens,including 12 count characters (supralabials,infralabials,infralabials-chin,loreal,preoculars,postoculars,temporals,supraoculars,dorsal scale rows,ventral scales,anal plate,and subcaudals),and 16 mensural characters (total length,tail length,perimeter at neck,perimeter at midbody,perimeter before vent,loreal height,loreal length,length of suture between internasals,length of suture between prefrontals,head width,head length,head height,eye length,eye width,rostral height,and rostral width) (Table 1).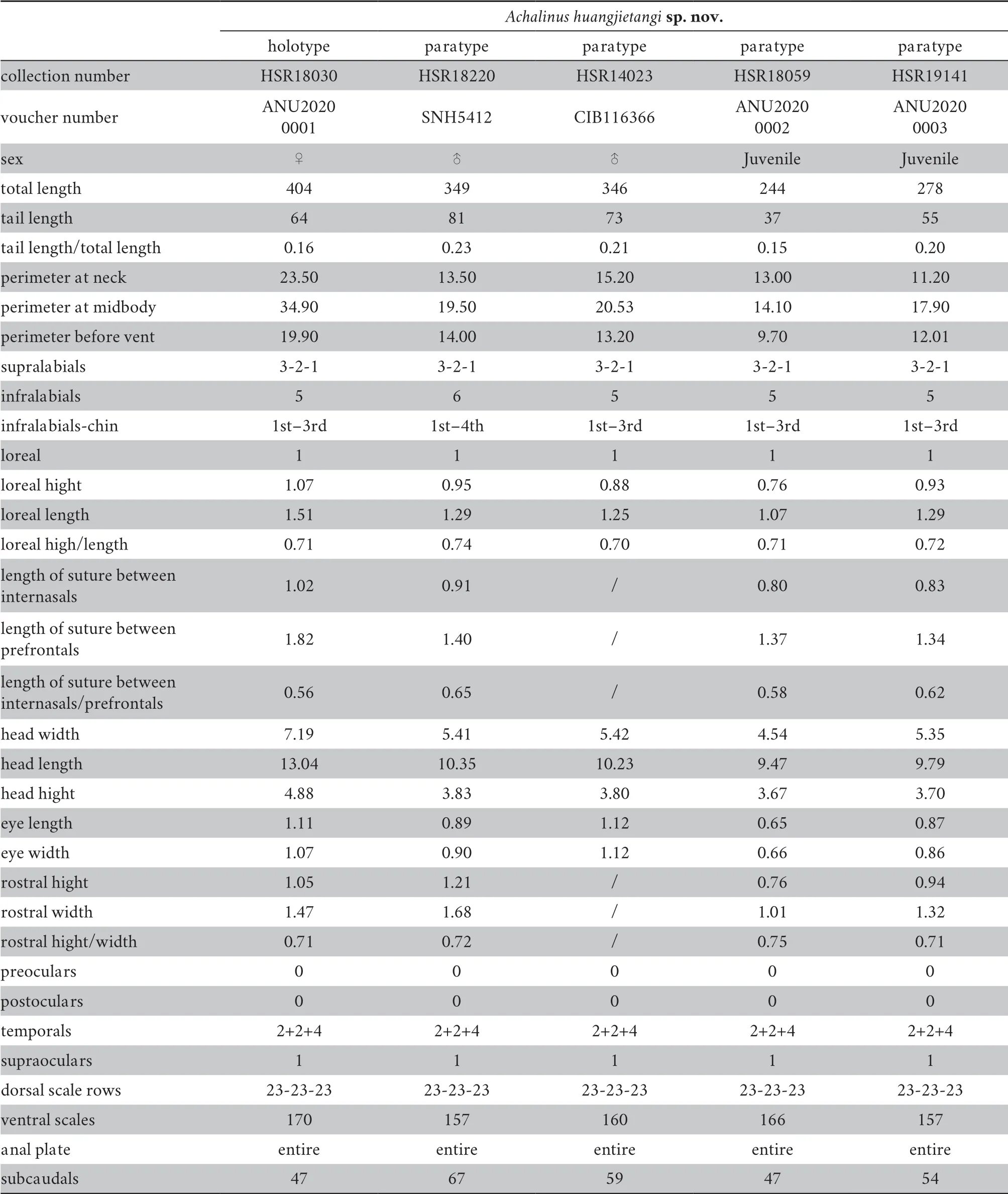
Table 1 Measurements (mm) and pholidosis for the holotype and paratypes of Achalinus huangjietangi sp.nov.
The lengths were measured using a ruler to the nearest 1 mm.The other measurements were measured with an electronic caliper to 0.01 mm.Standard terminology was used in measurements and scale counts (e.g.,Smith and Campbell,1994;Smithet al
.,2008;Vogel and David,2010;Vogel and Luo,2011;Penget al
.,2018).Symmetric mensural head characters were measured only on the right side,while asymmetric characters were recorded on both sides.Morphometric data from representativeAchalinus
species were obtained from the original descriptions (Peters,1869;Boulenger,1888,1908;Van Denburgh,1912;Bourret,1937;Hu and Zhao,1966;Huet al
.,1975;Zong and Ma,1983;Ziegleret al
.2019;Wanget al
.,2019),taxonomic re-definitions (Ota and Toyama,1989),and expanded descriptions (Zhaoet al.
, 1998;Zhao,2006) to perform comparative analysis.3.Results
3.1.Molecular analyses
The mitochondrial CO1 gene fragments of 10 known species ofAchalinus
and the five new specimens in the present study were used to construct phylogenetic tree (Figure 2) based on the Maximum likelihood (ML) method.Despite of the low backbone supports,the five specimens formed a monophyletic clade with a maximum likelihood bootstrap value of 99.Thep
-distances between the new species and other representatives ofAchalinus
ranged from 13.6% to 21.7% (Table 2).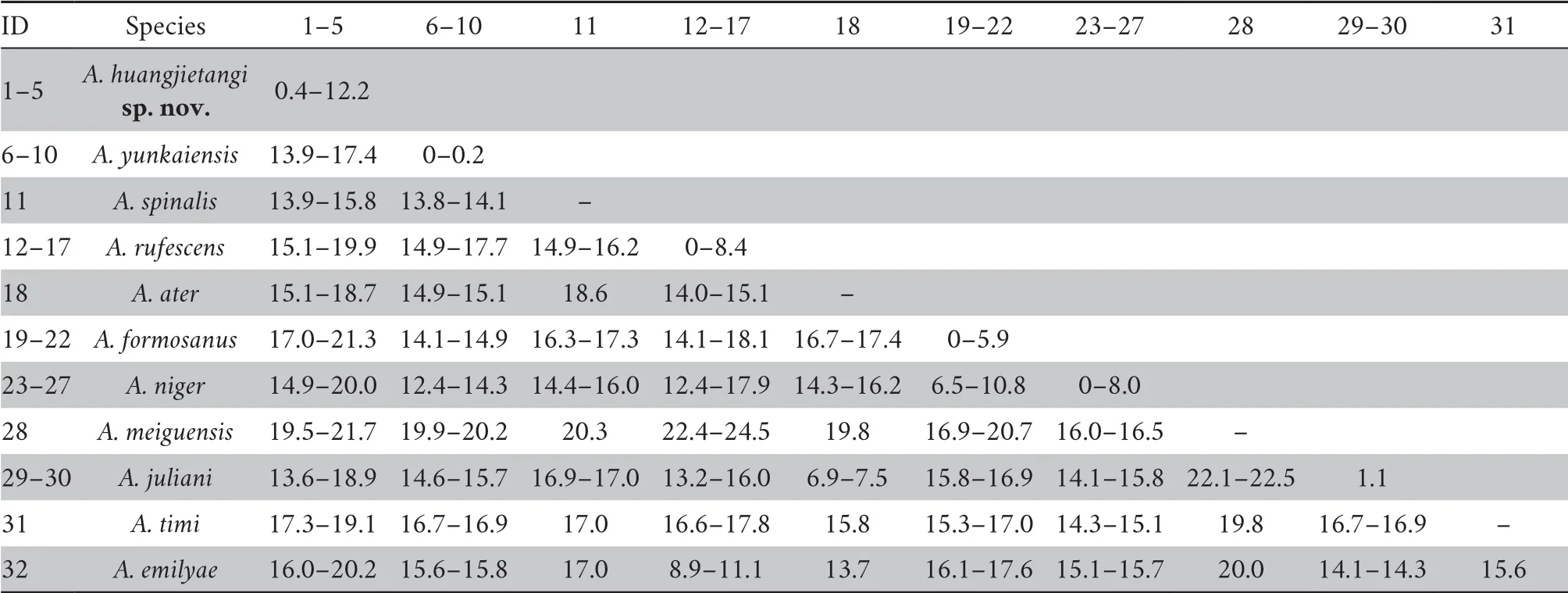
Table 2 Uncorrected p-distances among the genus Achalinus based on partial mitochondria CO1 gene.
3.2.Description of the new species
sp.nov.
Ruyi HUANG,Lifang PENG,and Song HUANGSuggested English name:
Huang’s Odd-scaled Snake.Suggested Chinese name:
黄家岭脊蛇 (Bopomofo:Huáng Jiā Lǐng Jǐ Shé).Holotype
ANU20200001 (HSR18030 collection number),adult female (Figure 3),Huangjialing Village,Qimen County,Huangshan City,Anhui Province,China (29°49′20″ N,117°32′24″ E,220 m a.s.l.),3 June 2018,collected on stone steps (Figure 1A) by R.HUANG,L.PENG,and S.HUANG.Paratypes
CIB116366 (HSR14023 collection number),adult male,Huangjialing Village,Huangshan City,Anhui Province,China (29°49′08″ N,117°32′17″ E,254 m a.s.l.),10 May 2014,collected on a path at the foot of mountains (Figure 1B) by R.HUANG,L.PENG,and S.HUANG.SNHM5412 (HSR18220 collection number),adult male (Figure 4),Huangjialing Village,Qimen County,Huangshan City,Anhui Province,China,17 June 2018,collected by local farmers.ANU20200002 (HSR18059 collection number),juvenile,Huangjialing Village,Qimen County,Huangshan City,Anhui Province,China,18 October 2018,collected by local farmers.
ANU20200003 (HSR19141),juvenile (Figure 1C),Fuxi Village,Huangshan District,Huangshan City,Anhui Province,China,(30°04′54″ N,118°08′52″ E,450 m a.s.l.),6 August 2018,collected from a roadside by J.CHANG,L.YU,and Y.XU.

Figure 3 General aspect of holotype (HSR18030,ANU20200001).Dorsal (A) and ventral (B) views;Dorsal (C),ventral (D),Right (E) and Left (F) views of head.
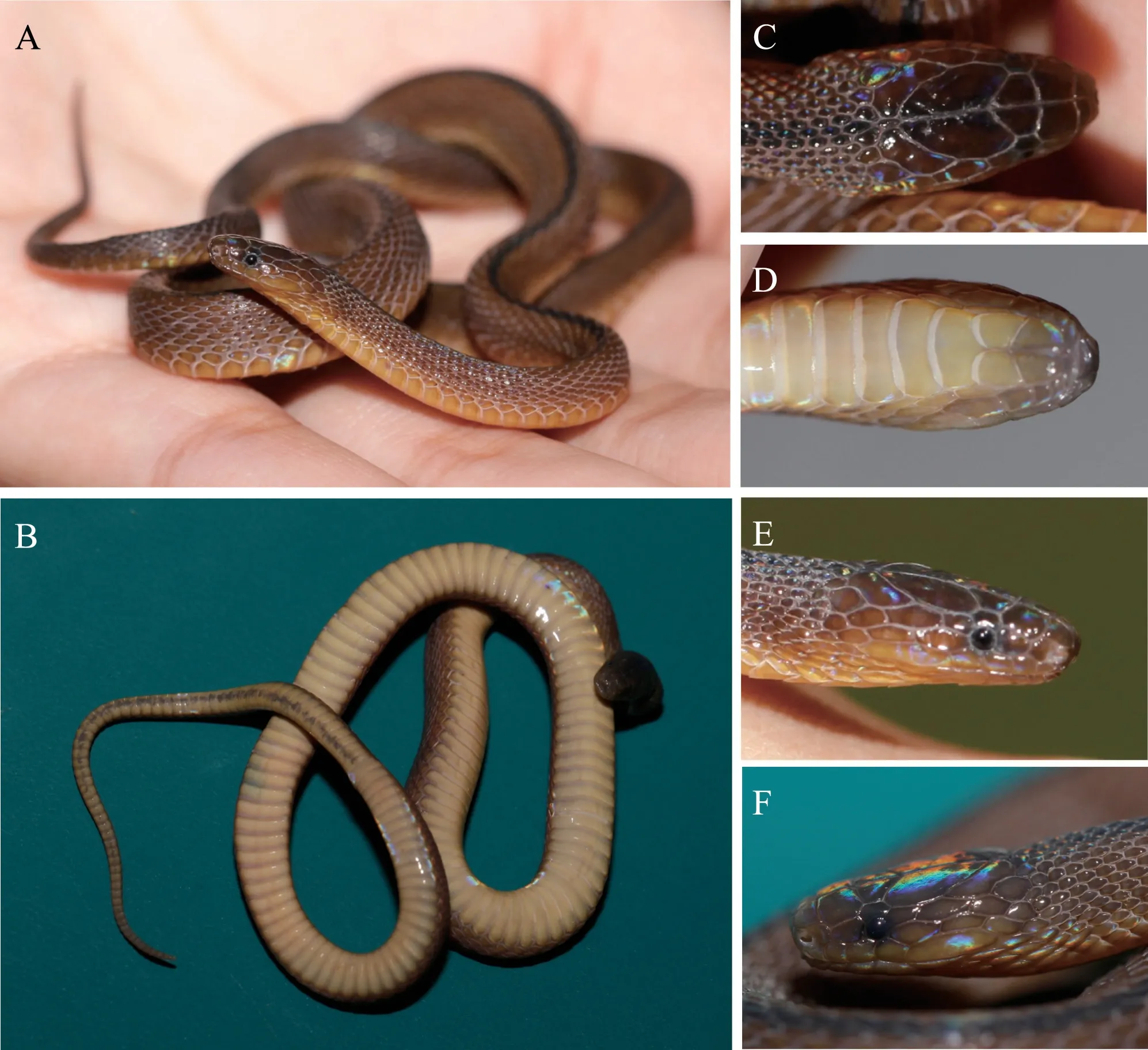

Figure 4 General aspect of paratype (HSR18220,SNHM5412) in life.Dorsal (A) and ventral (B) views;Dorsal (C),ventral (D),Right (E) and Left (F) views of head.The frontal dehiscence in the middle (C).
Diagnosis
The new species ofAchalinus
that can be differentiated from its congeners by the following combination of characters:an iridescent,black (in juveniles) or brown (in adults) dorsum with vertebral scales and about half of the adjacent dorsal scales dark,forming a longitudinal vertebral line from posterior margin of parietals to tail tip,a light brown venter,ventral shields wide and visible on both sides,light brown flanks,a black dot in the middle of each subcaudal scale,giving the appearance of a black subcaudal streak,dorsal scales weakly keeled and do not overlap,23 dorsal scale rows throughout the body,outermost dorsal row smooth and significantly enlarged,preocular and postocular absent,an internasal suture half of the length of the prefontal suture,temporals 2+2+4,elongated with the two anterior temporals in contact with eye,a pair of significantly enlarged uppermost posterior temporals (super-temporal) separated from each other by a small intertemporal behind the parietals.Description of Holotype
An adult female with a total length 404 mm (snout-vent length 340 mm and tail length 64 mm).Tail relatively short with a tail length/total length ratio of 0.16.Body slender and cylindrical.Head length 13.04 mm (from tip of snout to posterior margin of parietal),width 7.19 mm,andheight 4.88 mm.Head indistinct from neck.Eyes small with elliptical pupils.Rostral small,triangular,and scarcely visible from above.Rostral height/width ratio 0.71.Internasal suture (1.02 mm) about half of the length of the prefrontal suture (1.82 mm).Nostril in the anterior part of the nasal.Frontal pentagonal,nearly straight anteriorly,slightly broader than it is long,pointed backwards,and much shorter than the parietals.One loreal (high/length ratio 0.71),extending from the nasal to the eye.Two elongated anterior temporals,the upper one smaller,both in contact with eye.Two elongated middle temporals,the upper one much larger,and the lower one in contact with the sixth supralabial.Four elongated posterior temporals,the most upper one (super-temporal) significantly enlarged,surrounding the parietal.The super-temporals from two sides separated from each other behind parietals by one small intertemporal scale.One supraocular.Supralabials six,first very small,fourth and fifth in widely contacting eye,and sixth the longest and largest.One mental.Five infralabials,with the first pair in contact with each other.Two pairs of chin-shields followed by ventrals.First three infralabials in contact with anterior chin-shields on both sides.Dorsal scales 23 rows throughout the body,keeled very feebly,and the most outer row on the both sides smooth and significantly enlarged.Ventrals 170.Subcaudals 47,uniserial.Anal entire.
Coloration of holotype in life
Dorsum brown with metallic luster under light.All vertebral scales and about half of the adjacent dorsal scales dark,forming a longitudinal vertebral line from the posterior margin of parietals to the tail tip.Labial,chin,ventral and subcaudal shields light brown.Ventral shields wide and visible on both sides.Light brown flanks.A dark streak of black dots in the middle of subcaudal.Variation
Measurements,body proportions,scale count were listed in Table 1.All paratypes are morphologically very similar to the holotype excepting the following:the adult female HSR18220 has six infralabials on both sides (versus five in the holotype on both sides),the frontal dehiscence in the middle (Figure 4C),and first four infralabials in contact with anterior chin-shields on both sides (versus first three in the holotype).Comparisons
Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.can be differentiated from the remainingAchalinus
representatives by a combination of the following characters:a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral,two anterior temporals in contact with eye,and the flanks are light brown.By having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventralAchalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.can be differed from all other species inAchalinus
exceptA.spinalis
andA.werneri
.However,Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.can be distinguished fromA.spinalis
by two anterior temporals in contact with eye (versus upper anterior broadly in contact with eye),and it can be distinguished fromA.werneri
by the flanks are light brown (versus the flanks are yellow).Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.ater
by dorsum walnut-brown (versus black),verter brownish white (versus black brown),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.emilyae
by two anterior temporals in contact with eye (versus one),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.formosanus
by fewer midbody dorsal scale rows (23 versus 27),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.hainanus
by having a single intertemporal (versus not having intertemporal),two anterior temporals (versus only one),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.further differs fromA.jinggangensis
by dorsum walnut-brown (versus black),ventrals shields brownish white (versus black),edged with black (versus edged pale in color),the loreal not being fused with the prefrontal,and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.juliani
by fewer venteals (155-170 versus 173-179),fewer subcaudals (47-67 versus 77-91),having less dorsal scale rows in the anterior part of the body (23 versus 25),and having a black mid-dorsal line and a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.meiguensis
by fewer midbody dorsal scale rows (23 versus 27),internasal not fused to prefrontal (internasal fused to prefrontal),lacking postocular (having postocular),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.niger
by f different dorsal sacle row counts (23-23-23 versus 25-25-25),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.rufescens
by two pairs of chin shields (versus three pairs of chin shields),two anterior temporals in contact with eye (versus only the upper anterior temporal in contact with the eye),supralabials six,the fourth and fifth ones widely in contact with eye (versus supralabials five,third and fourth entering the eye),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.spinalis
by two anterior temporals in contact with eye (versus upper anterior broadly in contact with eye),and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.timi
by different dorsal sacle row counts (23-23-23 versus 25-25-23),the loreal not being fused with the prefrontal,and having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.werneri
by the flanks are light brown (versus the flanks are yellow).Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov
.differs fromA.yunkaiensis
by having a dark streak in the middle of caudal ventral.Etymology
The species name is derived from the name of Professor Jietang Huang (Huangshan Institude of Ophiology),a senior ophiologist who has been contributing substantially to snake researche over 50 years.Born and raised in Huangjialing Village,he was the first college graduate from the village.Distribution
The new species currently is only known from Huangshan City,southern Anhui Province,China.Natural History
Specimens were found in secondary conifer/broad-leaved mixed forests (Figure 1) at elevations from 220 to 450 m a.s.l.Achalinus huangjietangi
sp.nov.is a nocturnal,secretive and subterranean snake,living in the forest floor,and is usually hidden in deciduous and humic layers close to streams and ditches.4.Discussion
Two specimens (HSR18030,HSR14023) sampled from Huangjialing Village were also used in a large-scale systematics study of Chinese snakes (Liet al
.,in press),which reconstructed phylogenetic trees based on 5 mitochondrial and 91 nuclear markers.Their phylogenetic results also implied that the specimens from Huangjialing should be a potential new species ofAchalinus
(same specimens labelled as CHS008 and CHS009 in Liet al
.,in press).SNHM5412 (HSR14023 collection number) was the first specimen of the five in the present study.It was found on May 10,2014 on the mountain path at the foot of mountains beside Huangjialing Village.Morphologically,it corresponds with the broad characteristics ofA.rufescens
described inFauna Sinica
,Reptilia Vol
.3
,Squamata
:Serpentes
(Zhaoet al
.,1998) andThe snakes of China
(Zhao,2006).So,it was reported as a new record ofA.rufescens
in Anhui Province,China (Peng and Huang,2015).However,in the present study,detailed morphological and molecular studies show that it is a new species ofAchalinus
.Achalinus
species are rarely found in the wild due to their secretive and subterranean life style (Ota and Toyama,1989;Zhaoet al
.,1998;Zhao,2006;Ziegler,2019).Because of their low dispersal ability,as well as the known large genetic differences among geographical populations,some currently-recognized widespread and broadly described species of the genusAchalinus
,such asA.rufescens
Boulenger,1888 andA.spinalis
Peters,1869,may actually represent multiple cryptic species.At the species level,“subdivision” is recommendable.It will help us to understand and describe species’ natural history more effectively and precisely,and facilitate consistent communications and actions in taxonomy and the practices of conservation biology.According to the thought of “integrative taxonomy” (Dayrat,2005;Vinarski,2019),Achalinus
huangjietangi
sp.nov.conforms to the eclectic “four difference rule” of species delimitation (Penget al
.,2014):1) morphological difference compared with the closest species is perceptible;2) geographical and/or ecological difference implies the potential for natural reproductive isolation.To further confirm that the morphological difference possess taxonomic significance rather than representing intraspecific polymorphism,more evidences from 3) mitochondrial DNA difference (matrilineal divergence) and 4) nuclear DNA difference (patrilineal divergence) are required.At the genus level,“stability” is preferable,especially when alternatives are acceptable,due to the nonuniform and subjective criteria of genus delimitation.The scientific names (genus name + specific epithet) of organisms are often used in non-taxonomic science,literature,business,law,protection,education,and other social circles,and the stability of taxonomy on the genus level should be considered for avoiding confusion of non-taxonomic professionals.In the case ofAchalinus
,all described species in this genus (includingA
.meiguensis
) share common characteristics which could be distinguished from other closely-related genera,so we do not recommend separating the genus,although there are morphological and molecular differences in this genus.The description ofA
.huangjietangi
sp.nov.brings the total number ofAchalinus
to 14.There are 10 species reported in China with 6 of those species endemic to China.Huangshan area has been proposed as a Pleistocene refugium (Wuet al
.,2013),which harbors diverse lineages and high genetic diversity in a variety of organisms,such as the Giant SalamanderAndrias davidianus
(Murphyet al
.,2000),the Sharp-snouted PitviperDeinagkistrodon acutus
(Huanget al
.,2007),and a common minnowZacco platypus
(Zhenget al
.,2016).In this study,the intraspecies genetic divergences ofAchalinus
huangjietangi
sp.nov.are also found to be high (p
-distance range 0.4%-12.2%).All these emphasize the role Huangshan plays in promoting regional genetic- and biodiversity.As a result,we recommend future work to put more efforts on bioconservation in Huangshan.Acknowledgements
We thank Dr.Sara RUANE (Rutgers University-Newark) and Dr.Peter MORIN (Rutgers University-New Brunswick) for reading and commenting on earlier versions of this manuscript.This work was supported by Postdoctoral Research Program of Department of Human Resources and Social Security of Anhui Province (2020B422),Doctoral Research Starting Foundation of Anhui Normal University (752017),and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 31471968). Asian Herpetological Research2021年2期
Asian Herpetological Research2021年2期
- Asian Herpetological Research的其它文章
- A New Leaf Litter Toad of Leptobrachella Smith,1925 (Anura,Megophryidae) from Sichuan Province,China with Supplementary Description of L.oshanensis
- A New Species of Trimeresurus Lacépède,1804 (Squamata:Viperidae) from Southwestern China,Vietnam,Thailand and Myanmar
- Phylogeography and Cryptic Species Diversity of Paramesotriton caudopunctatus Species Group (Salamandridae:Paramesotriton) in Guizhou,China
- Phylogeny and Biogeography of Common Toad (Bufo bufo) in Xinjiang,China
- Evolution of Phenotype and Mitochondrial Genome Reveals Limbless and Body-elongated Squamates may Change Their Energy Basis for Locomotion
- Male Advertisement Call of the Endangered Leptobrachella tengchongensis (Anura:Megophryidae) from Mount Gaoligongshan,Yunnan Province,China
