Effects of astaxanthin against colorectal carcinogenesis by lipopolysaccharide challenge in vitro
WANG Wenjun,WANG Xinyu,HUANG Wenwei,TIAN Wei,ZENG Guoxiang*
(1 College of Life Sciences,South-Central Minzu University,Wuhan 430074,China;2 Department of General Surgery,People's Hospital of Hanchuan City,Hanchuan 432300,China)
Abstract To evaluate the chemoprotective ability of astaxanthin(ASTA)against colorectal carcinogenesis after lipopolysaccharide(LPS)challenge in HCT116 cells.IL-6 and IL-1β secretion,apoptosis,caspase-3 and anti-caspase-9,as well as NF-κB and Nrf2 transference into nuclear,and mRNA expression of NF-κB and Nrf2 were investigated in HCT116 cells with or without ASTA treatment after LPS challenge.The results indicated that LPS challenge significantly increased IL-1β and IL-6 secretion in HCT 116 cells,while the secretion was remarkably inhibited by ASTA in a concentration-dependent manner. ASTA increased the percentage of apoptotic cells,increased expression of caspase-9 and caspase-3,upregulated mRNA expression of Nrf2 and downregulated mRNA expressions of NF-κB in HCT116 cells. ASTA prevented the initiation and development of colorectal cancer(CRC)and regulated NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways in HCT116 cells.These findings suggested NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways might play a critical role for ASTA's prevention of CRC,and ASTA might be a new and attractive chemoprevention agent for inflammation-related cancer.
Keywords astaxanthin;colorectal cancer;lipopolysaccharide;NF-κB;Nrf2
Colorectal cancer(CRC)is the third most malignant neoplasm in the world and accounts for 10% of all cancer related deaths,which remains an important cause of mortality in Asian and Western countries[1]. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease(IBD)are at a significantly increased risk of developing CRC,while IL-6 and IL-1β are pleiotropic pro-inflammatory cytokines that have profound effects on several diseases including cancers[2-3]. The transcriptional factors nuclear factor-κB(NF-κB)and NF-E2-related factor 2(Nrf2)have been recently reported to have critical roles in protecting various tissues against inflammation and colitis-associated colorectal cancer(aberrant crypt foci)[4].
There are many studies aiming to investigating new chemopreventive agents against colorectal cancer. Recently,considerable attention has been drawn in identifying phytochemicals,particularly those included in our diet,which has the ability to interfere with carcinogenic or mutagenic processes. Astaxanthin(3,3'-dihydroxy-β,β'-carotene-4,4'-dione,ASTA,Fig.1)is a promising and non-provitamin A carotenoid found in the red pigment of shrimp,crab,salmon,asteroidean,yeast,and algae[5-6]. ASTA has been reported to possess antioxidant,anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties,which is known to play an important role in delaying or preventing degenerative diseases,and being a more powerful scavenger of singlet oxygen(1O2) and peroxyl radicals(H2O2)than β -carotene,Cantaxanthin(β,β-carotene-4,4'-dione)a n d Z e a x anthin(3,3'-dihydroxyl-β-carotene)due to its s p ec ia l s tructure[7-9]. Moreover,there is a staggering amount of literature that Nrf2 contributes to the protective effects of ASTA against cellular and tissue injury.But whether ASTA inhibits NF- κB activation and induces the activation of Nrf2 expression during the malignant transformation of inflammation is needed to be further investigated. Therefore,the present study was undertaken to examine the effects of ASTA on colitis-associated colorectal carcinogenesis and investigate its mechanisms in HCT116 cells by lipopolysaccharide challenge.
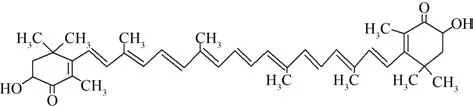
Fig.1 Structure of astaxanthin图1 虾青素的化学结构式
1 Meterials and methods
1.1 Reagents and cell culture
Astaxanthin and LPS were purchased from S i g m a-A l d r i c h (S t. L o u i s, M N, U S A).P r i m a ry antibodies against N F-κB and Nrf2,an d a n ti-caspase-3 and anti-caspase-9 antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology(Santa Cruz,CA,USA). Anti-β-actin antibody was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology(Beverly,MA,USA). ASTA was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide as a stock solution(100 mmol·L-1),and stored at -20 ℃,freshly diluted with Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium(DMEM,Gibco,Invitrogen,Carlsbad,CA,USA)to the final concentration(50 mmol·L-1).
Human colon carcinoma HCT116 cells was obtained from CBCAS(Cell Bank of the Chinese Academic of Sciences,Shanghai,China),cultured under a humidified environment with 5%CO2at 37 ℃in DMEM medium and supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum(Sijiqing,Hangzhou,China),100 mg·mL-1streptomycin and 100 U·mL-1benzyl penicillin. Other chemicals used in this study were purchased from commercial suppliers.
1.2 Culture of HCT116 cells with or without LPS challenge
HCT116 cells were seeded in 6 mm,6-well or 24-well tissue culture plates(Costar,Cambridge,MA,USA)at 1.6×104cells per well,grown to 80% confluence one day before treatment. Cells were left untreated or treated with 10 mg·L-1LPS + 1 mmmol·L-1ASTA,or 10 mg·mL-1LPS + 2.50 mmmol·L-1ASTA. HCT116 cells were left to adhere overnight and then exposed to three groups of medium mentioned above for 24 h.Then the anti-proliferation effects of ASTA were determined employing 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-d i p h e n yltetrazolium bromide (MTT)assay. Subsequently,20 mL of MTT solution(5 mg·mL-1)was transferred to each well. Plates were incubated for 4 h at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2. After incubation,supernatants were removed,and 100 mL DMSO was added to ensure total solubility of formazan crystals. Plates were placed on an orbital shaker for 2 min,and the absorbance was determined at 570 nm using a Universal Microplate Reader(EL800,BIO-TEK Instruments Inc.,Winooski,VT,USA).
1.3 Cytokine quantification by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
IL-6 and IL-1β secretions were collected from cell supernatants at various time points after LPS challenge and their concentrations were determined employing enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits(KeyGEN,Nanjing,China)according to the manufacturer's instructions. All samples were measured in triplicate and levels of cytokines were expressed in pg·mL-1.
1.4 Apoptosis assay
HCT116 cells treated in three groups(2×106cell·mL-1in 6-well tissue culture plates)were collected and washed twice with cold PBS. Then HCT116 cells were treated by fixation fluid and washed with PBS,subsequently cells were re-suspended in 500 μL 1×binding buffer. 5 μL Annexin V-FIFC(Ann-V)and 5 μL propidium iodide(PI)staining solution were respectively added and well-mixed,then incubated in dark for 20 min at room temperature.Cells were washed with PBS,centrifugated and re-suspended in 200 μL 1×binding buffer. Assay of apoptosis rate was conducted in an hour by flow cytometry(FACS,BD Biosciences,San Jose,CA,USA).
1.5 Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy
HCT116 cells were seeded onto glass coverslips in 6-well plates,and after 24 h,treated with ASTA as indicated and subjected to immunofluorescence staining as described in previous study[10].
1.6 Western blotting
HCT116 cells were treated with various concentrations of ASTA for the indicated times with or without LPS(10 mg·mL-1). Cell and tissue lysates were analyzed by western blotting as described previously[10].
1.7 Quantitative real-time PCR analysis
The RNA extracts of cells were prepared according to the modified method as described[10].Total RNA was isolated from HCT116 cells cultured in 6-well plates using Qiagen RNeasy Mini Kit(Qiagen Inc.,Valencia,CA,USA)according to the manufacturer's protocol.The relative amount of target mRNA was determined using the comparative threshold(Ct)method by normalizing target mRNA Ct values to those for β-actin(ΔCt)used as an internal control.The primers for real-time PCR analysis were listed in Tab.1. Fold changes,expressed as the mean ± standard deviation(SD),were calculated for the treated groups versus the vehicle control using the 2-ΔΔCTmethod.
1.8 Statistical analysis
The results of the statistical analyses wereexpressed as means±SD. Differences between groups were analyzed for statistical significance using t tests.Results for which P<0.05 or P<0.01 were inferred as statistically significant. These calculations were conducted employing SPSS 17.0 software(SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).
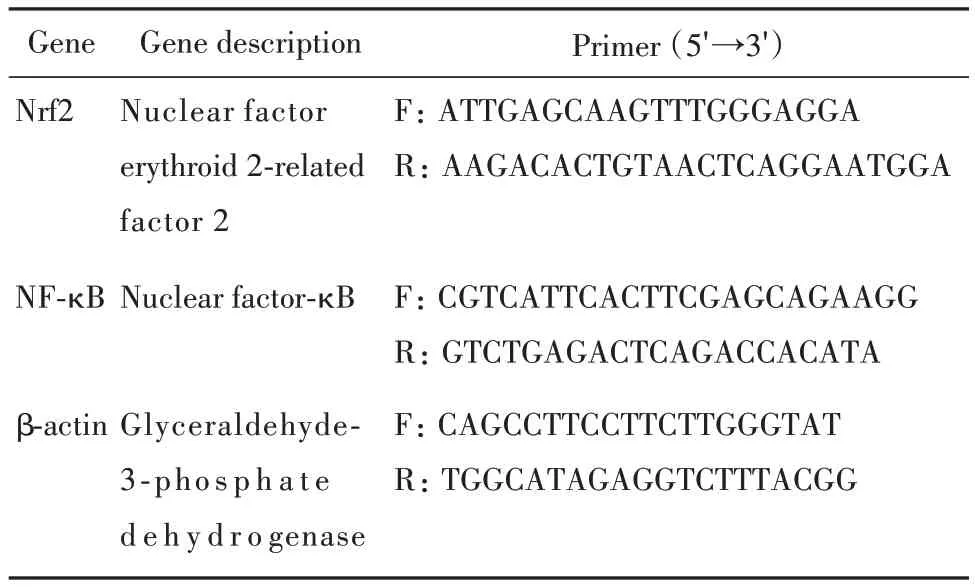
表1 定量PCR分析用引物序列Tab.1 Primer sequences for quantitative real-time PCR analysis
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Astaxanthin inhibits the growth of HCT116 cells exposed to lipopolysaccharide
It's well-known that the common events such as uncontrolled colonocyte proliferation occur at the cellular level during colon carcinogenesis. In our study,HCT116 cells were used to examine whether ASTA inhibited inflammation-induced proliferation of cancer cells after lipopolysaccharide(LPS)challenge employing MTT method. The results indicated LPS challenge increased the proliferation of HCT116 cells while ASTA inhibited the proliferation to some extent as shown in Fig.2.Recent studies indicated that aberrant bacterial LPS,mediated inflammatory mediators and signaling pathways in gut mucosa,may be involved in the pathogenesis of inflammation-related cancer.
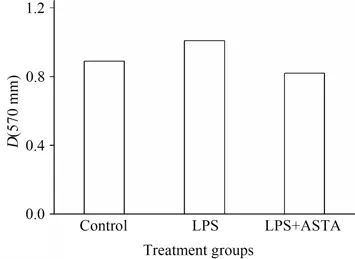
Fig.2 Effects of ASTA on the growth of HCT116 cells with LPS challenge图2 虾青素对LPS诱导的HCT116细胞生长的影响(HCT116 cells were seeded at a density of 1.6×106 cells·well-1 and cultured with or without the supernatant of 10 mg·L-1LPS and 2.5 mmol·L-1ASTA.)
2.2 Effects of ASTA on levels of cytokines in HCT116 cells
IL-1β and IL-6 were identified as the key endogenous factors if the inflammation-related events occur. There are documented studies indicated LPS challenge well stimulated the secretion and expression of IL-1β and IL-6. As shown in Fig.3,LPS treatment significantly increased IL-1β and IL-6 secretion in HCT 116 cells,while the secretion was remarkably inhibited by ASTA in a concentration-dependent manner.
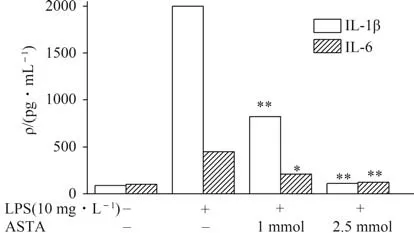
Fig.3 Effects of ASTA on levels of cytokines in HCT116 cells after LPS challenge for 12 h图3 虾青素对LPS诱导HCT116细胞12 h后细胞因子分泌的影响
2.3 Effects of ASTA on apoptosis in HCT116 cells
On the basis of the results in Fig.2,it's found that ASTA inhibited proliferation of CRC cancer cells. It is proposed that ASTA might inhibit proliferation of HCT116 cells by cell apoptosis. So HCT116 cells were used after LPS challenge to detect the interaction between inflammation and tumor progression and verify this hypothesis by flow cytometer and western blotting.The data indicated that only 4.5%of the cells underwent early apoptosis after 24 h at ASTA concentration of 1 mmol·L-1,while was increased to 13.2% early apoptosis and 1.8% late apoptosis when the cells were treated with 2.5 mmol·L-1ASTA for 24 h in a dose-dependent manner(Fig.4(a)). The translocation of apoptotic proteins such as caspase-3 and caspase-9 regulates the release of pro-apoptotic molecules.The western blotting results indicated apoptosis occured and showed that the caspase-3 and caspase-9 levels were increased in a dose-dependent manner after ASTA treatment at concentrations higher than 2.5 mmol·L-1(Fig.4(b)).These findings showed that ASTA could induce apoptosis of HCT116.
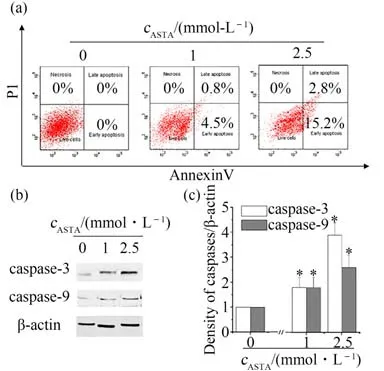
Fig.4 Effects of ASTA on apoptosis in HCT116 cells after LPS challenge for 12 h concentrations图4 虾青素对LPS诱导HCT116细胞12 h后细胞凋亡的影响
2.4 Effects of ASTA on NF-κB and Nrf-2 transferring into nuclear in HCT116 cells
The transcriptional factors nuclear factor-κB(NF-κB)and NF-E2-related factor 2(Nrf2)played critical roles in protecting against inflammation. Here LPS(10 mg·L-1)was used to induce inflammatory reaction in HCT116 cells in presence or absence of ASTA at concentration of 2.5 mmol·L-1and studied the effects of ASTA on the activation of NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathway by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. The results indicated LPS challenge activated the NF-κB transferring into nuclear in HCT116 cells while 2.5 mmol·L-1ASTA suppressed the NF-κB translocation into nuclear(Fig.5(a),(b)). The results of western blotting(Fig.5(c)) and immunofluorescence confocal microscopy(Fig.5(d))showed that ASTA promotedthe nuclear translocation of Nrf2. These findings suggested both the important transcriptional factors NF-κB and Nrf2 were involved in protecting against inflammation ,and it is hypothesized that the increased translocation of Nrf2 probably activated the a battery of genes encoding various phase II detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes by binding to antioxidant response elements(ARE)and the depressed expression of NF-κB transferring into nuclear significantly alleviated the inflammatory reaction by activating the NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathway in the presence of ASTA.
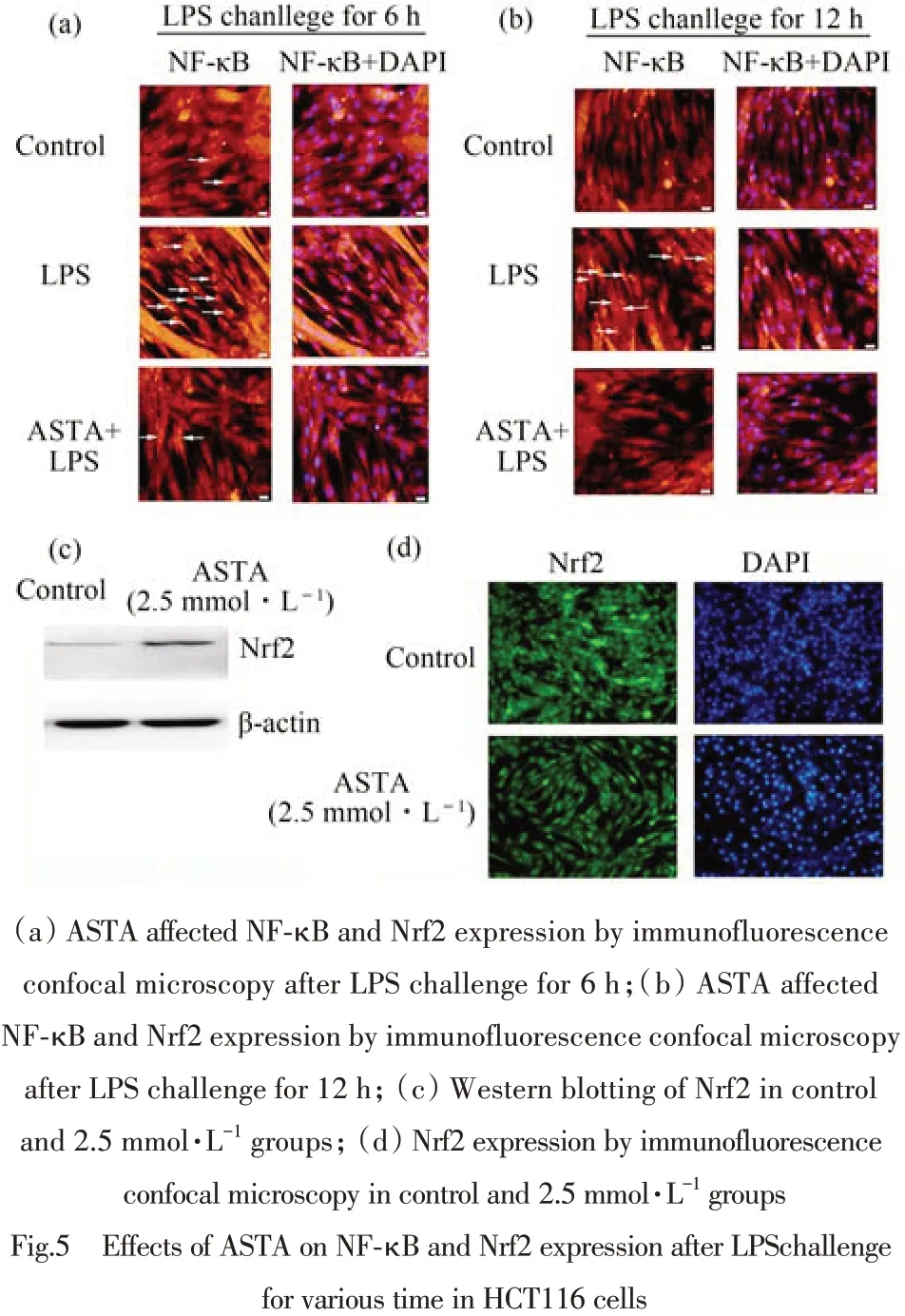
图5 虾青素对LPS诱导HCT116细胞后不同时间时NF-κB和Nrf2表达的影响(HCT116 cells were stained by Hoechst 33258 and corresponding anti-bodies such as NF-κB(red)Nrf2(green).)
2.5 Effects of ASTA on NF-κB and Nrf-2 gene expressions in HCT116 cells
Nrf2 has emerged as an indispensable regulator of both constitutive and inducible expression of phase II detoxifying and antioxidant enzyme genes in various cells[11]. The mRNA levels of NF-κB and Nrf-2 were examined by quantitative real time PCR to investigate the ASTA-induced effects. As shown in Fig.6,the results indicated that there was a significant increase in the mRNA levels of NF-κB and Nrf-2 in HCT116 cells challenged by LPS(10 mg·L-1),compared respectively with those in the control. The decrease in the mRNA levels of NF-κB was detected in presence of ASTA in a dose-dependent manner,while there was an increase in mRNA levels of Nrf-2 along with ASTA concentration.The results indicated that LPS challenge might cause inflammatory and oxidative stress and induced the subsequent procedure of NF-κB and Nrf-2 expression in HCT116 cells.
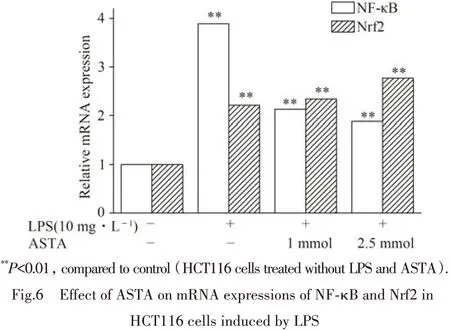
图6 虾青素对LPS诱导HCT116细胞后NF-κB和Nrf2的mRNA表达的影响(mRNA expressions of NF-κB and Nrf2 were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR.β-action was used as an internal control.)
3 Discussion
Increasing evidences suggest that the major tumor-promoting mechanism of inflammation is that cytokines produced by immune/inflammatory cells result in the activation of transcription factors ,such as NF-κB,STAT3 and AP-1 in premalignant cells,which induce genes expression that stimulates cell proliferation and survival[12]. The inflammatory microenvironment which is considered as a target for cancer therapy is an integral and essential part of the cancer[13].This study demonstrated the effect of ASTA on the expression and nuclear localization of NF-κB and Nrf2 in vitro and the results indicated the LPS challenge caused adverse effects while ASTA could alleviate these effects to some extent in HCT116 cells.
Nrf2 induces the gene expression of antioxidant and detoxification enzymes and has been reported to exert anti-inflammatory effect by regulating several pro-inflammatory genes,including TNF-a,IL-1β and IL-6 in inflammatory cells[14-16]. The Nrf2 signal pathway is regarded as one of the most important defense systems for the protection against oxidative damage.The activation of Nrf2 and consequent upregulation of its target genes not only counteract oxidative and electrophilic assault but also limit the severity of inflammatory tissue damage,which represent a potential mechanism of cancer chemoprevention[17-18]. However,Nrf2 has also been demonstrated to be beneficial for tumor survival,which could decrease the accumulation of ROS,maintain a favorable redox balance and upregulate ARE-dependent genes to generate antioxidants in cancer cells to promote their survival and development and Nrf2 is advantageous for cancer development and should be inhibited rather than induction during cancer therapy[19-20].
IL-6 and IL-1β contribute to cellular transformation and growth in a paracrine or autocrine manner. In this paper,the treatment of ASTA remarkably suppressed the secretion of IL-6 and IL-1β in HCT116 cells.The results suggested that ASTA decreased the production of IL-6 and IL-1β by modulating NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways.
SONG et al reported that ASTA activated of caspase-9,caspase-3,Nrf-2 and other cytoprotective genes through the ROS dependent mitochondrial signalling pathway and may be of potential therapeutic value in lung fibrosis treatment[21]. Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans[22]. ASTA inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators by blocking NF-κB activation and as a consequent suppression of IKK activity and IκB-α degradation probably due to its antioxidant activity[23]. ASTA reduces ocular inflammation in eyes with endotoxin-induced uveitis by downregulating proinflammatory factors induced by LPS and by inhibiting the NF-κB-dependent signaling pathway[24].
A great deal of studies suggested that many cytotoxic anticancer agents lead to apoptosis,enhancing the interesting possibility that evasion in apoptotic programs conduce to treatment failure[25-26]. Defect of apoptosis may cause carcinogenesis,tumor progression and treatment resistance,because most of present anticancer therapies including chemotherapy,radio- and immunotherapy primarily work by inducing cell death pathways including apoptosis in cancer cells[27]. Astaxanthin , a promising anticancer agent,inhibited NF-κ B and Wnt signal pathways by downregulating expression of the key regulatory enzymes IKK β and GSK-3 β ,and also downregulated the expression of antiapoptotic Bcl-2,p-Bad and survivin to induce caspase-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis,and upregulated proapoptotic Bax and Bad,accompanied by exudation of Smac/Diablo and cytochrome-c into the cytosol,and induced cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase(PARP)[28]. ASTA is a promising candidate agent for cancer prevention and therapy by targeting the key molecules in oncogenic signaling pathways and inducing apoptosis[28-29].
Taken together,the obove results suggested that ASTA prevented the initiation and development of CRC and regulated NF- κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways in HCT116 cells. NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways might play a critical role for ASTA's prevention of CRC which indicated ASTA might be a new and attractive chemoprevention agent for inflammation-related cancer.

