基于虚拟筛选的新型吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶抑制剂的发现及活性评价
刘伊彤,周睿,姜艺菲,连晓芳,郑瑞芳,山广志
·论著·
基于虚拟筛选的新型吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶抑制剂的发现及活性评价
刘伊彤,周睿,姜艺菲,连晓芳,郑瑞芳,山广志
100050 北京,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院医药生物技术研究所分析测试中心(刘伊彤、姜艺菲、连晓芳、山广志),免疫生物学室(周睿);830004 乌鲁木齐,新疆维吾尔自治区药物研究所新疆维吾尔药重点实验室(郑瑞芳)
应用药效团模型及分子对接的综合虚拟筛选策略,对 Specs 及 Chembridge 数据库进行筛选并进行生物学活性评价,以期发现新型吲哚胺 2,3-双加氧酶(IDO1)抑制剂。基于已报道 IDO1 抑制剂,利用 Discovery Studio 2019 软件的 Pharmacophores(Hiphop)模块构建药效团模型。通过最优药效团模型初步筛选了 Specs 及 Chembridge 数据库,后采用 LibDock 及 CDOCKER 程序靶向 IDO1 活性位点进行层级分子对接,最终保留了 40 个苗头化合物,并在 100 μmol/L 浓度下进行了细胞水平 IDO1 酶抑制活性初筛。选取初筛抑制率大于 50% 的 11 个化合物进行细胞水平及生化水平抑酶活性的进一步测定。采用 SPR 及分子对接模型进一步确证及阐明化合物与 IDO1 酶之间的相互作用方式。发现羟基嘧啶类化合物 29 在细胞水平及生化水平上均呈现了IDO1 酶抑制活性,EC50和 IC50分别为(53.93 ± 1.22)μmol/L和(179 ± 8.12)μmol/L。SPR 研究进一步确证了化合物 29 与 IDO1 之间的直接结合(D= 65.92 μmol/L)。分子对接模型研究显示羟基嘧啶基团与 IDO1 的卟啉环之间存在较为丰富的相互作用,是靶向识别的关键基团。羟基嘧啶类化合物 29 是一类新型 IDO1 抑制剂,可作为 IDO1 酶抑制剂的先导物,通过进一步结构改造及优化,有望获得高效、结构新颖的 IDO1 抑制剂及新型肿瘤免疫治疗药物。
吲哚胺 2,3-双加氧酶; 抑制剂; 药效团模型; 分子对接; 酶活性评价
L-色氨酸(L-tryptophan,L-Trp)是人体最重要的必需氨基酸之一,正常人体 L-Trp 血浆浓度为 40 ~ 80 μmol/L,目前被认为是参与人体免疫系统功能的关键氨基酸之一[1]。L-Trp 在体内主要有三条代谢途径:约 5% 的 L-Trp 用于蛋白质合成或通过 5-羟色胺途径代谢为 5-羟色胺和褪黑素,剩余 95% 的 L-Trp 均通过犬尿氨酸(kynurenine,Kyn)途径分解为色氨酸代谢物,即一系列犬尿氨酸衍生物[2]。在过去的十年中,色氨酸分解代谢被确认为是先天和适应性免疫耐受的主要机制之一,通过调节由不受控制或过度的免疫反应引起的自身免疫或免疫病理,维持免疫稳态[3]。
吲哚胺 2,3-双加氧酶(indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase 1,IDO1)是一种含亚铁血红素的单体酶,是催化 L-Trp 沿犬尿氨酸途径转化为 Kyn 及其衍生物的第一步和限速步骤酶[4]。研究显示,在多种癌症中如非小细胞肺癌[5]、乳腺癌、结直肠癌和恶性胶质瘤等[6],均存在 IDO1 的过表达。肿瘤微环境中 IDO1 的过表达导致了色氨酸耗竭和犬尿氨酸衍生物的积累,破坏了免疫调节机制,形成免疫抑制微环境,促进肿瘤局部耐受。
T 细胞对低水平 L-Trp 特别敏感。当 T 细胞通过未带电的 tRNAs 感知到 L-Trp 水平下降时,压力应答激酶(general control nonderepressible 2,GCN2)被诱导激活,引起了真核细胞转录起始因子 2α(eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α,eIF2α)磷酸化,阻止了体内大部分 mRNA 的翻译及蛋白质合成[7]。此外,GCN2 的激活导致了感知氨基酸水平充足或缺乏的信号蛋白——丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶激酶激酶 3(mitogen-activatedprotein kinase kinase kinase kinase 3,MAP4K3/GLK)受到抑制,进而导致哺乳动物雷帕霉素(丝/苏氨酸蛋白激酶)复合物(mammalian target of rapamycin1,mTORC1)失活。激活的 GCN2 和失活的 mTORC1 对 T 细胞信号通路产生干扰,使 G1 期细胞周期阻滞,导致 T 细胞分化或凋亡[3, 8]。
犬尿氨酸途径的下游代谢物 Kyn 是芳香烃受体(AhR)的内源性配体[9]。AhR是螺旋环螺旋(helix-loop-helix,bHLH)蛋白家族的配体激活成员之一。激活后的 AhR 在细胞质中从分子伴侣复合物中解离,与 AhR 核转运子结合,调节细胞核中的靶基因的转录[3]。Kyn 可激活 AhR,促进人叉头框蛋白 P3(FOXP3)调节 T 细胞(Tregs)的分化,抑制抗肿瘤免疫反应,最终导致了效应 T 细胞无能及 Tregs 免疫抑制功能激活,协助肿瘤逃避免疫监视[10-12]。因此,IDO1 被认为是逆转免疫抑制效应和恢复肿瘤免疫反应的一个重要靶点[13]。
在近年研究中,IDO1 抑制剂的研发领域十分活跃,已发表的文献报道了各种结构类型的 IDO1 抑制剂。在已进入临床阶段的 IDO1 抑制剂中(图 1),indoximod 是一种天然底物类似物,通过刺激 KP 下游的 mTORC1 表现出抑制作用[14]。Epacadostat(INCB024360)是一种含羟基脒的血红素结合型 IDO1 抑制剂,可与游离的含亚铁-IDO1 结合,呈现出较强的底物竞争作用[15]。Navoximod(NLG919,GDC-919)是一种含 4-苯基咪唑取代芳烃的血红素结合抑制剂,通过与血红素中心铁离子结合呈现酶抑制活性[16]。Linrodostat(BMS-986025)是一个血红素取代型抑制剂,可以取代血红素并靶向不含铁的 Apo-IDO1[17]。PF-06840003则属于一种非色氨酸竞争性、非血红素结合的 IDO1 抑制剂[18]。目前只有少数候选物的临床研究取得进展,尚未有药物完成临床试验获批上市。因此,发现新型结构基团的 IDO1 抑制剂用于癌症免疫治疗仍然具有研发前景。
虚拟筛选(virtual screening,VS)具有筛选通量高、耗时少、费用低等优势,是识别新结构类型化合物的常用方法,而药效团模型筛选是计算机辅助药物设计(CADD)的典型策略之一,其可识别活性化合物的基本特征类型和体积、特征间距离及分子排阻体积等[19]。本研究为了改善单独的 VS 方法导致评分函数准确性不足的问题,采用药效团建模(HipHop)和级联分子对接手段,探索开发了一种数据库筛选组合策略,将研究范围缩小到小部分有希望的化合物,以期发现靶向 IDO1 的新型酶抑制剂。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
人宫颈癌细胞系 HeLa 细胞购于 ATCC;DH5α 大肠杆菌购自北京擎科生物科技有限公司;BL21(DE3)大肠杆菌购自北京全式金生物技术公司;质粒提取试剂盒购自康为世纪生物科技股份有限公司;蛋白酶抑制剂 Cocktail(不含EDTA,100× DMSO 储备液)购自美国 Bimake 公司;HisTrap excel(1 ml)预装柱购自美国 Cytiva公司;阳性抑制剂 epacadostat 购自上海 MCE 公司;过氧化氢酶购自美国 Sigma-Aldrich 公司;干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)购自江苏金斯瑞生物科技有限公司;5-氨基乙酰丙酸(5-ALA)购自韶远化学科技(上海)有限公司;异丙基-β-D-硫代半乳糖苷(IPTG)、抗坏血酸、L-Trp、亚甲基蓝、对二甲氨基苯甲醛(-DMAB)和咪唑等均购自北京百灵威科技有限公司;EnSpire 酶标仪系统购自美国 PerkinElmer 公司。
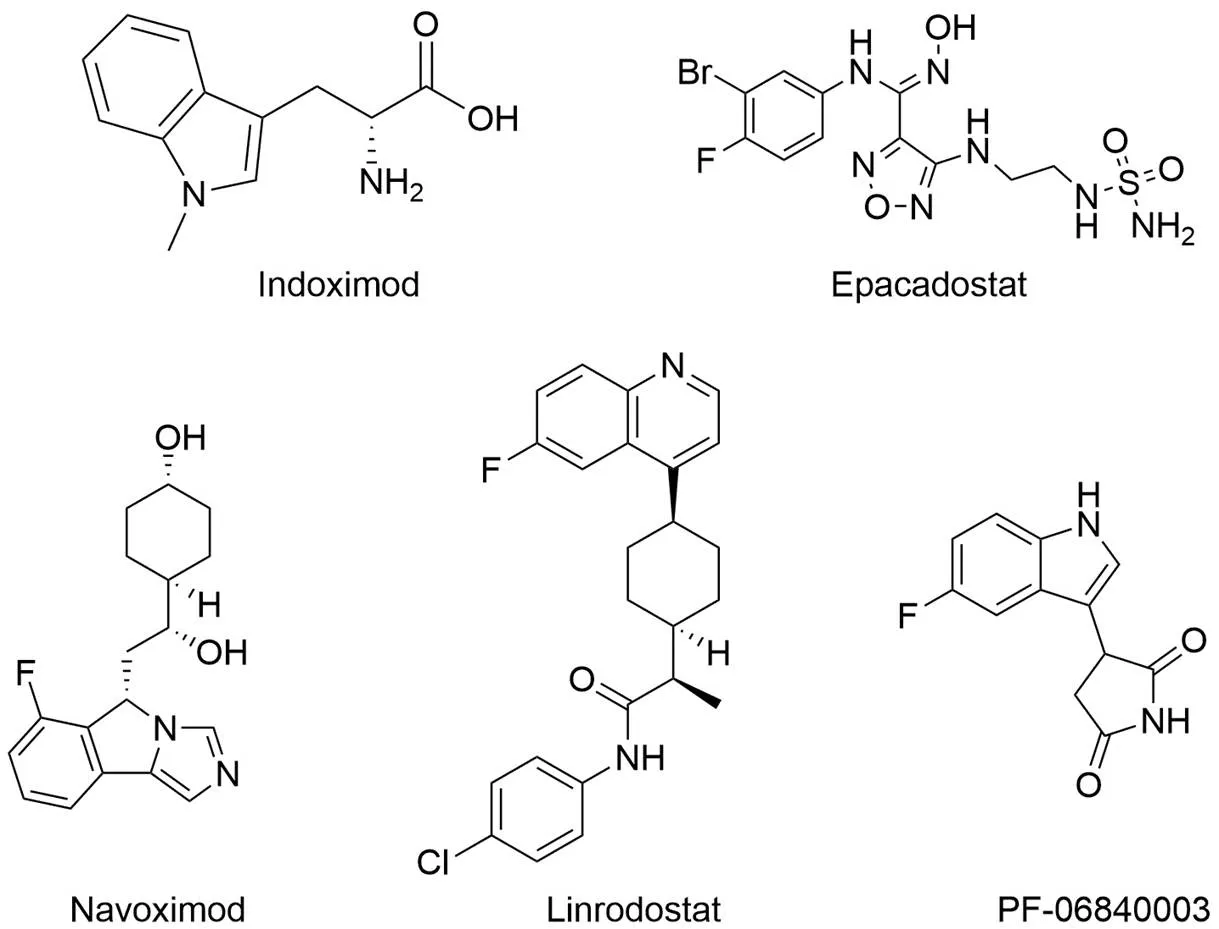
图1 临床阶段的 IDO1 抑制剂
Figure 1 IDO1 inhibitors in clinical trials
1.2 方法
1.2.1 质粒构建 委托深圳华大基因股份有限公司基于 genebank 序列号为 NM_002164.6 的人 IDO1 基因序列进行 IDO1 氨基酸序列全合成,并以H I和I 为酶切位点连接于 pET28a(+) 载体(图 2)。
1.2.2 细胞培养 HeLa 细胞培养于 MEM 培养基,HEK293T细胞培养于 DMEM 培养基,培养基中均添加 10% 胎牛血清及 100 U/ml 青霉素、100 U/ml 链霉素。HeLa 与 HEK293T 细胞均于 5% CO2的 37 ℃恒温培养箱中培养传代。
1.2.3 虚拟筛选
1.2.3.1 蛋白预处理 从 RCSB PDB 蛋白质数据库(https://www.rcsb.org/)下载 IDO1 和Navoximod 复合物(PDB ID:6O3I)的晶体结构,基于 Discovery Studio(DS)2019 软件中的 Prepare Protein 模块进行去除水分子、质子化、修复缺失环区和最小化能量等预处理。
1.2.3.2 数据库预处理 基于 DS 2019 中的 Prepare or Filter Ligands 模块,利用“Lipinski′s Rule of Five”和“Veber Rules”筛选过滤了含有约176 万个化合物的 Chembridge 和 Specs 数据库,并形成一个 3D 类药数据库。
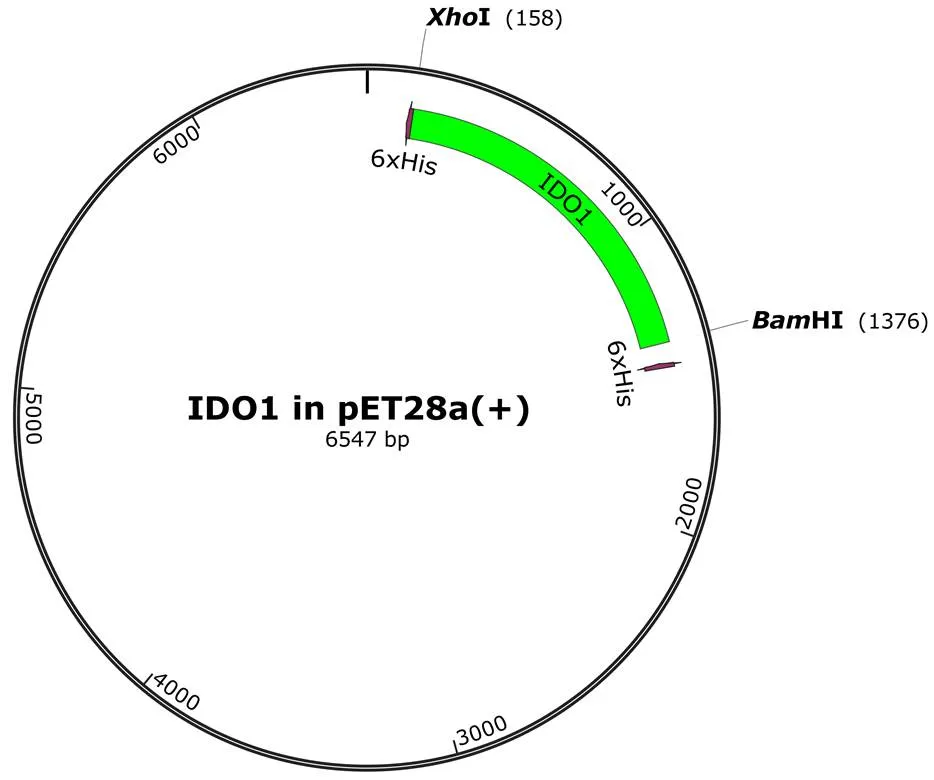
图2 IDO1-pET28a(+) 质粒构建图谱
Figure 2 IDO1-pET28a (+) plasmid construction map
1.2.3.3 训练集及测试集预处理 从文献[20-26]中选取 39 个活性化合物作为药效团构建的活性数据集。定义 6 个活性分子作为训练集(图 3)。剩余 33 个 IDO1 抑制剂与从 Directory of Useful Decoys(DUD·E)网站(https://dude.docking.org/)生成的诱饵分子组合形成了两个测试集—— Test 1 和 Test 2,活性分子的百分比分别为 1.5% 和 10%。
1.2.3.4 基于配体的 HipHop 药效团模型构建及筛选 基于训练集结构,应用 DS 2019 中的 Common Feature Pharmacophore Generation 程序生成药效团模型。Principal 和 MaxOmitFeat 属性分别定义为 2 和 0。构象生成设置为 BEST,能量阈值设置为 10。在 10 个药效团中选择灵敏度和特异度最优模型作为最终药效团模型。
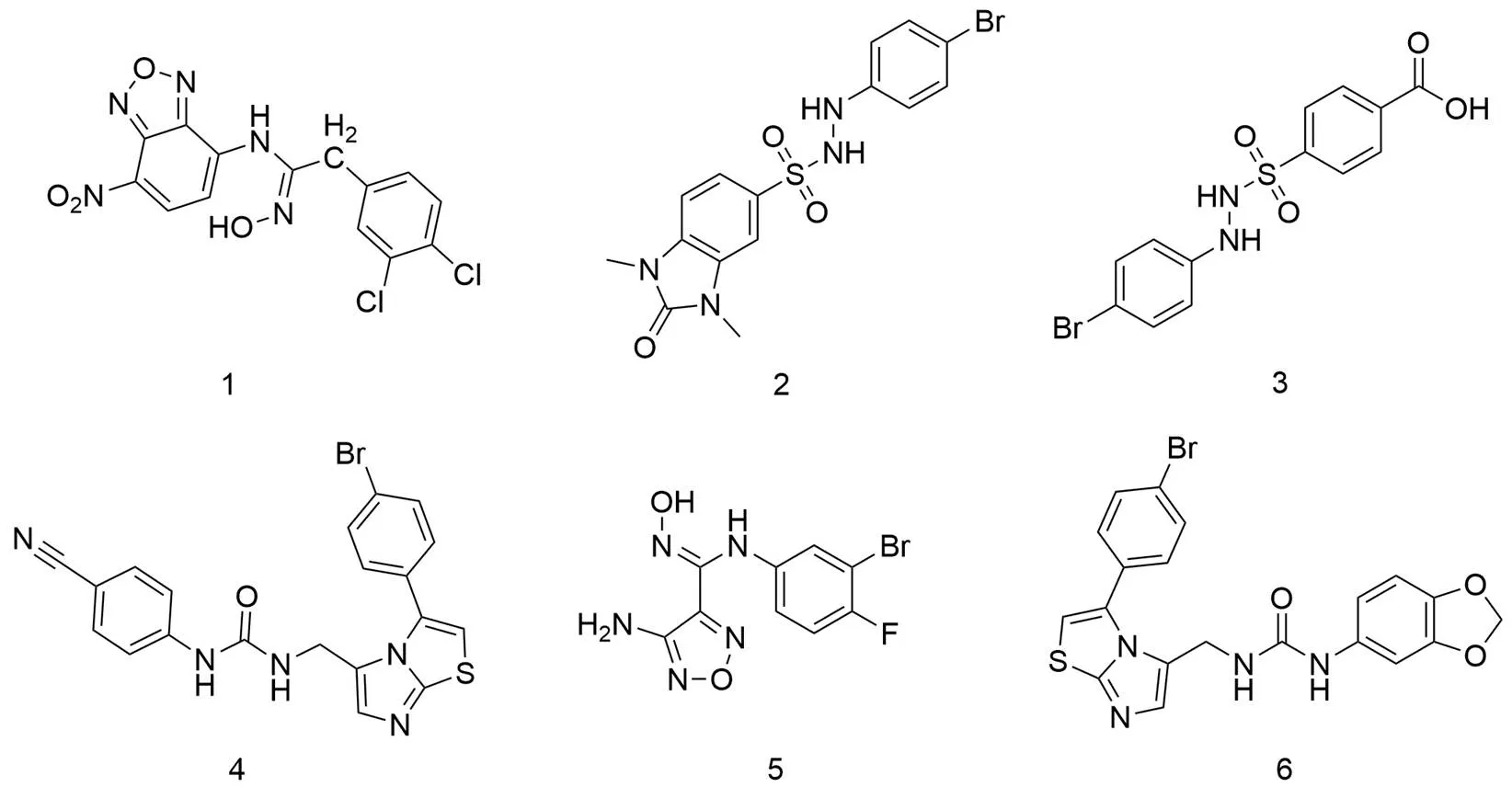
图3 药效团模型训练集—— 6 个 IDO1 抑制剂结构
Figure 3 Pharmacophore model training set-structures of six IDO1 inhibitors
基于 DS 2019 的 Search, Screen and Profile 模块,采用最可靠的药效团 9 筛选潜在的活性抑制剂。HYDROPHOBIC_3, HBD_4, HBA_5 设置为必需药效团特征,构象生成设置为 FAST,最大构象设置为 200,能量阈值设置为 10。
拟合值是匹配结果最关键的评价标准。在 MedCalc 软件(http://www.medcalc.org)的ROC曲线分析中导入两个测试集分子及其对应的拟合值,预测活性化合物的拟合值阈值。最终保留拟合值> 2.90465的分子用于进一步筛选。
1.2.3.5 基于分子对接的虚拟筛选 蛋白晶体结构预处理方法如上所述。对接位点定义在以天然配体 LKP502 为中心的12 Å 半径球体内,球心 x、y、z 坐标分别为 10.721、27.366、164.210。利用 DS 2019 的 LibDock 和 CDOCKER 模块进行层级分子对接筛选,通过逐步提高对接精度以增加命中化合物数目。将 LKP502 重新对接到 6O3I 的活性位点,得到 LibDock 和 CDOCKER 模块对接后预测构象与原构象的均方根偏差(RMSD)分别为 0.6243、0.2153 Å,证明该方法可准确预测受体与配体间结合模式。排序前 10% 的分子被保留以进行后续筛选。
1.2.3.6 PAINS 及 ADMET 筛选 采用 FAF-Drugs4 程序[27]进行 pan-assay interference compounds(PAINS)filter 和 ADMET(Absorption、Distribution、Metabolism、Excretion、Toxicity)筛选。在 Bank-Formatter 模块中将上述化合物转换为对应的 SDF 输入格式文件,选择“Drug-like soft”作为“physchem filters”。“PAINS Filter”与“Retrieve covalent inhibitors”均设置为“true”,“Lilly MedChem Rules”设置为“regular”。选择除 PAINS 和共价抑制剂外的所有化合物进行检查。
1.2.4 生物活性评价
1.2.4.1 IDO1 蛋白表达及纯化 将人 IDO1 全长 cDNA 克隆到带有 N 端 6× His 标签的pET28a(+) 载体上。pET28a-IDO1 质粒转化于大肠杆菌 BL21(DE3)中,涂板于含50 μg/ml 卡那霉素的 LB 培养基中上。过夜培养后挑取单克隆菌落,于 37 ℃、200 r/min 条件下在液体培养基中扩增至260为 0.6 ~ 0.8。然后加入 0.5 mmol/L IPTG 和 5-ALA 继续于 37 ℃诱导 3 h。在 4 ℃下,8000 r/min 离心 10 min,收集菌体,用裂解缓冲液(20 mmol/L Na2HPO4,200 mmol/L NaCl,10 mmol/L 咪唑,1× 蛋白酶抑制剂Cocktail,pH 7.4)重悬,冰上超声 30 min。4 ℃下 12 000 r/min 离心 1 h,0.22 μm 过滤器过滤。将上清液上样于 HisTrap excel 预装柱,并在结合缓冲液(20 mmol/L Na2HPO4,200 mmol/L NaCl,10 mmol/L 咪唑,pH 7.4)中平衡,后用洗脱缓冲液(20 mmol/L Na2HPO4,200 mmol/L NaCl,400 mmol/L 咪唑,pH 7.4)梯度洗脱以获得高纯度 IDO1 蛋白。纯化后的蛋白用分子量为 30 000 D 的 Amicon Ultra(Millipore)离心管浓缩,–80 ℃冻存。
1.2.4.2 生化水平酶抑制活性评价 100 μl 反应体系中,由 50 mmol/L 磷酸钾缓冲液(pH 6.5)、10 mmol/L 抗坏血酸、10 μmol/L 亚甲蓝、100 μg/ml 过氧化氢酶、100 μmol/L L-Trp、100 nmol/L IDO1 及不同浓度待测化合物组成。在 37 ℃下反应30 min,加40 μl 40%()三氯乙酸终止反应。将样品置于 65 ℃孵育 15 min 以促进 Kyn 产生,最后加入 60 μl 3.75%()-DMAB-冰醋酸溶液进行显色,并于 490 nm 条件下进行吸光度测定。利用 GraphPad Prism 9进行非线性回归分析,确定 IC50值。
1.2.4.3 细胞水平酶抑制活性评价 将 HeLa 细胞以 2 × 104/孔(200 μl)接种于96 孔培养板中,置 37 ℃、5% CO2恒温培养箱中培养过夜。次日,弃原有培养基,更换为含终浓度为 100 ng/ml 人干扰素-γ、50 μmol/L L-Trp 和不同浓度待测化合物的细胞培养基 200 μl。置 37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养 48 h,取 140 μl 上清液与 10 μl 40%()三氯乙酸混合,65 ℃孵育 15 min。后将混合物以 2500 r/min 的速度离心 10 min 去除沉淀物。取上清液 100 μl 与等体积 2%()-DMAB-冰醋酸溶液混合,室温孵育 10 min,于 490 nm 波长处读取吸光度,计算化合物对 IDO1 抑制率,使用 GraphPad Prism 9 计算 EC50值。
1.2.4.4 表面等离子体共振 SPR 分析 使用基于 SPR 技术的 Biacore T200生物分子互作分析系统评价化合物 29 与 IDO1 蛋白间特异性结合。通过 EDC/NHS 活化 CM5 芯片,后基于氨基偶联法固定 IDO1 酶蛋白并使用乙醇胺封闭剩余未结合羧基位点。运行缓冲液为 5% DMSO PBS-P 溶液(20 mmol/L PBS,2.7 mmol/L KCl,137 mmol/L NaCl,0.05% 吐温 20,pH 7.4)。结合与解离时间均设定为 100 s,运行流速为 30 μl/min。实时记录结合响应值,并应用 Biacore T200 Evaluation Software 计算待测化合物的D值。
2 结果
2.1 HipHop 药效团模型评价
利用 DS 2019 的 HipHop 模块,基于 6 个已知 IDO1 抑制剂结构构建了 10 个药效团模型。通过两个测试集对 10 个药效团模型进行进一步表征评价,结果显示药效团 9 综合敏感性和特异性最好(图 4和图 5)。药效团 9 包括 1 个氢键供体(HBD)特征、1 个氢键受体(HBA)特征、1 个疏水(HYD)特征和 2 个芳香环(RA)特征(图 4A)。以 epacadostat 为模板化合物验证药效团 9 的识别能力,结果显示 epacadostat 与药效团 9 的 3D 叠合情况良好,拟合值为 3.853(图 4B)。因此,选择药效团 9 作为下一步虚拟筛选的药效团模型。
2.2 Specs 和 Chembridge 数据库的虚拟筛选
首先将 Specs 和 Chembridge 库基于“Lipinski's Rule of Five”和“Veber Rules”进行初步筛选。后以药效团模型 9 为 3D 药效团查询式,对含 170 万个化合物的数据库进行二次筛选。经药效团筛选,拟合值 > 2.90465 的 92861 个化合物通过 LibDock 和 CDOCKER 模块层级对接到 IDO1 的对接位点。然后,通过 PAINS 和 ADMET 特性筛选对接打分前 10% 的化合物以得到类药化合物集。利用 FCFP_6 指纹进行聚类,选择 186 个具有理想结合构象的化合物进行检查。最终选择 40 种商业可获得化合物用于后续的生物评价。
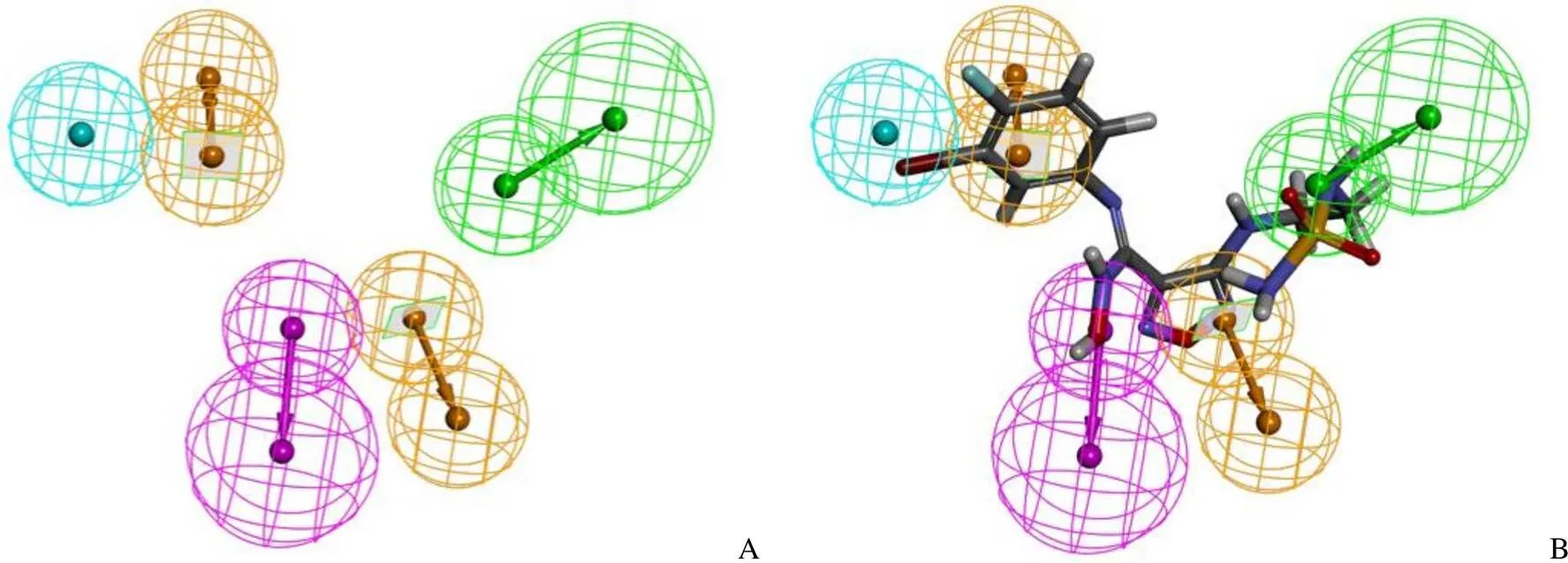
图4 药效团模型 9(A)及其与 epacadostat 叠合情况(B)
Figure 4 Pharmacophore model 9 (A) and superposition with epacadostat (B)

图5 10 个药效团模型评价结果[A:10 个药效团模型的 Test 1 的验证结果;B:药效团 9 的 Test 1 的 ROC 曲线(Quality 0.794:Fair);C:10 个药效团模型的 Test 2 的验证结果;D:药效团 9 的 Test 2 的 ROC 曲线(Quality 0.786:Fair)]
Figure 5 Evaluation results of 10 pharmacophore models [A: The validation results of 10 pharmacophore models of Test 1; B: The ROC curve for Test 1 of pharmacophore 9 (Quality 0.794: Fair); C: The validation results of 10 pharmacophore models of Test 2; D: The ROC curve for Test 2 of pharmacophore 9 (Quality 0.786: Fair)]
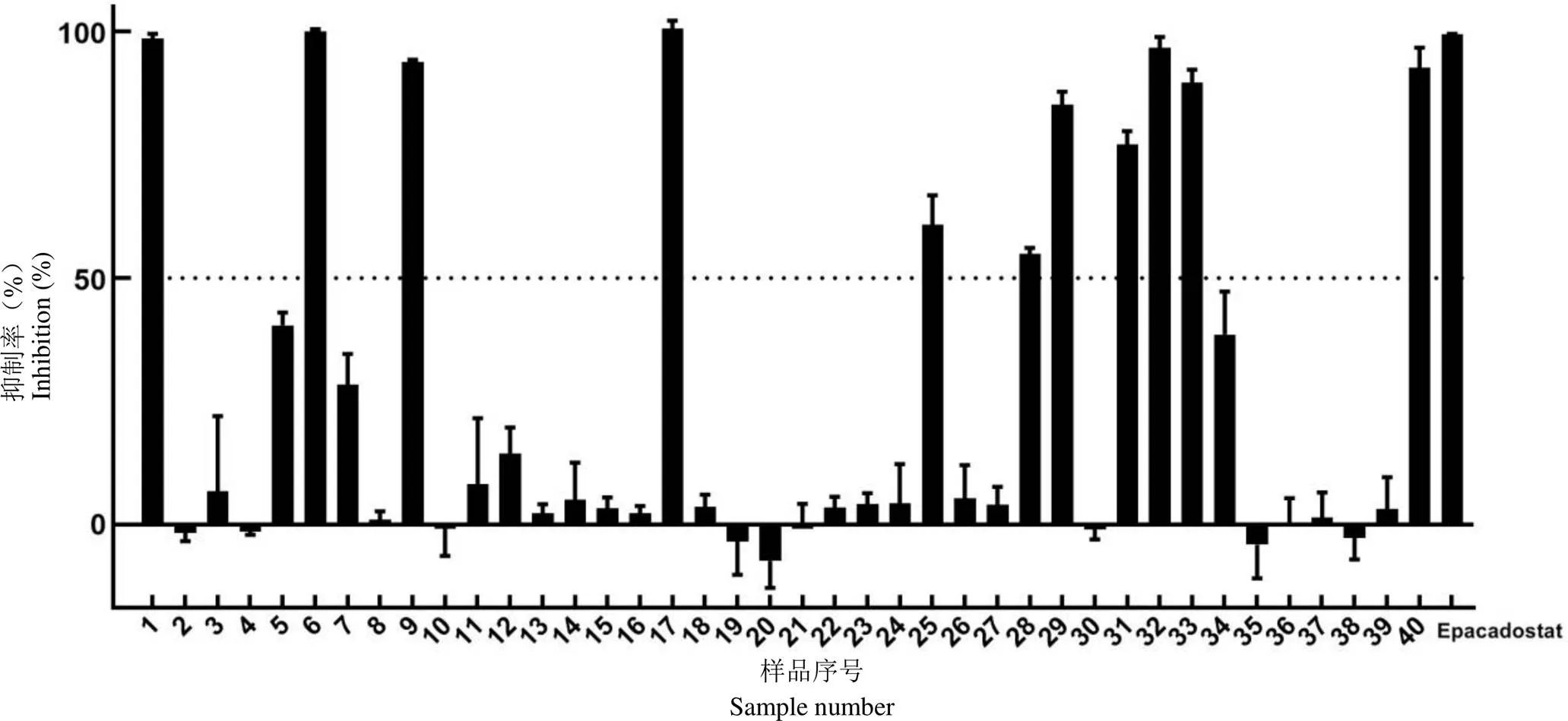
图6 40 个化合物在 100 μmol/L 浓度下对细胞水平 IDO1 酶抑制率(n = 3)
Figure 6 Inhibition rate at the cellular level of 40 compounds at 100 μmol/L (n = 3)
2.3 IDO1 酶抑制活性评价
通过测定细胞培养基上清中 Kyn 和-DMAB 发生缩合反应后,产物在 490 nm 下较强的吸光值变化,初步评价了 40 个可获得化合物在细胞水平对 IDO1 酶活性的抑制作用。以 epacadostat 为阳性对照,在 100 μmol/L 浓度下对 40 个候选物进行了活性初筛,结果显示,11 个化合物的抑制率大于 50%(图 6)。
将上述 11 个化合物进行细胞水平及生化水平 IDO1 酶水平抑制活性评价,测定并计算这些化合物的剂量反应曲线抑制活性(表 1)。结果显示,化合物29(Cp29,图 7A)具有明显的 IDO1 酶抑制效果,在细胞水平对 IDO1 酶抑制的 EC50=(53.93 ± 1.22)μmol/L,生化水平的 IC50=(179 ± 8.12)μmol/L(图 7B、C)。
2.4 Cp29 与 IDO1 蛋白的 SPR 研究
因 SPR 具有无标记、高灵敏度、多功能性且可实时读取和监测结合动力学等优势,近年来已成为表征和量化生物分子间相互作用的“金标准”[28]。为了更精确地验证 Cp29 为潜在的 IDO1 抑制剂,本研究使用 SPR 手段确证了 Cp29 与 IDO1 之间的直接相互作用。由传感图及分析结果可知,Cp29 与 IDO1之间存在直接结合,结合的平衡解离常数(D)约为 65.92 μmol/L(图 8)。
表1 11 个化合物的 IDO1 酶抑制活性测定结果(n = 3)
Table 1 IDO1 enzyme inhibitory activity of 11 compounds (n = 3)
化合物编号CompoundsnumberIDO1-HeLaIC50(μmol/L) 抑制率(%)Inhibition ratio (%)EC50(μmol/L) 198.5622.11 ± 3.13/ 699.9910.74 ± 0.86/ 993.861.881 ± 0.26/ 17100.54718.45 ± 2.14/ 2560.8138.52 ± 4.11/ 2854.9219.37 ± 8.34/ 2985.2053.93 ± 1.22179 ± 8.12 3177.1123.14 ± 0.84/ 3296.7443.19 ± 1.40/ 3389.7247.40 ± 3.67/ 4092.6534.54 ± 2.97/
注:“/”表示无活性。
Note: “/” represents no activity.
2.5 分子对接模型研究
为进一步探索 Cp29 与 IDO1 的相互作用机制,采用分子对接研究了 IDO1 蛋白与Cp29 的结合构象。如图 9所示,在 A 口袋中,取代嘧啶占据了血红素上方的疏水口袋,取代嘧啶羟基基团的氧原子与血红素铁原子形成了配位相互作用。嘧啶环与 Phe163 及亚铁血红素的吡咯基形成了三个 π-π 相互作用,同时与 Ala264 形成了 Amide-π 疏水相互作用。此外,取代嘧啶的羟基氧原子与 Ala264 间还存在氢键相互作用。B 口袋中,Cp29酰胺键的氧原子与氢原子分别与侧链 Ser235 与 Gly262 形成了两个氢键相互作用。

Figure 7 A: 2D structure of Cp29; B: The EC50curve of Cp29; C: The IC50curve of Cp29 (n = 3)
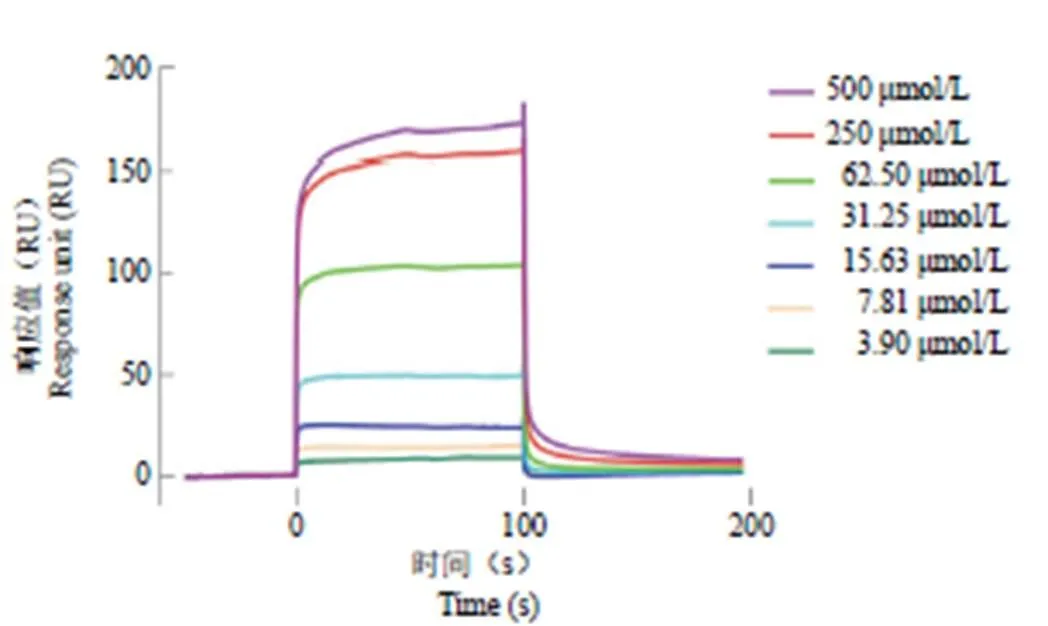
图8 Cp29 与 IDO1 结合传感图
Figure 8 The sensorgram of Cp29 binding to IDO1
3 讨论
本研究采用了组合虚拟筛选策略,首先基于最优药效团模型 9 对 Specs 及 Chembridge 数据库进行初筛,后通过层级分子对接进一步缩小筛选范围,最终选择并购买了 40 个命中化合物。
HeLa 细胞实验初步筛选以上所有化合物,将抑制率大于 50% 的 11 个化合物进行了细胞水平及生化水平抑酶活性的进一步测定,最终发现了羟基嘧啶类化合物 29 在细胞水平及生化水平对 IDO1 酶均存在明显抑制活性。
SPR 确证研究表明,Cp29 与 IDO1 酶存在直接结合。分子对接模型进一步阐述了两者间的可能作用机制。羟基嘧啶氧原子与血红素辅基的亚铁离子形成配位结合,Cp20 的嘧啶环、酰胺键等结构与氨基酸侧链形成了多个氢键、π-π 和 Amide-π 疏水等相互作用,为两者互作结合提供了合理解释,支持了 Cp29 作为新结构 IDO1 抑制剂先导物的结论。
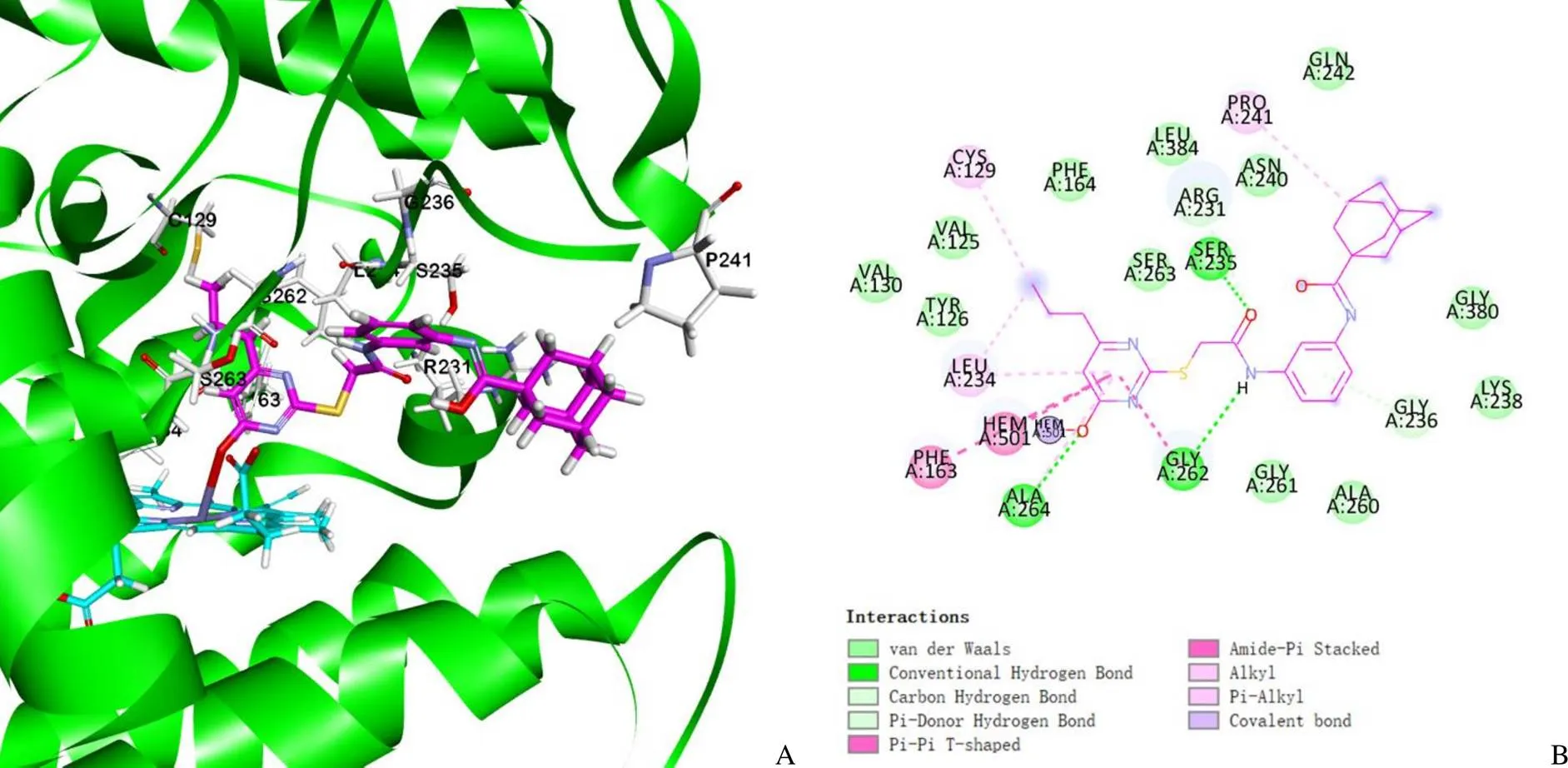
图9 IDO1 蛋白与 Cp29 的分子对接预测结合模型(A:IDO1 与 Cp29 相互作用三维图;B:IDO1 与 Cp29 相互作用二维图)
Figure 9 Prediction docking model between IDO1 protein and Cp29 (A: 3D interaction plot between IDO1 and Cp29; B: 2D interaction plot between IDO1 and Cp29)
羟基嘧啶类化合物 Cp29 是一类新型 IDO1 抑制剂,为新骨架 IDO1 抑制剂的研发提供了理论基础。后续通过对 Cp29 进一步的结构改造及修饰研究来提高其活性及改善药代动力学等特性,探索发现结构新颖、高效的 IDO1 抑制剂。
[1] Armstrong MD, Stave U. A study of plasma free amino acid levels. II. Normal values for children and adults. Metabolism, 1973, 22(4):561- 569.
[2] Song X, Si Q, Qi R, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1: a promising therapeutic target in malignant tumor. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 800630.
[3] Amobi A, Qian F, Lugade AA, et al. Tryptophan catabolism and cancer immunotherapy targeting IDO mediated immune suppression. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 1036:129-144.
[4] Meireson A, Devos M, Brochez L. IDO expression in cancer: different compartment, different functionality? Front Immunol, 2020, 11:531491.
[5] Chu CE, Porten SP, Grossfeld GD, et al. Role of indoleamine-2,3- dioxygenase inhibitors in salvage therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Urol Clin North Am, 2020, 47(1):111-118.
[6] Davar D, Bahary N. Modulating tumor immunology by inhibiting indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO): recent developments and first clinical experiences. Target Oncol, 2018, 13(2):125-140.
[7] Wek RC, Jiang HY, Anthony TG. Coping with stress: eIF2 kinases and translational control. Biochem Soc Trans, 2006, 34(1):7-11.
[8] Brincks EL, Adams J, Wang L, et al. Indoximod opposes the immunosuppressive effects mediated by IDO and TDO via modulation of AhR function and activation of mTORC1. Oncotarget, 2020, 11(25):2438-2461.
[9] Opitz CA, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F, et al. An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature, 2011, 478(7368):197-203.
[10] Moon YW, Hajjar J, Hwu P, et al. Targeting the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase pathway in cancer. J Immunother Cancer, 2015, 3:51.
[11] Platten M, von Knebel Doeberitz N, Oezen I, et al. Cancer immunotherapy by targeting IDO1/TDO and their downstream effectors. Front Immunol, 2014, 5:673.
[12] Zhang KP, Zhang Q, Yu KY, et al. Clinical research status of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors. Chin J Front Med Sci (Electronic Version), 2020, 12(1):20-26. (in Chinese)
张康平, 张琪, 于恺英, 等. 吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶抑制剂临床研究现状. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2020, 12(1):20-26.
[13] Li F, Zhang R, Li S, et al. IDO1: an important immunotherapy target in cancer treatment. Int Immunopharmacol, 2017, 47:70-77.
[14] Kuffel MJ, Buhrow SA, Reid JM, et al. Kynurenine: a biomarker for in vitro and in vivo modulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by 1-Methyl-[D]-tryptophan (NSC 721782). Cancer Res, 2005, 65(9_Supplement):982.
[15] Liu X, Shin N, Koblish HK, et al. Selective inhibition of IDO1 effectively regulates mediators of antitumor immunity. Blood, 2010, 115(17):3520-3530.
[16] Zhou Y, Peng J, Li P, et al. Discovery of novel indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors by virtual screening. Comput Biol Chem, 2019, 78:306-316.
[17] Cherney EC, Zhang L, Guo W, et al. Conformational-analysis-guided discovery of 2,3-disubstituted pyridine IDO1 inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett, 2021, 12(7):1143-1150.
[18] Sun L. Advances in the discovery and development of selective heme-displacing IDO1 inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Discov, 2020, 15(10):1223-1232.
[19] Braun J, Fayne D. Mapping of protein binding sites using clustering algorithms - development of a pharmacophore based drug discovery tool. J Mol Graph Model, 2022, 115:108228.
[20] Röhrig UF, Majjigapu SR, Chambon M, et al. Detailed analysis and follow-up studies of a high-throughput screening for indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem, 2014, 84:284-301.
[21] Dolušić E, Larrieu P, Blanc S, et al. Discovery and preliminary SARs of keto-indoles as novel indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem, 2011, 46(7):3058-3065.
[22] Cheng MF, Hung MS, Song JS, et al. Discovery and structure-activity relationships of phenyl benzenesulfonylhydrazides as novel indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2014, 24(15): 3403-3406.
[23] Wu JS, Lin SY, Liao FY, et al. Identification of substituted naphthotriazolediones as novel tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) inhibitors through structure-based virtual screening. J Med Chem, 2015, 58(19):7807-7819.
[24] Fallarini S, Massarotti A, Gesù A, et al. In silico-driven multicomponent synthesis of 4,5- and 1,5-disubstituted imidazoles as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors. MedChemComm, 2016, 7(3):409-419.
[25] Paul S, Roy A, Deka SJ, et al. Nitrobenzofurazan derivatives of N'-hydroxyamidines as potent inhibitors of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1. Eur J Med Chem, 2016, 121:364-375.
[26] Lin SY, Yeh TK, Kuo CC, et al. Phenyl benzenesulfonylhydrazides exhibit selective indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibition with potent in vivo pharmacodynamic activity and antitumor efficacy. J Med Chem, 2016, 59(1):419-430.
[27] Lagorce D, Bouslama L, Becot J, et al. FAF-Drugs4: free ADME-tox filtering computations for chemical biology and early stages drug discovery. Bioinformatics, 2017, 33(22):3658-3660.
[28] Peltomaa R, Glahn-Martínez B, Benito-Peña E, et al. Optical biosensors for label-free detection of small molecules. Sensors (Basel), 2018, 18(12):4126.
Discovery and biological evaluation of novel IDO1 inhibitors based on virtual screening
LIU Yi-tong, ZHOU Rui, JIANG Yi-fei, LIAN Xiao-fang, ZHENG Rui-fang, SHAN Guang-zhi
Author Affiliation: Analysis and Testing Center (LIU Yi-tong, JIANG Yi-fei, LIAN Xiao-fang, SHAN Guang-zhi), Department ofImmunology (ZHOU Rui), Institute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100050, China; Xinjiang Institute of Materia Medica, Urumqi 830004, China (ZHENG Rui-fang)
Based on a comprehensive virtual screening strategy of pharmacophore model and molecular docking, the study aims to screen and evaluate the biological activities of new potential IDO1 inhibitors from Specs and Chembridge databases.Based on known IDO1 inhibitors, the Pharmacophores (Hiphop) module of Discovery Studio 2019 software was used to construct the pharmacophore model. The Specs and Chembridge databases were initially screened by the optimal pharmacophore model, and then the hierarchical molecular docking was carried out by using LibDock and CDOCKER programs to target the active site of IDO1. Finally, 40 promising compounds were retained for preliminary screening of IDO1 enzyme inhibitory activity at the cellular level at 100 μmol/L. Eleven compounds with inhibition rates greater than 50% were selected for further determination of the enzyme inhibitory activities at the cellular and biochemical levels. SPR and molecular docking models were used to further confirm and clarify the interaction between the compounds and IDO1 enzyme.Through the biological activity determination, hydroxypyrimidine compound 29 was found to demonstrate IDO1 enzyme inhibitory activity at the cellular level and biochemical level, with an EC50of (53.93 ± 1.22) μmol/L and an IC50of (179 ± 8.12) μmol/L, respectively. Direct binding between compound 29 and IDO1 was further confirmed by SPR studies (D= 65.92 μmol/L). Molecular docking model study showed that the hydroxy pyrimidine group interacts with the porphyrin ring of IDO1, which was the key group for targeted recognition.Hydroxypyrimidine compound 29 is a new class of IDO1 inhibitors and can be used as a lead compound. Through further structural modification and optimization, efficient and novel IDO1 inhibitors and new tumor immunotherapy drugs are expected to obtain.
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; inhibitors; pharmacophore model; molecular docking; enzyme activity evaluation
s:SHAN Guang-zhi, Email: shanguangzhi@imb.pumc.edu.cn; ZHENG Rui-fang, Email: zrfangdd@ 163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1673-713X.2023.03.001
中国医学科学院生物医药关键核心技术研发工程(2021- I2M-1-070)
山广志,Email:shanguangzhi@imb.pumc.edu.cn;郑瑞芳,Email:zrfangdd@163.com
2023-02-21

