Resveratrol combats chronic diseases through enhancing mitochondrial quality
Weichu Tao,Hu Zhang,Xia Jiang,Ning Chen
a Tianjiu Research and Development Center for Exercise Nutrition and Foods, Hubei Key Laboratory of Exercise Training and Monitoring,College of Sports Medicine, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, China
b The University Hospital of Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, China
Keywords: Resveratrol Functional food Mitochondrial quality Chronic disease Anti-inf lammation Anti-oxidation
ABSTRACT Resveratrol (RSV),as a functional food component extracted from natural plants,has been widely studied and recognized in preventing and treating various diseases,with major mechanisms including executing anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation functions,and improving mitochondrial quality.Chronic diseases as non-communicable diseases are mainly caused by multiple factors,such as physiological decline and dysfunction in the body,and have become a significant challenge on public health worldwide.It is worth noting that chronic diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD),Parkinson’s disease (PD),muscle atrophy,cardiovascular disease,obesity,and cancer are accompanied by abnormal mitochondrial function.Therefore,targeted regulation of mitochondria may be a meaningful way to prevent and treat chronic diseases.Increasing evidence has confirmed that RSV is actively involved in regulating mitochondria,and it has become an essential consideration to prevent and treat chronic diseases through targeting mitochondria and improving corresponding functions.In this article,current studies on RSV to optimize mitochondrial quality for preventing and alleviating chronic disease are systematically summarized,which can provide a theoretical reference for the development of functional foods or drugs to combat chronic diseases.
1.Introduction
With the improvement of global technology and the development of economy and medicine,the lifespan of humans has been signif icantly extended,which also leads to a high incidence of chronic diseases[1].According to the latest report released by the World Health Organization (WHO) on September,2022,the number of deaths from non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cancers and diabetes has surpassed that from infectious diseases,with the death number of approximately 41 million each year[2].Therefore,NCDs are the biggest challenge all over the world.The prevention and treatment strategies for chronic diseases are based on exercise,nutrition or functional foods,drugs,and even surgery.Although pathological mechanisms of chronic diseases are super intricate,mitochondrial dysfunction is the common characteristics for Alzheimer’s disease(AD)[3],Parkinson’s disease (PD)[4],skeletal muscle atrophy[5],cardiovascular diseases[6],obesity[7]and cancer[8-9].Similarly,the normal aging process is also accompanied by mitochondrial dysfunction[9],thereby optimizing mitochondrial function is one of the promising strategies for the prevention and treatments of these chronic diseases,especially the prevention through functional foods.Many drugs targeting mitochondria such as hexokinase inhibitors,Bcl-2 family analogs,and thiol redox inhibitors can act on mitochondria-related ion channels and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)functions including redox electron transport chain;however,these drugs cannot optimize mitochondrial generation,fusion and f ission,and autophagy to improve mitochondrial quality and function.Exercise is an important way to improve the mitochondrial quality and function in the body.Since chronic diseases are more common in the elderly,seeking non-stimulant interventions such as functional foods or diets is particularly important.Among them,resveratrol(RSV) is a bioactive polyphenol compound extracted from natural products to target mitochondria through continuous excavation of its molecular mechanisms.Many studies have confirmed its biological functions to regulate and optimize mitochondrial dynamics and quality[10].Therefore,this article systematically collects,sorts out,and summarizes relevant results and molecular mechanisms of RSV in preventing and treating chronic diseases based on the regulation and optimization of mitochondrial function and quality,which can provide a theoretical reference for countering chronic diseases caused by global population aging,and propose future precision directions for the development of functional foods or drugs to prevent and combat chronic diseases.
2.RSV
RSV is a polyphenol compound extracted from natural plants,also known as 3,5,4’-trihydroxystilbene,with a molecular formula of C14H12O3and a relative molecular weight of 228.25 Da.RSV,a non-flavonoid polyphenol widely present in plants,such as grapes,mulberries,soybeans,peanuts,and others[11](Fig.1),with multiple functions including anti-oxidation,anti-inflammation,anti-cancer,and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular protection functions.In 1939,RSV was first discovered and extracted fromVeratrum grandiflorumO.Loes[12].It hascis-andtrans-structures and widely used due to relatively high stability of itstrans-structure.Although RSV has an absorption rate of more than 75%[13]and can be obtained in a daily diet,the good therapeutic effect on diseases have not been comprehensively reported,especially the lack of the precision studies on the interventional efficacy of low-dose RSV during daily diets.RSV is mainly metabolized into glucuronic acid,sulfate,or free form in the body;and free RSV is mainly combined with albumin and then transported to various tissues and organs of the body to execute its functions.In clinical trials of cancer treatment,the halflife of 500 mg/kg body weight is approximately 2 h[14],which further reduces the utilization rate of RSV after liver and kidney metabolism during oral administration.The utilization of RSV can be improved through compound formulation and drug delivery,and it can play a beneficial role in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases such as AD,PD,muscle atrophy,cardiovascular disease,obesity,and cancer.Notably,based on the evaluation of the European Food Safety Authority,daily intake of 150 mg is also within the safe range[15].Therefore,RSV may be a potential natural product in preventing and treating chronic diseases.

Fig.1 Sources of RSV in foods (red grape[16],apple[17],peanut [18],beer[19],skin of tomato dry weight[20],and dark chocolate[21]).
3.Introduction of mitochondria
Mitochondria,as the primary energy converter of eukaryotic cells,are densely distributed in tissues and organs with vital metabolic functions,in multiple shapes such as spindles,rods,and dumbbells,with a general diameter of 0.5-10 μm.Similarly,as highly dynamic organelles,mitochondria can produce newborn mitochondria with optimal functions through biogenesis.During the process of mitochondrial biogenesis,the activation of peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) can promote the transcription and expression of mitochondrial biogenesis-related genes including mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM),nuclear respiratory factor 1/2 (Nrf1/2) and estrogen-related receptor α(ERRα),thereby increasing the copy number of mtDNA to improve mitochondrial quality (Fig.2A)[22].Aging and damaged mitochondria can execute fusion and fission between each other to produce healthy mitochondria,thereby completing the clearance of damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria through mitophagy and other signal pathways;however,in the case of severe damage to mitochondrial function,these mitochondria can release pro-apoptotic factors for triggering endogenous apoptosis of cells.The mitochondrial structure mainly comprises outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM),inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM),mitochondrial inner and outer membrane space,the mitochondrial ridge formed by IMM folding,and the matrix in IMM.OMM is an organelle isolation component and has good permeability and small molecular substances can enter the IMM through the active and passive transport to pass the OMM.The oxidative phosphorylation reaction of the protease and the electron transport chain on the mitochondrial ridge provides the body with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to maintain regular functions of cells.The mitochondrial matrix mainly gathers mtDNA,enzymes,ribosomes,and other substances[23].Various metabolisms in the cytoplasm and mitochondria generate high potential reduced coenzyme I(NADH) and accumulate in the intima space to form a mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP).NADH can gradually release energy through NADH-Q oxidoreductase (complex (COX) I),succinate-Q oxidoreductase (COX II),UQ-cytochrome C oxidoreductase (COX III),cytochrome C oxidase (COX IV) and ATP synthase (COX V) to produce a large amount of ATP (Fig.2B),while it is also an essential source of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Mitochondrial dynamics is mainly manifested in the process of mitochondrial fusion and division.A series of GTPases participate in the dynamic process of regulating mitochondrial membrane structure,such as optic atrophy protein 1 (OPA1),mitochondrial fusion protein 1 and 2(Mfn1/2),mitochondrial dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1),dynamin-2 (Dyn2),and mitochondrial fission protein 1 (Fis1).Mfn1/2 is responsible for the fusion of two OMMs.The GTP hydrolysis of Mfn promotes the oligomerization of the GTPase domain of Mfn,and induces the binding of OMM[24-25].OPA1 is involved in the regulation of IMM fusion[26],and different phosphorylation sites can regulate the activity of Drp1 to participate in mitochondrial fission[27].With the assistance of Dyn2,a circular oligomer is partially formed around two OMMs that are about to split,and the hydrolysis of GTP promotes the contraction of cyclic oligomers and accelerates the separation of mitochondria[28].Abnormal mitochondria from mitochondrial fission are degraded through mitophagy,while normal mitochondria participate in normal physiological activities.In the process of impaired mitophagy,it is mainly completed by mitochondria-induced autophagy labeling,autophagic vesicle packaging,and binding to lysosomes,which are mainly regulated by Bcl-2 interacting protein 3(BNIP3),NIP3-like protein X (Nix)[29],PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1 (PINK1),ubiquitin ligase Parkin,FUN14 domain containing protein-1 (FUNDC1),microtubule-associated protein-1 light chain 3(LC3),sequestosome-1 (p62) and other critical regulatory proteins.However,when mitochondria are severely damaged,they will cause the release of pro-apoptotic factors in the mitochondrial membrane space or matrix,such as cytochrome C (Cyt-C),thereby activating the endogenous apoptotic pathway to induce cell death[30-31](Fig.2C).
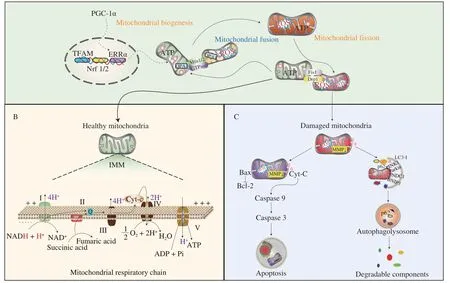
Fig.2 Molecular mechanisms for mitochondrial dynamics,mitophagy,apoptosis,and electron transport chain.(A) PGC-1α induces mitochondrial biogenesis by promoting the transcription of TFAM,Nrf 1/2 and ERRα.Aging or damaged mitochondria are fused into one mitochondrion by Mfn1/2,OPA1 and GTPase;or separated into functional mitochondria through Fis1 or Drp1.(B) Normal mitochondria usually function in the respiratory chain.(C) Aging or damaged mitochondria can be degraded through mitophagy with the involvement of PINK1,Parkin,FUNDC1,BNIP3 and other regulatory proteins or the released apoptosis factors such as Cyt-C to induce apoptosis.
4.Mitochondrial dysfunction and chronic diseases
Current studies have found that chronic diseases such as AD,PD,muscular atrophy,cardiovascular diseases,obesity,and cancer,with high incidence in the elderly,show mitochondrial dysfunction[32].Although the current understanding of mitochondrial dysfunction is limited,it mainly reflects abnormal number,shape and structure of mitochondria,weaken mitochondrial respiration,damaged membrane structure,reduced MMP,increased ROS,and dysfunctional mtDNA,mitochondrial biogenesis,fusion,fission and autophagy.It is noteworthy that these cascade reactions caused by mitochondrial dysfunction have also become the essential factors for exacerbating pathological changes in the body,such as endogenous apoptosis induced by released apoptosis factors in mitochondria[33],inflammation induced by increased ROS[34],reduced ATP supply due to decreased mitochondrial enzyme activity[35],intracellular Ca2+disturbance caused by mitochondrial damage[36].Among them,abnormal changes in mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics are shown in neurodegenerative diseases,including AD and PD[37],which may lead to the lower energy provided by mitochondria in neurons than the energy consumed by cells themselves[38],so that the function of neurons is at a lower operation status.Abnormal mitochondrial function in cancer may be an important factor in stimulating the proliferation and invasion of cancer cells[39],and targeting mitochondrial damage is also a potential strategy for the prevention and therapy of cancers[40].Exercise,nutrients or drugs are essential in reversing skeletal muscle atrophy and improving skeletal muscle function by enhancing mitochondrial quality[41-42],whereas mitochondrial dysfunction has also been detected in cardiovascular diseases[6].Mitochondrial dysfunction is also an essential mechanism in cardiovascular diseases[43],arthritis[44],and cancer[45].The improvement of mitochondrial function accompanies the improvement or cure of the disease,and the functional foods or drugs that regulate the function and quality of mitochondria can delay the progression of diseases.Therefore,judging from the current evidence,mitochondrial dysfunction is an important mechanism for developing and exacerbating chronic diseases,and targeted mitochondrial regulation may also be the key to unraveling the puzzle of chronic diseases.
5.RSV regulates mitochondrial function to combat chronic diseases
The role of RSV in regulating mitochondrial function and quality has been widely reported,and its molecular mechanism has also been gradually discovered.Therefore,we made a systematic statement and summary of the research advances of RSV in chronic diseases such as AD,PD,ischemic stroke,muscular atrophy,cardiovascular diseases,brain injury,obesity,arthritis,and cancer.
5.1 RSV enhances mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of AD
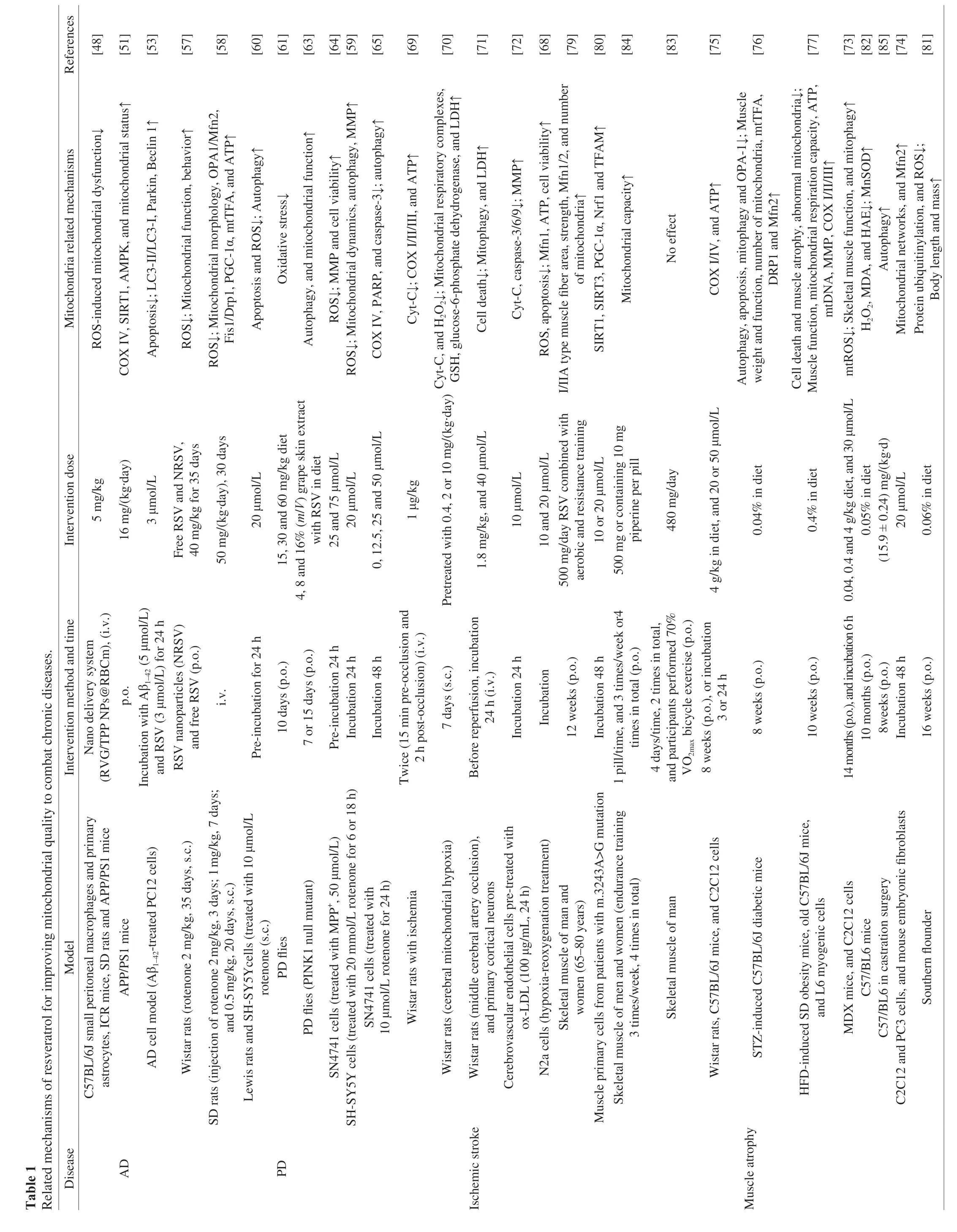
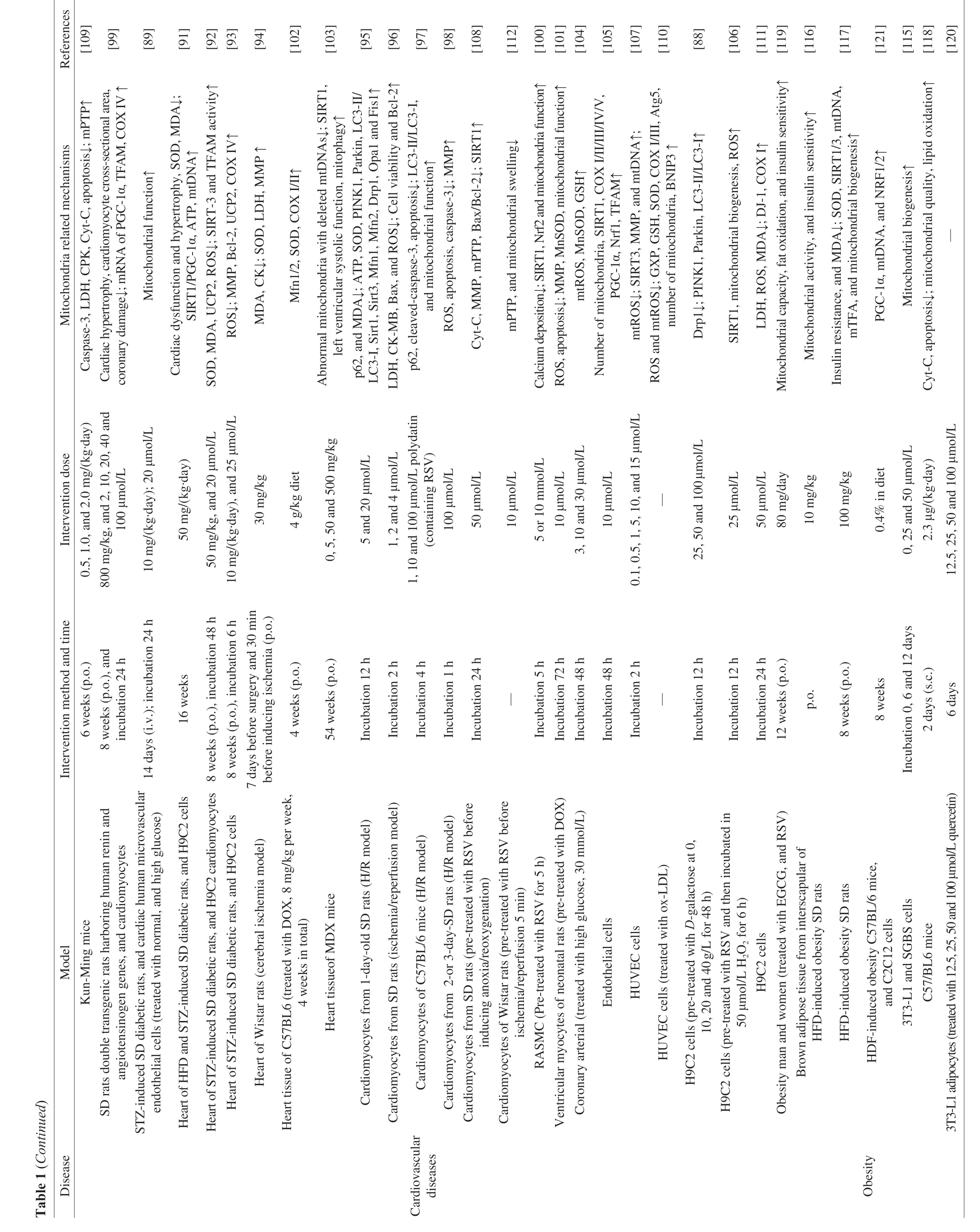
As a central degenerative disease with a high incidence in the elderly,AD mainly manifests as changes in learning,memory,emotion,and behavior.It has gradually become a potential disease that threatens the life and health of the elderly.Mitochondria in AD exhibit dysfunction,such as reduced ATP supply,impaired mitochondrial respiration,damaged mtDNA[46],and abnormal expression of mitochondrial fusion and fission genes[47].In relevant studies on RSV,it is found that the delivery of RSV to mitochondria in neurons by systemic administration of a novel biomimetic nanosystem containing RSV,bothin vivoandin vitrostudies have shown the inhibition of ROS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction with stronger anti-AD effect[48-50].In AD model (APP/PS1) mice,it has also shown the increased mitochondrial COX IV protein[51],activated sirtuin 1 (SIRT1),increased succinate dehydrogenase (SDH),and increased PGC-1α deacetylation and reduced ROS level,thereby improving mitochondrial function[52].When amyloid β peptide 1-42(Aβ1-42) is used to induce AD model cells (PC12),the administration of RSV can promote the down-regulation of autophagy-related proteins such as Beclin1,LC3-II/I and Parkin.Meanwhile,RSV also can reduce neuronal damage caused by AD through targeting signal pathways of mitophagy[53].It is worth noting that RSV intake through the dietary route has also revealed to trigger mitophagy for accelerating the clearance of aging,damaged,and dysfunctional mitochondria,which could become a vital protector of brain health in the future[54].Therefore,RSV has a positive regulatory effect on mitochondrial function in AD animal and cell models,and has a great potential to overcome neurodegenerative diseases in the manner of functional foods or novel drugs (Fig.3A).However,there are still many difficulties in exploring its absorption rate and precision targets in human experiments.
5.2 RSV improves mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of PD
PD is a classic motor phenotype of the central nervous system disease,usually accompanied by behavioral characteristics such as tremors,rigid movements,cognitive and mental abnormalities.One in every 100 people over 60 years old worldwide is affected by PD[55].Dietary regulation has gradually gained public attention[56],and the abnormality of mitochondrial function has also attracted the extensive attention of researchers.Rotenone,as an inducer of PD-causing mitochondrial dysfunction,is currently being used extensively.On the other hand,the administration of RSV nanoparticles in rotenone-induced neural cell PD model can significantly alleviate mitochondrial dysfunction,and exhibit less PD-like behavior[57].Therefore,improving mitochondrial function may be an important strategy for preventing and treating PD.In cell-related studies,RSV intervention in nerve and PC12 cells can activate PGC-1α and mitochondrial transcription factor A (mtTFA) to induce mitochondrial biogenesis and increase the copy number of mtDNA,as well as optimize mitochondrial dynamics through regulating OPA1/Mfn2 and Fis1/Drp1,reduce ROS level,and increase ATP production in nerve cells,ultimately improving the toxicity of rotenone to the central nervous system[58].In human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y),RSV also can ameliorate declined MMP and mitochondrial fragmentation,inhibit increased ROS and decreased mitochondrial apoptosis through extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) for optimizing autophagic flux[59].In the rotenone-induced PD rat and SH-SY5Y cell models,RSV can also suppress neuronal apoptosis by inducing heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)-mediated autophagy[60].Among antioxidant effects,RSV intervention ameliorates the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2),nitric oxide (NO),and malondialdehyde (MDA)in aParkingene deletion-induced PDDrosophilamodel and finally exhibits the mitigation of motor deficits[61],through executing the reduction of oxidative stress[62].In the PINK1 mutation-induced PDDrosophilamodel,RSV also can prevent the onset of PD and prolong lifespan by inducing autophagy and enhancing mitochondrial function to improve muscle function[63].In addition,RSV can diminish MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in mouse dopaminergic neurons (SN4741 cells) by activating protein kinase B (Akt)/glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β) signal pathway and reducing Bax/Bcl-2 ratio[64],and clear damaged mitochondria in nerve cells through AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/SIRT1 signal axis-mediated autophagy to completing its protective role(Fig.3B)[65].Therefore,RSV plays an active role in gene deletion and drug-induced PD by reducing ROS,optimizing mitochondrial dynamics,enhancing mitochondrial respiration and autophagy,and activating these corresponding molecular signal pathways.
5.3 RSV strengthens mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke
Stroke is a disease with high disability and mortality among middle-aged and older adults.In 2016,there are 13.7 million new cases all over the world[66-67].Stroke is mainly divided into hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke by judging whether there is a hemorrhage in the brain.Ischemia-reperfusion is an essential factor for aggravating this disease.Currently,cerebral vascular ligation is used to simulate an ischemic stroke.In the refocus model of cerebral ischemia,RSV can activate the AMPK-Mfn1 signaling pathway[68],increase mitochondrial glutathione,reduce lipid peroxidation and intracellular H2O2[69],and regulate COX III,stabilize mitochondrial membrane structure[70]and trigger autophagy[71]to achieve the effect of mitochondrial protection,thereby suppressing the occurrence of stroke,mitigating the symptoms of stroke,and preventing secondary injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion.In addition,in cerebrovascular endothelial cells,RSV can protect cells from apoptosis caused by oxidized low-density lipoproteins by down-regulating the lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) receptor-1(LOX-1)-mediated Bax/mitochondrion/Cyt-C/Caspase signal pathway (Fig.3C)[72].Therefore,RSV plays a positive protective role in ischemic stroke by improving mitochondrial quality,reducing oxidative stress,and suppressing apoptosis.
5.4 RSV promotes mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of muscle atrophy
As an important manifestation of body degeneration,skeletal muscle atrophy is mainly manifested as the loss of mass and strength of skeletal muscle,with the major mechanism of imbalanced protein synthesis and protein degradation,impaired autophagy,and reduced mitochondrial quantity and function.RSV can significantly up-regulate autophagy-related genes or proteins such as BNIP3,FUNDC1,Atg5,Beclin1,Map1lc3b,TFEB and Lamp1,optimize autophagy flux,and suppress the production and accumulation of ROS in Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse model and C2C12 cells.These benefits are suppressed by the knockdown of Atg5 or PINK1[73],thus further confirming the targeted activation of mitophagy by RSV in skeletal muscle.At the same time,RSV can target Mfn2 to regulate the process of mitochondrial fusion,participate in cell metabolism and growth[74],and induce PGC-1α deacetylation and activation by up-regulating AMPK and SIRT1 to accelerate mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle[75].Even in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic amyotrophic mice,RSV also can increase mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy to suppress the loss of skeletal muscle mass[76].RSV can rescue the declined mitochondrial function and prevent skeletal muscle atrophy in obese mice through the PKA/serine threonine kinase 11 (LKB1)/AMPK signaling pathway[77].Similarly,RSV can improve oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle of the elderly through increasing the number of mitochondria[78].In the elderly population with the age of 65-80 years old,12 weeks of aerobic exercise and resistance exercise training combined with RSV can increase the mean fiber area,total myonuclei,mitochondrial density,and antioxidant activity of vastus lateralis muscle fibers,as well as strength and metabolic capacity[79].In addition,RSV also shows an improvement effect on mitochondrial respiratory factors in skeletal muscle cells from patients with m.3243A>G mutation[80].In southern flounderParalichthys lethostigma,although RSV intervention can reduce the degradation of skeletal muscle through ubiquitin proteases,there is no significant difference in mitochondrial volume,density,and autophagy-related proteins[81].Previous studies have also documented that long-term RSV administration does not reduce skeletal muscle atrophy,but reveals an increase in antioxidant capacity[82].The 4-day oral administration of RSV in humans does not up-regulate the expression of the genes related to mitochondrial biosynthesis in skeletal muscle[83],however,when lower-intensity exercise training combined with RSV or piperine can result in the increase in the number of mitochondria by 40%[84],suggesting that the molecular mechanisms of RSV in alleviating skeletal muscle atrophy is complex,rather than targeting mitochondria alone.In gonadal castration mice,the suppression of gonad function can lead to the reduced secretion of androgen,thereby resulting in the mass loss of skeletal muscle,but RSV exhibits the suppression of skeletal muscle degradation at a certain degree by reducing ROS and mitochondrial degradation in skeletal muscle to maintain its strength and mass(Fig.3D)[85].Therefore,RSV may play a positive role in preventing and treating skeletal muscle atrophy by improving mitochondrial function and quality although some conflicting results are observed,which may be correlated with intervention individuals,disease types or progression,and administration dose during RSV intervention.
5.5 RSV improves mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases have always been a kind of diseases that plague the elderly.The mortality rate of cardiovascular diseases among the elderly over 65 years old is usually high,even with continuous increase due to the population aging[86].A series of chain reactions caused by mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases can be triggered and exacerbated the progression of aging and diseases[87].InD-galactose-induced aging cardiomyocytes,RSV can enhance cardiovascular function by activating mitophagyrelated proteins such as PINK1,Parkin,and LC3-II and inhibiting the phosphorylation of PINK1 and Parkin for enhancing mitochondrial quality in cardiomyocytes[88].In middle-aged and older adults with a high incidence of diabetes are often accompanied by myocardial injury,and RSV can execute its positive protective effect on vascular endothelial cells under a high glucose environment by improving mitochondrial quality[89].The primary mechanism of RSV in diabetic cardioprotection may improve mitochondrial respiration and biogenesis through activating SIRT1[90]and inducing PGC-1α deacetylation to increase mtDNA copy number,enhance ATP supply,and reduce superoxide dismutase (SOD) accumulation in cardiomyocytes[91].In addition,RSV also regulates the acetylation of TFAM by activating SIRT3 to maintain mitochondrial size and function[92]and inhibits uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) to improve functional status of mitochondria through reducing ROS,mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening,and Cyt-C-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes[93].In the ischemia-reperfusion model,RSV can also protect myocardial mitochondria by activating autophagy,improving MMP,and reducing oxidative stress,thereby improving cardiac function[94],which may be correlated with the activation of SIRT1/3-Mfn2-Parkin-PGC-1α signal pathway.Enhanced mitochondrial quality regulated by phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway can suppress the damage of myocardial tissues through reducing lactate dehydrogenase (LDH),creatine kinase-MB isoform (CK-MB) and MDA and SOD[95-96].Even in a myocardial ischemia-reperfusion neonatal rat model,RSV can activate autophagy to reduce damaged mitochondria and ROS production in cardiomyocytes[97],suppress Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity,and increase SIRT1 and MMP to alleviate myocardial damage[98].In angiotensin II-induced myocardial injury,RSV is beneficial to cardiac remodeling by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis through up-regulation of TFAM,Nrf1 and COX IV[99],and the activation of SIRT1 and Nrf2,thereby ameliorating vascular calcification and mitochondrial dysfunction[100],as well as improving SIRT1-mediated mitochondrial function for suppressing myocardial damage[101].RSV can up-regulate Mfn1/2,and promote mitochondrial electron remodeling of doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury at the level of transport chain complexes (Fig.3E)[102].RSV can also protect cardiomyocytes in MDX mice by activating mitophagy,inhibiting mtDNA loss,and reducing ROS level[103].It is worth noting that in human coronary artery endothelial cells,RSV can increase the expression of manganese SOD,superoxide dismutase 2 (MnSOD) and glutathione (GSH) by activating the SIRT1 signal pathway,reduce mitochondrial oxidative stress and improve mitochondrial function of vascular endothelium[104],and activating SIRT1/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) signal pathway to induce mitochondrial biogenesis factors such as PGC-1α,Nrf2 and TFAM,thereby further increasing mtDNA content to enhance mitochondrial quality and mitigate vascular endothelial dysfunction[105].RSV induces mitochondrial biogenesis throughSIRT1and mitochondrial MnSOD,NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit A 1/2 (NDUFA1/2),andNDUFA13genes,which can significantly inhibit ROS production[106]and activate AMPK/PGC-1α/ERRα/SIRT3 signaling pathway to participate in regulation of endothelial cell mtROS homeostasis[107],and SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) for increasing the binding capacity to Bax,and reducing the attachment of Bax to the mitochondrial outer membrane,thereby inhibiting the opening of mPTP and the release of apoptosis-inducing factors to prevent myocardial damage[108-109].RSV can also suppress endothelial damage in hyperlipidemia by activating BNIP3-associated mitophagy to induce the increase of mitochondrial respiratory complexes and maintain MMP[110].In addition,in-depth studies have confirmed that the protective effect of RSV may increase mitochondrial COX I by promoting Parkinson disease protein 7 (PARK7,also called DJ-1) expression[111],regulating the targeted transfer of GSK-3β from the cytoplasm to mitochondria,and interacting with cyclophilin D (CypD) protein to regulate mPTP and prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury[112].Therefore,RSV can accomplish a positive protection effect on cardiovascular diseases by directly and indirectly improving cardiovascular mitochondrial quality.
5.6 RSV raises mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of obesity
Obesity,as a common chronic metabolic disease,is mainly manifested as a significant increase in white adipose tissue caused by overeating and reduced physical activity,which eventually leads to chronic systemic inflammation and insulin resistance.Obesity also becomes the hotbed and triggers multiple diseases.Relevant studies have shown that RSV can prevent diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1α to improve mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation function[113-114].RSV also can reduce the accumulation of fat in obesity by inhibiting mitochondrial biogenesis,inducing preadipocyte differentiation[115],and alleviating insulin resistance by increasing mitochondrial activity in brown adipose tissue[116].RSV can increase mtDNA content to induce mitochondrial biosynthesis,reduce mitochondrial oxidative stress,promote subsarcolemmal and intermyofibrillar insulin sensitivity,and suppress HFD-induced insulin resistance[117].In the elderly,RSV can inhibit fatty acid synthesis by increasing the phosphorylation of AMPK in the body and improving the transport and oxidation of fatty acids[118].In a randomized controlled trial,the consumption of RSV and epigallocatechin-3-gallate can increase mitochondrial volume and fat oxidation[119].RSV combined with quercetin can inhibit the release of mitochondrial Cyt-C,thereby suppressing preadipocyte differentiation and inducing apoptosis of mature adipocytes for accomplishing the prevention and treatment of obesity[120].Moreover,RSV can improve mitochondrial biogenesis by activating AMPK/PGC-1α signal pathway to suppress obesity-induced skeletal muscle damage(Fig.3F)[121].From the above statement,it can conclude that RSV has a positive effect on the intervention of obesity,which may be closely related to the role of RSV in reducing fat content by directly participating in the regulation of mitochondrial function and quality,and mitigating peripheral insulin resistance.
5.7 RSV stimulates mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of arthritis
Arthritis is a joint-specific tissue inflammation,mainly manifested as redness,swelling,heat,pain,and joint deformity,which seriously affects the quality of life of patients.Increasing evidence has reported that nearly one-third of the elderly over 65 years old can be suffered by arthritis[122].Mitochondrial dysfunction is an important cause of arthritis and optimizing mitochondrial functional status is a key player for the prevention and treatment of arthritis[123-124].In rheumatoid arthritis cell MH7A,RSV can induce caspase-9/3 signal pathway by destroying MMP and promoting Cyt-C release,thus leading to apoptosis of rheumatoid cells[125].In addition,RSV can also reduce chondrocyte injury by inhibiting MMP depolarization,ATP depletion,and IL-1β-induced Cyt-C release[126].RSV treatment in fibroblastlike synoviocytes can induce autophagy,increase mtROS production,induce MMP abnormal activation of caspase-3/12 and Bax,and reduce Bcl-2,thereby triggering apoptosis (Fig.3G)[127-129].RSV has also shown to reduce mitochondrial membrane depolarization and improve chondrocyte function in ongoing osteoarthritis[126].Similarly,RSV can induce mitochondrial apoptosis by activating caspase-8 and then promoting BH3 interacting domain death agonis (Bid)cleavage[130].Therefore,RSV plays a potential dietary or therapeutic role in arthritis by enhancing mitochondrial quality and function.
5.8 RSV optimizes inhibition of mitochondrial function for the prevention and treatment of cancers
As the second leading cause of human death,cancer is well known for its poor curability,easy invasion,and unlimited growth.Mitochondrial biogenesis and quality control can be activated in cancerous tissues,and optimizing mitochondrial function and quality may also become a therapeutic approach for cancers[36].Many scholars have confirmed RSV can target mitochondria to be beneficial for the prevention and treatment of cancers.RSV can inhibit the growth of cancer cells mainly by destroying mitochondrial function and inducing mitochondrial apoptosis of cancer cells.RSV could inhibit the growth of cancer cells by 80% and reduce the viability of cancer cells by 70%-90%,which is mainly due to triggering MMP abnormality and inducing the apoptosis of cancer cells through activating mitochondrial pathway[131].In prostate cancer cells,RSV induces apoptosis through disrupting MMP of cancer cells;however,it does not depend on the caspase pathway[132].On the other hand,in HT-29 cells,RSV induces apoptosis of cancer cells in a mitochondrial pathway-dependent manner[133],suggesting that RSV may induce cancer cell death through multiple pathways,as also confirmed in human lung adenocarcinoma cells (ASTC-a-1)[134].RSV can induce the apoptosis of various cancer cells by destroying mitochondrial function,thus presenting more obvious anti-cancer effects[135-137].Furthermore,the administration of RSV can inhibit cancer cell proliferation by suppressing mtDNA replication and respiratory function,increasing intracellular ROS and autophagy level[138],downregulating H-Ras,activating Akt,activating Bax[139]to induce cancer cell apoptosis.The addition of RSV to thyroid cancer cells (THJ-16T)has shown the growth arrest and oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial swelling[140].It could also destroy MMP balance by increasing intracellular Ca2+concentration,increasing MMP,and the subsequent release of Cyt-C to trigger apoptosis of cancer cells(Fig.3H)[141].However,RSV can alleviate the pain from bone cancer by activating AMPK to improve mitochondrial function,reducing Drp1 and inhibiting the decrease of MMP caused by tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)[142].In addition,RSV can also induce mitochondrial dysfunction by promoting miR-326 and inhibiting pyruvate kinase 2(PKM2) expression from accelerating the apoptosis of tumor cells[143].Therefore,RSV exhibits mitochondria-targeted destructiveness in the treatment of cancers,thereby inducing apoptosis to inhibit cancer growth and reproduction.

Fig.3 Molecular mechanisms of RSV for optimizing mitochondrial function in chronic diseases.(A) RSV inhibits ROS,activates autophagy,and increases mitochondrial complexes to reduce mitochondrial damage and alleviate AD.(B) RSV inhibits ROS and activates mitophagy and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α signal pathway to mitigate PD.(C) RSV activates AMPK/Mfn1 signal pathway,increases antioxidant substances and inhibits ROS generation,and inhibits apoptosis induced by LOX-1/Bax/mitochondria/Cyt-C/Caspase to ameliorate ischemic stroke.(D) RSV improves mitochondrial quality by activating PKA/LKB1/AMPK signal pathway,enhancing Mfn2 to optimize mitochondrial dynamics and activating mitophagy for suppressing skeletal muscle atrophy.(E) RSV alleviates cardiovascular diseases by activating SIRT1/3/PGC-1α/Mfn2/Parkin signal pathway,inducing mitophagy,increasing DJ-1/COX I and inhibiting ROS production to enhance mitochondrial function.(F) RSV induces the browning of white fat by activating SIRT1/ PGC-1α signal pathway to improve mitochondrial function.(G) RSV promotes endogenous mitochondrial apoptosis in rheumatoid cells,inhibits Cyt-C release in chondrocytes to alleviate arthritis.(H) RSV disrupts mitochondrial dynamics and MMP to induce the release of Cyt-C,increase ROS production and trigger apoptosis in cancer cells.
6.Opportunities and challenges of RSV targeting mitochondria in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases
RSV plays an active role in preventing and treating diseases by optimizing mitochondrial function and quality through regulating corresponding signal pathways or mitochondrial targets (Table 1),but some studies do not show corresponding positive effects,which may be due to different intervention individuals,disease models,and RSV administration dosages,thereby reflecting its limited stability.RSV also has specific drug toxicity,such as inducing DNA breakage,increasing ROS,and inhibiting the activity of COX-I/II[144].Although human body has certain absorbing capacity of RSV,multiple factors have always restricted its pharmacological efficacy.Similarly,although currently used nanocarriers[145]can better deliver RSV to tissues and organs for preventing its degradation,future studies in the human body with more precise guidance are still needed to explored to target corresponding tissues and organs.RSV plays a vital role in the body by targeting mitochondria;however,how to target mitochondria through circulation system has become a current technical difficulty.Therefore,it is encouraging that future studies should focus on applications of RSV combined with other drugs,natural products,and exercise,and the development of RSV analogs to reduce its shortcomings in the body.For example,the combination of RSV and curcumin is more effective than RSV alone in the prevention and treatment of lung cancer,through targeting aging mitochondria and inducing apoptosis of cancer cells[146].The combination of marine products and RSV also can enhance the endogenous apoptosis of human liver cancer HepG2 cells induced by the destruction of MMP[147].The RSV analog HS-1793 has also shown to improve mitochondrial function,attenuate the heart from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury[148]and strengthen a positive proapoptotic effect in prostate cancer cells[149].Therefore,RSV targeting mitochondria and optimizing corresponding function and quality may become an important breakthrough in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases in the future.What must be paid attention to is how resveratrol recognizes harmful tissues and cells in the body,such as rheumatoid cells,chondrocytes,cancer cells,and normal cells;however,many technical barriers and unclear molecular mechanisms still need to be further explored and clarified.
7.Conclusion
The pathogenesis of various chronic diseases may differ,but mitochondrial dysfunction has become a common feature of these chronic diseases.Based on increasing mechanistic exploration of RSV for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases,mitochondria have confirmed as the critical target of RSV through regulating mitochondrial dynamics,mitophagy,endogenous mitochondrial apoptosis,oxidative stress,mitochondrial membrane homeostasis,and respiratory chain function and mitochondrial quality control to execute the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases,as shown in the updated evidence from medicine,nutrition and food fields.Even though RSV has disadvantages such as poor utilization in human disease intervention,further exploration of RSV analogs,targeted delivery,and combined application of exercise,diets and other drugs may be a more promising direction for the functional effects of RSV as functional foods or novel drugs in the future.Moreover,further screening of target genes,microRNAs and proteins associated with optimizing mitochondrial function and quality during RSV intervention is worthwhile,which will contribute to more benefits to the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases in precision targeting and optimizing mitochondrial function and quality through in the manner of functional foods or novel target drugs.
Conflict of interest
Ning Chen is an associate editor forFood Science and Human Wellnessand was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article.All authors declare that there are no competing interests.The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.32071176),the 14thFive-Year-Plan Advantageous and Characteristic Disciplines (Groups) of Colleges and Universities in Hubei Province for Exercise and Brain Science from Hubei Provincial Department of Education and the Chutian Scholar Program and Innovative Start-Up Foundation from Wuhan Sports University to Ning Chen.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Protective effects of oleic acid and polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil on cardiovascular diseases
- Diet and physical activity inf luence the composition of gut microbiota,benef it on Alzheimer’s disease
- Inf luence of nitrogen status on fermentation performances ofnon-Saccharomyces yeasts: a review
- Ganoderma lucidum: a comprehensive review of phytochemistry,eff icacy,safety and clinical study
- Demonstration of safety characteristics and effects on gut microbiota of Lactobacillus gasseri HMV18
- Cyanidin-3-glucoside protects the photooxidative damage of retinal pigment epithelium cells by regulating sphingolipid signaling and inhibiting MAPK pathway

