The modulatory effect of oolong tea polyphenols on intestinal f lora and hypothalamus gene expression in a circadian rhythm disturbance mouse model
Ruonn Yn,Chi-Tng Ho,Ynn Liu,Shengnn Zhn,Zufng Wu,Xin Zhng,
a Department of Food Science and Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
b Department of Food Science, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey 08901, USA
Keywords: Gut microbiota Circadian rhythm Oolong tea polyphenols Single-cell sequencing Metabolism
ABSTRACT The interaction between host circadian rhythm and gut microbes through the gut-brain axis provides new clues for tea polyphenols to improve host health.Our present research showed that oolong tea polyphenols (OTP)improved the structural disorder of the intestinal f lora caused by continuous darkness,thereby modulating the production of metabolites related to pyruvate metabolism,glycolysis/gluconeogenesis,and tryptophan metabolism to alleviate the steady-state imbalance.After fecal microbiota transplantation from the OTP group,the single-cell transcriptomic analysis revealed that OTP signif icantly increased the number of hypothalamus cell clusters,up-regulated the number of astrocytes and f ibroblasts,and enhanced the expression of circadian rhythm genes Cry2,Per3,Bhlhe41, Nr1d1, Nr1d2,Dbp and Rorb in hypothalamic cells.Our results conf irmed that OTP can actively improve the intestinal environmental state as well as internal/peripheral circadian rhythm disorders and cognitive impairment,with potential prebiotic functional characteristics to notably contribute to host health.
1.Introduction
The circadian rhythm is an indispensable and important factor in the host’s life cycle,which enables the host metabolism regularly within 24 h[1].The mammalian circadian clock system consists of a master clock located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus and a peripheral clock composed of organs such as the intestine,liver,and heart,etc.Through them,the metabolism of the host was synchronized with the light-dark cycle[2].Interestingly,the biological clock can improve the learning ability which depended on the hippocampus and exert a powerful influence on cognitive function[3].Disturbance of circadian rhythm is usually accompanied by sleep disturbance,which was one of the main health problems nowadays[4].Studies using animals with knock-out specific clock genes in the system or tissue have shown that changes in the circadian rhythm can lead to abnormal metabolic phenotypes,including obesity,dyslipidemia,impaired insulin secretion,etc.[5].
In mammals,host cellular and behavioral processes showed 24 h circadian oscillations synchronized with the external light/dark cycle.The gut microbiota also has circadian rhythm fluctuations,and the host circadian rhythm disturbance could affect the composition and function of the intestinal microbiota[6].The gut microbiota was a complex micro-ecological environment,with trillions of microbes inhabiting the intestines of adults[7].From a genetic point of view,more than 99% of human genes were microbial genes[8].Recent research found that the loss or variation of the gut microbiota may affect neurogenesis and blood-brain barrier functions,as well as the host’s cognitive function,learning ability,and emotion[9],which were partly similar to the harmful effects caused by circadian rhythm disorders.Most of the gut microbiota coexists with intestinal epithelial cells.It also acted a major role in food intake and metabolism,maintaining the intestinal barrier and the structure and function of the gastrointestinal tract[10].
Tea polyphenols can improve memory impairment caused by rhythm disorders through mechanisms related to the biological clock[11].Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the most abundant active ingredient in tea polyphenols.As theO-methylated form of EGCG,(-)-epigallocatechin 3-O-(3-O-methyl) gallate (EGCG3’’Me),which was rich in oolong tea polyphenols (OTP) indicated a potential activity similar to prebiotics[12].OTP not only modulate the composition of the intestinal flora,but also have a positive regulatory effect on the key circadian rhythm genes in the liver[13].Due to the low bioavailability,most OTP were metabolized by the intestinal flora into metabolic derivatives in the colon to exert biologically active functions[14].Active metabolites can act as an intermediary between the intestine and the brain to participate in the modulation of host circadian rhythm disorders[15],but the relationship among intestinal metabolites,intestinal microbiota and rhythm genes is still unclear.Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has recently been used to understand the development and interaction of heterogeneous cells,and to detect the expression and transcription subtypes of a large number of genes throughout the genome[16].This allows us to fairly evaluate multiple different cells and genes in the hypothalamus at the single-cell level,to better explore the link between the gut and the hypothalamus.
In this study,a mouse model of circadian rhythm disturbance was established to investigate OTP-mediated changes in intestinal microbiota,metabolites,and clock genes.Subsequently,the feces of OTP ingested mice were transplanted,and the effects of OTP intervention on mice with circadian rhythm disorders were characterized internally and externally through maze behavior experiment and hypothalamus scRNA-seq.Through fecal microbiota transplantation,a comprehensive analysis of the role of OTP in the internal and external circadian clock may provide valuable theoretical support for revealing that OTP can improve circadian rhythm disturbance via the GBA.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Chemicals and reagents
Oolong tea was produced in Baifeng tea garden,Beilun District,Ningbo City,Zhejiang Province.Polyamide resin was purchased from Ocean Chemical Co.,Ltd.(Qingdao,China).Sterile male mice C57BL/6J were purchased from Hunan Slack Experimental Animal Co.,Ltd.Ordinary animal feed is provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Ningbo University.
2.2 Preparation of OTP
Briefly,we took the tea powder and add distilled water,and place it at 96 °C for 40 min.The extract was centrifuged at 4 500 ×gfor 15 min.According to the method we previously reported,the residue is dissolved,sorted and purified through a polyamide column[17].The eluate was analyzed using high performance liquid chromatography,then collect,concentrate,load on the polyamide column and process the required fractions as described above.The components containing OTP were concentrated and freeze-dried through a freeze-drying system to obtain finished products.
2.3 Animals and experimental design
Animal studies were carried out in the Centre for Laboratory Animals,Ningbo University (Permission No.SYXK [Zhejiang] 2013-0191).All the animal-related operations were strictly in compliance with the relevant laws and regulations on the use and care of laboratory animals in China.All mice were individually placed in a sterile barrier environment with a room temperature of 22.30 °C and a humidity of 55.50%.Adapt to the environment for 7 days under a 12 h light-dark cycle period (ZT0=6 am,lights on;ZT12=6 pm,lights off).7 days later,they were randomly divided into 4 groups(18 animals in each group),namely CT group,CD group,VF group and OTP group.The CT group continued to grow in a 12 h light-dark cycle environment,the CD and VF group was placed in a completely dark environment,and the OTP group was placed in a completely dark environment and fed with 0.10% (m/m) OTP once a day[18].At the same time,the CT,CD and VF group were given the same amount of sterile water per day.The body weight,water and food consumption of CT,CD,OTP and VF group were recorded every week.After 4 weeks of continuous administration,laparotomy was conducted on 3 mice of CT,CD and OTP group under pentobarbital anesthesia every 12 h over 48 h,which can be divided into 5 groups according to time points and fresh feces were collected respectively for intestinal microbiota analysis.The contents of the cecum were collected immediately after euthanasia for analysis of differential metabolites.
After sampling,the intestinal flora of the remaining 3 mice in the OTP group was transplanted into the mice in the VF group for subsequent verification tests.Briefly,fresh fecal samples from the OTP group collected as above mentioned were mixed with sterile saline and centrifuged at 3 000 ×gfor 5 min.The supernatant was collected and homogenized into 400 mg/mL faecal liquid and gavage once a day 0.20 mL last 1 week[19].The remaining mice in the CT and CD groups group were given the same amount of sterile water per day continue to be cultured for 4 weeks until the 8thweek under the original culture conditions.After 8 weeks,behavioral tests were performed,the anesthesia procedure was repeated,the mice were euthanized,and the hypothalamus was removed.
2.4 Animal behavioral tests
Five mice in each group were randomly selected for Y maze test.After 1 h of dark adaptation,all mice were put into the center of the Y-maze device and explored freely in the Y-maze for 8 min.The correct rate of spontaneous alternation=[the number of correct spontaneous alternation/(total number of arm advance -2)] × 100%[20].
The Morris water maze (MWM) experiment was completed in a total of 6 days.5 mice in each group were randomly selected for the MWM test.Record the swimming time and trajectory of the mouse within 60 s in the quadrant where the original escape platform was located (quadrant II),and calculate the percentage of the mouse’s swimming time in the target quadrant.These data were measured by photoelectric sensors and analyzed using a video tracking system connected to a computer (SuperMaze software,Shenzhen Rayward Life Technology Co.Ltd,China).
2.5 DNA extractions and intestinal microbiota analysis
DNA extraction and high-throughput sequencing were performed based on the methods we reported earlier,and some of the procedures were modified appropriately[18].DNA was extracted using the E.Z.N.A.®Stool DNA Kit (D4015,Omega,Inc.,USA),and the total DNA was detected by PCR.The sequencing Library was built using Illumina’s (NEB,Ipswich,MA,USA) NEB Next Ultra DNA Library Prep Kit,its quality was evaluated using a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (Life Technologies,Carl Lsbad,CA,USA) and an Agilent BioAnalyzer 2100 system.Finally,sequencing was performed on Illumina MiSeq platform.
2.6 Metabolite extraction and metabolomics data processing
The ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) system(SCIEX,UK) was used for chromatographic separation.The reversedphase separation adopts ACQUITY UPLC T3 column (100 mm ×2.10 mm,1.80 mm,Waters,UK),the column temperature is 35 °C,and the mobile phase and flow rate refer to the recommendations of Want et al.[21].The eluted metabolites were detected using the TripleTOF 5600 Plus system (SCIEX,Warrington,UK).
2.7 Single-cell preparation and scRNA-seq
The hypothalamus of mice (0.20-0.90 g) was transferred from the cardioplegic solution into gentle MACS C-tubes (Miltenyi Biotec).Hypothalamus was minced using scissors (FST).Filtered and centrifugation and resuspended in a base solution containing 0.20% FBS (Gibco).Single cells were processed using Chromium Controller (10X Genomics) according to the manufacturer’s protocol,then prepared through a library preparation by LC Sciences.Postprocessing and quality control were carried out by 10X Cell Ranger package (v1.2.0;10X Genomics).The bioinformatics analysis of scRNA-seq was conducted by LC-bio (Hangzhou.China).
2.8 Bioinformatic analysis of scRNA-seq data
Bioinformatic analysis of scRNA-seq was conducted by LC-bio (Hangzhou,China),and the R package Seurat (version 3.0)with default parameters was used to further analyze the expressed genes.Clustering analysis was carried out with standard seurat package procedures with a resolution at 1.20.In order to identify unbiased cell types of sRNA-seq,we used single-cell transcriptomics R to annotate cell clusters and compared them with the immune genome project (reference mouse data set)[22].In order to further determine the enrichment process in clustering,we used Original Path Analysis (IPA) to analyze the enrichment pathway.The top gene ontology (GO) package in R (Bioconductor) was used for GO enrichment analysis,and the Clue GO plug-in of Cytoscape software was used for Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)pathway enrichment analysis.
2.9 Statistical analysis
The data obtained in this study were analyzed by SPSS (SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA,v 17.0.0).Comparison between groups was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with theposthocTukey test for multiple comparisons.P< 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Contents of tea catechins in OTP
In the present study,high purity (> 95%) of OTP was prepared(Table 1).Results indicated that the EGCG content was the highest,making it the main tea catechin,while the content of EGCG3’’Me was high.

Table 1 Contents of tea catechins in OTP.
3.2 Influence of OTP on body weight,food and water consumption of the mouse model
In Fig.S1a-c,after 4 weeks of OTP feeding,although the fractional body weight showed an increasing trend,it was slower than that of the CD group.The average body weight in OTP group was (23.88 ± 3.99) g,which was lower than the average of(25.77 ± 5.09) g in the CD group in the same period (P< 0.05).Eight weeks later,the average weight of the verification group (VF group)was (27.86 ± 5.17) g (P< 0.05).There was no significant difference in food and water intake during the feeding process among all groups(P> 0.05).
3.3 Influence of OTP on the cognitive ability of the mouse model
As shown in Fig.S2a,the total number of times of entering the maze arm of different groups of mice indicated no significant differences (P> 0.05).In Fig.S2b,the accuracy of spontaneous alternation of the arm in the CD group was (45.30 ± 1.60)%,which was prominently lower than that of (62.80 ± 2.30)% in the CT group (P< 0.05).After OTP intervention,the spontaneous alternation accuracy rate of mice in the OTP group increased to(60.40 ± 3.20)% (P< 0.05).
On the 6thday of the experiment,the escape latency to the platform for the first time was reduced to (17.50 ± 0.40) s in CD group which was prominently higher than that of the CT group((11.20 ± 0.16) s) and the OTP group ((14.30 ± 0.19) s) (P< 0.05)(Fig.S3a,b).This showed that the cognitive ability of the CD group has obvious defects compared to the CT group,the supplementation of OTP has improved this cognitive defect caused by the rhythm disorders.After the platform was removed,the swimming time percentages of the mice in the CT,CD and OTP group in the quadrant of the original platform were (37.00 ± 2.00)%,(24.00 ± 1.30)%,and(30.50 ± 1.60)%,respectively (P< 0.05) (Figs.S3c,d).It can be seen that the rhythm disorders have significantly reduced the percentage of mice’s swimming time in the target quadrant,while supplementing the OTP can increase the percentage of the swimming time of mice.The results all manifested that the OTP effectively relieves the ability of cognizance damage in mice with rhythm disorders.
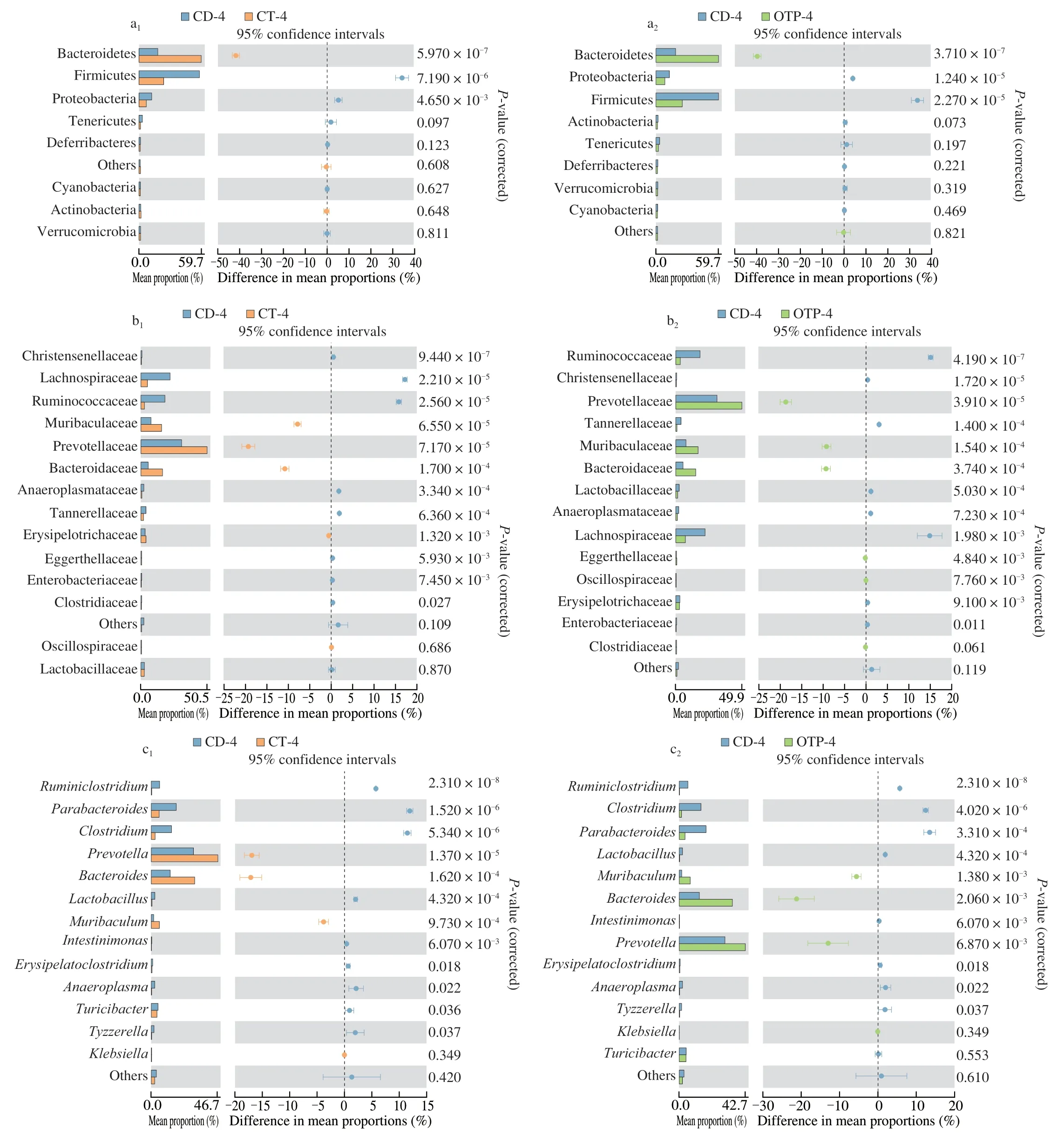
Fig.1 The relative abundance of intestinal flora at the phylum (a),family (b) and genus (c) from samples (the relative abundance of intestinal flora of each input sample was analyzed using STAMP).
3.4 Influence of OTP on the diversity and diurnal oscillation of intestinal microbiota of the mice model
As shown in Table 2,the Chao1 index of all groups showed an upward trend after 4 weeks,while the CD group was prominently lower than that of the CT group and OTP group (P< 0.05).At the 4thweek,both Shannon and Simpson indexes showed that the fecal microbial diversity of the OTP group was significantly higher than that of the CD group (P< 0.05).
Four weeks later of the intervention of OTP,the ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes (F/B) in CD group was decreased from 158.72% to 53.94%,which was similar to that in the CT group(50.18%) (Fig.1a).Fig.1b manifested that the relative abundance of Lactobacillaceae reached 33.33% in the CD group,which was notably reduced after OTP treatment (P< 0.05).At the genus level shown in Fig.1c,OTP treatment could significantly improve the decrease in the relative abundance ofPrevotellaandBacteroides(P< 0.05).
As shown in Fig.2a,the main intestinal flora at the phylum level of the CT group manifested obvious rhythmic changes,while the CD group of mice intestinal flora has no obvious regularity.And there is an opposite phenomenon in the oscillation mode of the CT group and the CD group.At the same time,the results showed that the intervention of OTP can modulate the rhythmless fluctuations of the mice model.For example,when we found that at ZT 24 and ZT 48,the abundance of Firmicutes in the CD group was at the highest peak,while the CT group reached the highest peak at ZT 12.The relative abundance of the CT group and the OTP group reached the highest peak at the ZT 24,which is notably higher than the relative abundance of the CD group.The relative abundance of the OTP group is considerably lower than the CD group (P< 0.05) at ZT 36,indicating that supplementary OTP can actively improve the disorders of intestinal flora caused by constant dark conditions.
The rhythmic oscillation of the intestinal flora at different conditions was analyzed and shown in Fig.2b.After OTP intervention,the oscillation ofPrevotella,BacteroidesandParabacteroidesin circadian rhythms disorder mice was closer to the oscillation of the CT group,and the obvious rhythmic oscillation was displayed,while the oscillation of the CD group exhibited a disturbed state.Prevotellahas increased trends during the day in the CT group and the OTP group,which showed a downward trend at night.And at ZT 12,the relative abundance of the CD group was prominently lower than the CT group and the OTP group.The relative abundance of theBacteroidesin the CT group and the OTP group was the highest at ZT 24,and the CD group is the highest at ZT 36.
3.5 Influence of OTP on metabolites of the mouse model
The close grouping of QC samples in the PCA score chart further confirms the high repeatability and stability of the entire test process(Fig.S4).In the human metabolome database superclass analysis,whether in positive ion mode (PIM) or negative ion mode (NIM),the most abundant metabolites belong to lipids and lipid molecules (Fig.3a).
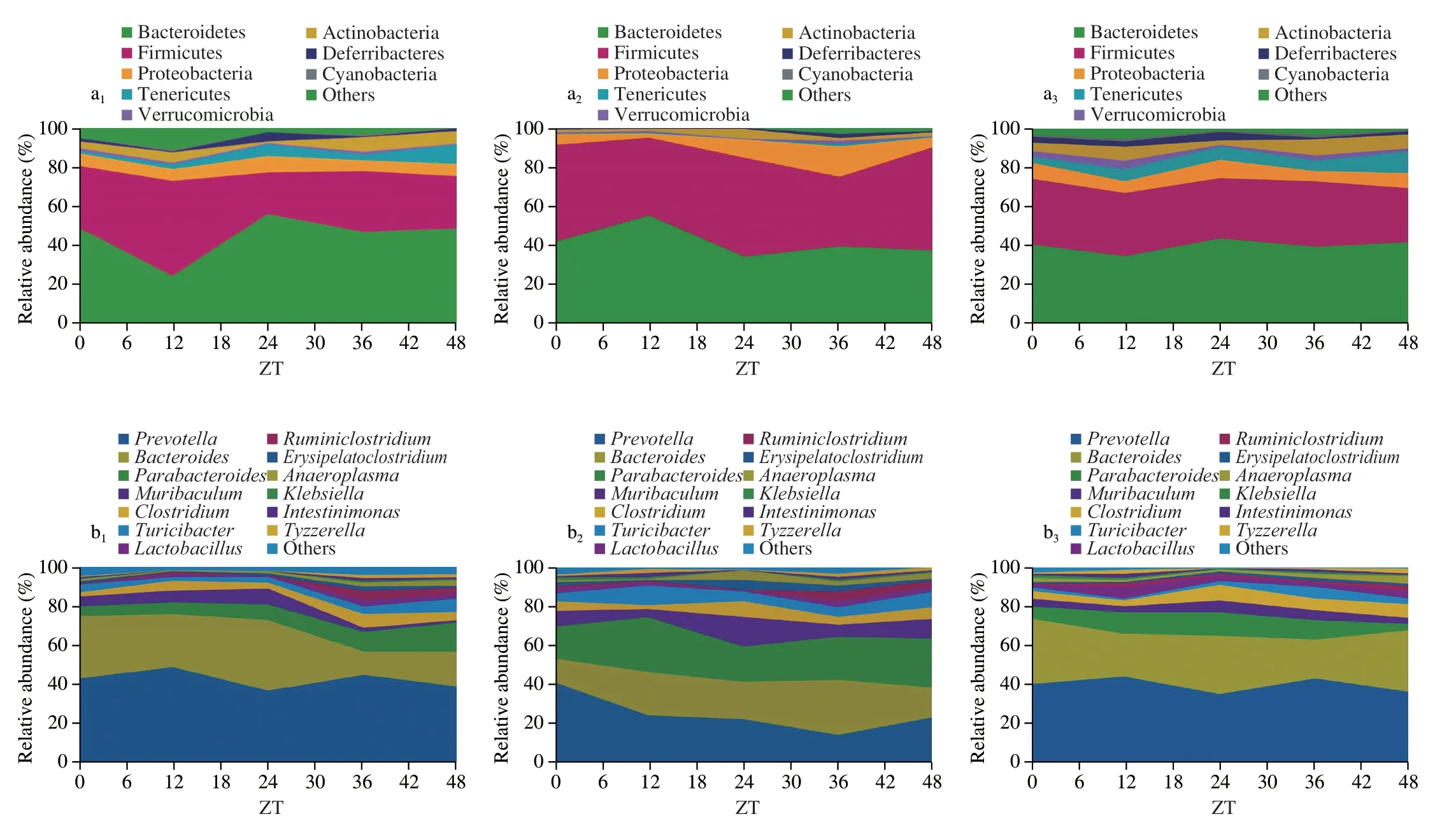
Fig.2 The variation in the diurnal oscillations of the representative bacteria at the phylum level (a) and the genus level (b).(1-3) CT,CD,OTP,respectively.

Fig.3 Effects of OTP on metabolomic changes in the circadian rhythm disorder mice model.(a) HMDB super class identification classification and annotation diagram of first-level metabolites;(b) volcano plots of the different metabolites in the OTP and CD groups;(c) heat map of significantly differential metabolites between the CD group and OTP group;(d) KEGG enrichment pathways of significantly down-regulated differential metabolites between the CD group and CT group;(e) KEGG enrichment pathways of significantly up-regulated differential metabolites between the CD group and OTP group.*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01.
The results of mass spectroscopy indicated that 104 significantly different secondary metabolites were obtained under PIM and NIM conditions (53 down-regulated metabolites,51 up-regulated metabolites) (Figs.3b-c).Isoleucyl-isoleucine,(R)-2-benzylsuccinate,4-isopropylbenzoic acid,2-phenoxyethanol,(-)-catechin which were the top 5 significantly different metabolites.Additionally,other metabolites associated with circadian rhythm and neuroprotection such as acetic acid,3,4-methylenesebacic acid,hydroxyphenyllactic acid,Tryptophan-Asparagine (Trp-Asn) and some other metabolites were also significantly up-regulated after OTP intervention.Inversely,the levels of carcinogens o-toluidine and acylcarnitine,which can cause neurological disorders,were found to be significantly reduced after OTP supplementation.
The pathways with significant differences in the enrichment of differential metabolites whose metabolite levels decreased considerably in CD group included “glycerophospholipid metabolism”,“tryptophan metabolism”,“arginine biosynthesis”,etc.(Fig.3d).After OTP intervened in mice living in constantly dark conditions,the identified differential metabolite enrichment pathways were “pyruvate metabolism”,“glycolysis/gluconeogenesis”,“glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism” and “tryptophan metabolism” (Fig.3e).Pyruvate metabolism was enriched to the highest degree,and the pathway mechanism involved was shown in the Fig.S5,from which it could be seen that acetic acid was significantly up-regulated after OTP intervention.
As shown in Fig.4a,the microbiota most relevant to the significantly different intestinal metabolites between the CD group and OTP group were Bacteroidetes,Acidobacteria,Patescibacteria and Firmicutes.The correlation between acetic acid,polyethylene oxidized,Gln-Ile,O-acetyl-L-carnitine and Bacteroidetes was extremely significant (P< 0.01).Interestingly,metabolites mentioned above were negatively correlated with Firmicutes,and their significance remained unchanged.The correlation network diagram of intestinal differential metabolites and intestinal flora in the CD and OTP groups was shown in Fig.4b.
3.6 Different cell clustering identified in the hypothalamus of the mouse model
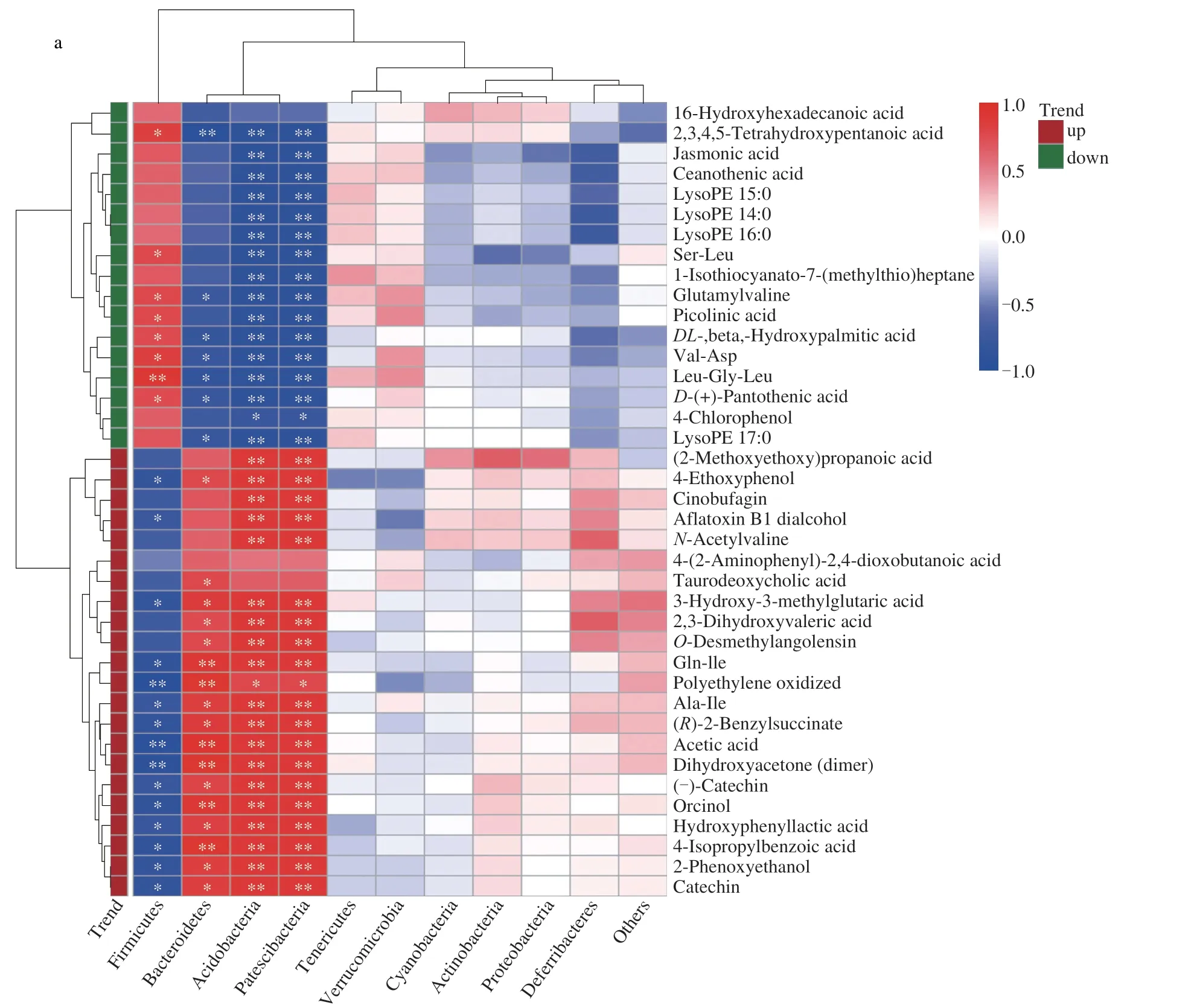
Fig.4 The correlation between intestinal microbiota and intestinal differential metabolites.(a) correlation heat map between intestinal differential metabolites and microbiota in CD and OTP groups in NIM;(b) network diagram of intestinal differential metabolites and microbiota.*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01.
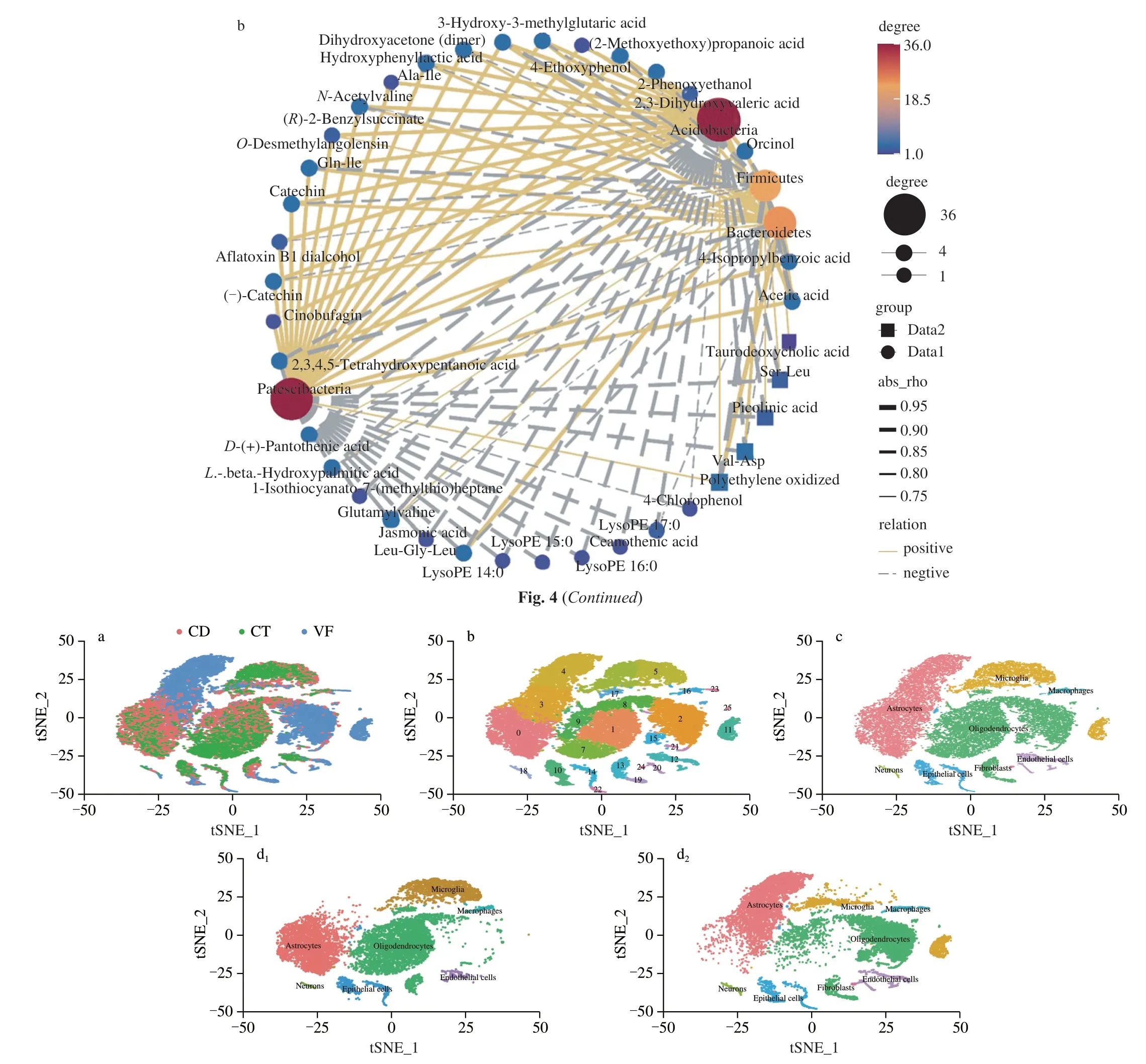
Fig.5 Effects of OTP on hypothalamic cell types in the mice model with rhythm disturbance.(a) t-SNE map of single cells of hypothalamus in three groups;(b) t-SNE images of total hypothalamic cells in different clusters;(c) t-SNE identification map of hypothalamic single-cell in the CT,CD and VF group of samples;(d) distribution of cells from the (d1) CD group and (d2) VF group across all cell types.
A total of 29 635 effective cells were detected,of which 14 114 cells belonged to the VF group,12 035 cells belonged to the CD group,3 486 cells belonged to the CT group.The results of different samples and subgroups of cells were shown in the Figs.5a-b,respectively.The proportion of cells in each cluster in the sample and the percentage of different sample cells in each cluster were shown in Fig.S6.The results manifested that there were 22 clusters in the CD group and 25 clusters in the VF group.
The highest corresponding cell type of each cluster was selected as the result of cell type identification of this cluster.The results of cell identification in the CT,CD and VF groups were shown in Fig.5c.As shown in Fig.5d,the main cell types identified by the CD and VF group included astrocytes,oligodendrocytes,microglia,macrophages,neurons,epithelial cells,endothelial cell,and fibroblast.Fibroblasts uniquely existed in the VF group,but not in the CD group.Cluster 15 and cluster 25 were identified as oligodendrocytes,which acted an indispensable role in neuron protection and development,and the number of cells in the VF group was notably higher than that in the CD group.In cluster 19,79.11% were identified as oligodendrocytes,16.00% were neurons,and 4.89% were astrocytes which were important parts of the central nervous system cells.
3.7 Circadian rhythm genes expression of each cell types in the hypothalamus
We selected a total of 16 co-expressed rhythmic genes from the top 8 major cell types,which were mainly core clock genes and genes involved in coding clock gene proteins.The expression levels of circadian genes in fibroblasts,epithelial cells,endothelial cell,neurons and astrocytes were relatively high (Fig.S7a).Moreover,the expression level in VF group was higher than that in CD group,especially the percent expressed ratio of rhythm genesCry2,Per3,Bhlhe41,Nr1d1,Nr1d2,Dbp,Rorbin each cell in the VF group (Fig.S7b).
In Fig.6a,it was found that the average expression of other rhythm genesClock,Bmal1,Cry1,Per2,Per3,Nr1d2,DbpandRorbin neurons of the VF group was also relatively high.The t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) map was used to cluster and identify the expression patterns of circadian rhythm genes in neurons of the CD and VF group,as shown in Figs.6b-c.The violin plot can clearly indicate the expression of circadian rhythm genes in each cell in the hypothalamus.Compared with the CD group,theClock,Cry2,Per3,Bhlhe41,Nr1d1,Nr1d2,Dbpand other genes related to the circadian rhythm in the VF group were better expressed in each cell (Fig.7a).As shown in Fig.7b,the top 3 cells with the expression levels of the core clock genesClockandBmal1were astrocytes,oligodendrocytes and epithelial cells in the CD group.
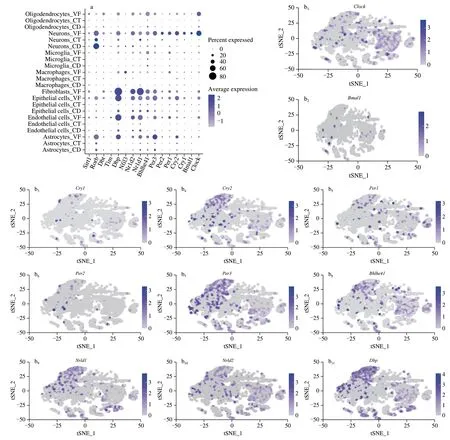
Fig.6 Effects of OTP on hypothalamic genes in the mice model with rhythm disturbance.(a) Dot plots of circadian rhythm genes expression level of specific cell in the three groups;(b) t-SNE map of the expression of rhythm genes in neurons in the VF group;(c) t-SNE map of the expression of rhythm genes in neurons in the CD group.
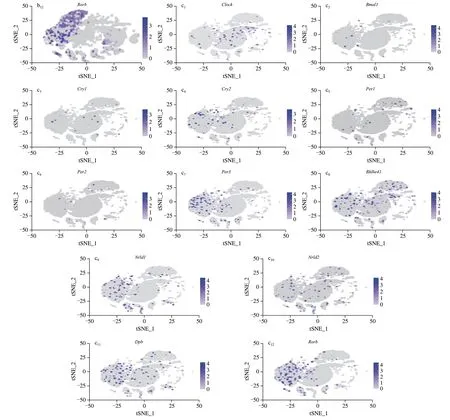
Fig.6 (Continued)
3.8 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in mice model hypothalamus
As shown in Fig.8a,GO analysis reflected the enrichment of DEGs from three modules of biological process,cell component and molecular function.The top 3 DEGs in the biological process field in the hypothalamus were mainly “positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II”,“multicellular organism development”and “signal transduction”.For cell components,the top 3 were cell membrane,cytoplasm and nucleus.Additionally,DEGs annotated to molecular functional modules mainly enriched GO items including protein binding,metal ion binding and nucleotide binding,etc.In order to better clarify the distribution of DEGs in each pathway,we used KEGG analysis to improve the results of DEGs enrichment pathway in mouse hypothalamus on the basis of GO annotation classification.The top 3 pathways with the highest degree of DEGs enrichment in CD group and VF group were “Proximal tubule bicarbonate reclamation”,“Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption” and “Ribosome”,respectively (Fig.8b).
4.Discussion

Fig.7 (Continued)
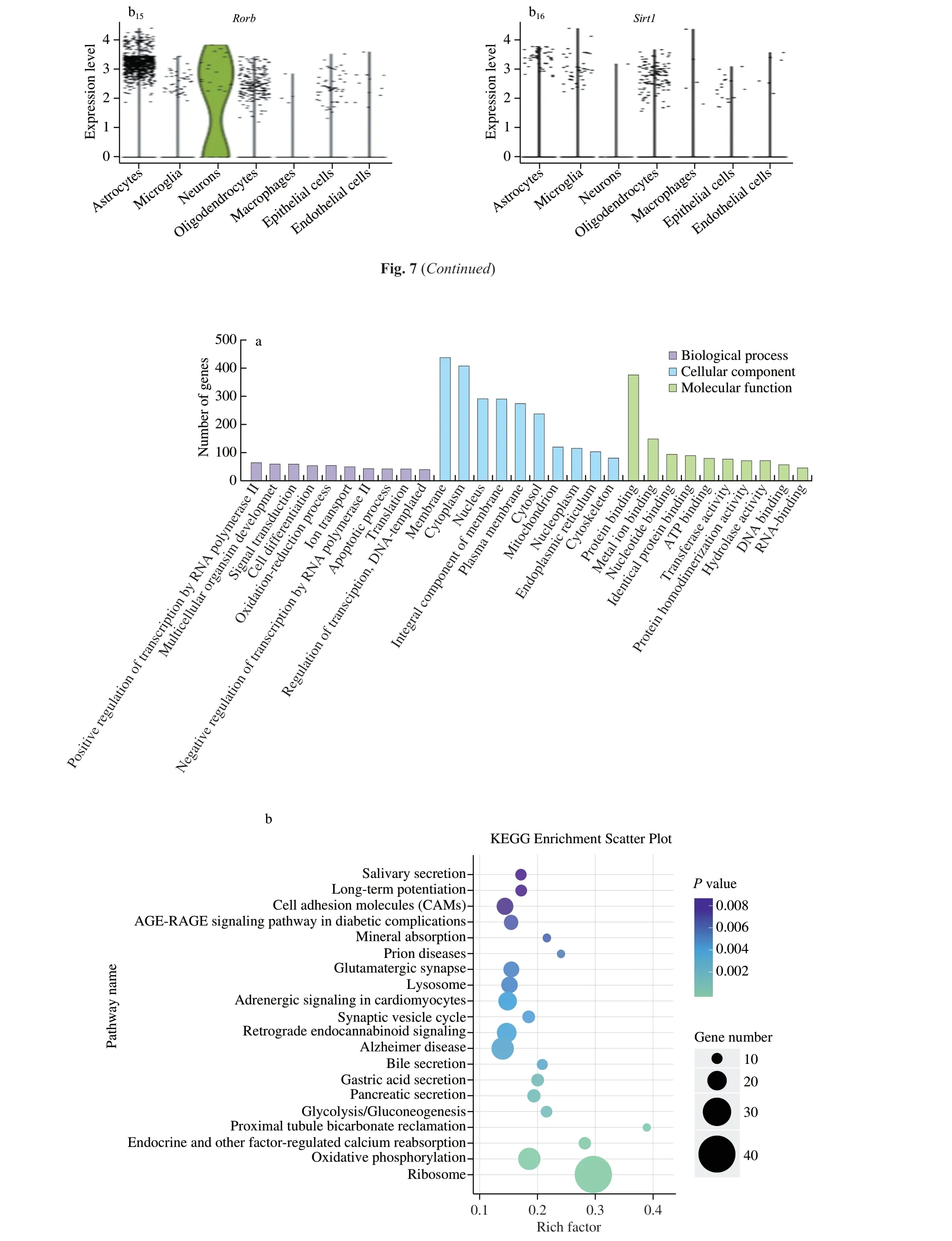
Fig.8 Influences of OTP on gene enrichment pathway in hypothalamus.(a) GO classification analysis in hypothalamus between the CD group and VF group;(b) KEGG pathway analysis between the CD group and VF group.
As a basic component of the living body,the circadian rhythm is an endogenous and guidable biological process[23].Each cell of the host contained an internal biological clock,which performed normal turnover via a series of rhythmic genes or molecular oscillations[24].Irregular lifestyle and diet or circadian rhythm disorders caused by long-term shift work may cause the host’s central-peripheral circadian clock disorder and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases,cognitive impairment and other metabolic diseases[25].The study by Thaiss et al.[26]found that transplanting the gut microbiota with jet lag into mice resulted in a significant increase in host fat.In our research,it was found that after transplanting the intestinal flora of mice supplemented with OTP into mice with circadian rhythm disorders,the weight of the mice increased extremely slowly and approached mice living in a normal environment.Research result showed that the intake of OTP can improve the negative effects of circadian rhythm disorders on weight.
The host’s circadian rhythm pattern can be measured by biological and behavioral indicators.The activity-rest cycle is the characteristic that we spend 24 h a day inducing physiological and cellular adaptation to various processes[27].In addition to having the extensive effects on physiology,the circadian rhythm also affects the host’s learning and memory abilities.Similar to the cognitive impairment of mice with circadian rhythm disorders observed in this experiment,study has shown that mice with disrupted circadian rhythm genes also indicated poor performance in various learning behavior tasks[28].Similarly,the disturbance of humans’ circadian rhythm can also lead to the decline of cognitive function.For example,flying across time zones for several years would increase the cognitive impairment of the host[29].After supplementary of OTP,the long-term cognitive learning impairment assessed in the Morris water maze and the short-term memory impairment in the Y-maze were reversed.This phenomenon was similar to the findings of Biasibetti et al.[30]that tea catechins can reduce oxidative stress in peripheral and brain tissues and inhibit behavioral changes related to cognitive deficits.
Previous study by others has indicated that disruptions in circadian rhythm led to variations in gut microbiota characterized by an increase in pro-inflammatory bacteria and a decrease in bacteria which produce anti-inflammatory short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)[31].In this study,we observed that the value of F/B was higher than that of normal mice in mice with circadian rhythm disorders.After OTP intervention,the ratio of F/B in the gut microbiota of mice with circadian rhythm disorders decreased,and Bacteroidetes increased significantly.Bacteroidetes are one of the most abundant phyla in the intestinal tract[13].Due to their diversity metabolic modes,Bacteroidetes can proliferate in the colon and rectum.They can decompose dietary fibers in the host food and mainly generate acetic acid,propionic acid and succinic acid which are beneficial to the host[7,9].Additionally,supplementation of OTP for 4 weeks also significantly increased the relative abundance of Muribaculaceae which belong to Bacteroidetes.The relatively high relative abundance of Muribaculaceae (previously named S24-7) was related to the extension of lifespan[32].Muribaculaceae has been also reported to contribute to the production of SCFAs[33].SCFAs were the main metabolites of the gut microbiota.As signal molecules,SCFAs can activate multiple pathways,such as activating AMP-activated protein kinase in peripheral tissues (such as liver and muscle) and cholesterol or lipids metabolism[34].Additionally,studies have shown that SCFAs may affect cognitive function and mood through a variety of mechanisms,included regulation of histone acetylation and methylation,promotion of secretion of various hormones and neurochemicals (such as serotonin),and induction of vagal nerve signals[35].It was observed that the relative abundance of acetate and butyrate-producing bacteria in mice supplemented with OTP presented an increasing trend in our research.
Metabolites can drive the relationship between the host and microbiota,and were considered to be cellular transmitters of circadian rhythms in various tissues[36].Microbial-derived SCFAs or lactate were found to regulate the phase of the host’s peripheral clockinvivo[37].Trp is a dietary essential amino acid,which can be directly metabolized in the gastrointestinal tract through the microbiota or serotonin pathway and transmit signals from the intestine to endogenous or exogenous neurons.The metabolism of tryptophan by the microbiota included the conversion of tryptophan to indole and its derivatives,of which 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA)is main metabolite[38].The enrichment pathways that significantly down-regulated differential metabolites in the CD group included tryptophan and glycerophospholipid metabolism.Study has shown that phospholipid compounds involved in glycerophospholipid metabolism participate in diseases such as atherosclerosis,vascular dementia,and spinal cord injury by activating the PPARγ pathway[39].Choline is a strong organic base that exists in sphingomyelin and can be used as a precursor of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine[40].The content of choline and 5-HIAA in mice that have lived in constant dark conditions for a long period has a downward trend which indicated that the disorder or destruction of the circadian rhythm may affect the synthesis and transport of neurotransmitters,etc.
The activity of TP depended largely on its conversion in the intestine.Due to the limited bioavailability of TP in the body,most TP exerted functional activities through their metabolic derivatives[12].The good relationship between intestinal flora and intestinal metabolites suggests that OTP helped the intestinal flora to repair the intestinal environment and promote the production of metabolites.In this study,OTP and its metabolites have shown various positive effects on metabolic disorders caused by circadian rhythm disorders.In the OTP group,the content of multiple metabolites that originally showed down in the CD group has now increased significantly after the intervention of OTP.Some representative metabolites were screened out,such as acetic acid,(-)-catechin,O-acetyl-Lcarnitine,2-indolecarboxylic acid,3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid,etc.The protein kinase C-related properties of catechins make it have a positive impact on the anti-neurodegenerative disease Alzheimer’s disease[41].The metabolic levels of various amino acids such as tryptophan,glutamine (Gln),alanine,and tyrosine(Tyr) were significantly increased after OTP supplementation.Metabolic syndrome and neurological features (prominently anxiety,depression,and autism),were mostly affected by the final product of tryptophan metabolism[38].2-Indolecarboxylic acid was one of the tryptophan pathways and has been found to be involved in immune regulation,inflammation and affect intestinal function[42].Gln can effectively enhance the function,proliferation and life cycle of small intestinal epithelial cells,and may indirectly support the optimal neuropsychological environment by protecting the intestinal wall from damage and chronic inflammation[43].In another study,after long-term supplementation of Gln,the ratio of F/B,a common indicator of obesity,was prominently reduced.An optimized intestinal microecological environment was more likely to perform neurotransmitter synthesis and other functions more effectively[44].Tyr was also a precursor of neurotransmitter formation,and the increase of Tyr can increase the level of neurotransmitters in the body[45].The supplementation of OTP can increase the level of Gln and Tyr.An optimized intestinal microecological environment was more likely to perform neurotransmitter synthesis and other functions more effectively.Abnormal “pyruvate metabolism”often leads to cancer,heart failure and neurodegenerative diseases.KEGG enrichment analysis of differential metabolites significantly up-regulated after OTP intervention presented that the degree of enrichment of “pyruvate metabolism” was the highest which can be explained that the intervention of OTP is beneficial to the reversal of these abnormal phenomena[46].
The liver and intestine were both typical peripheral clock models in the biological clock system.They were synchronized with the circadian rhythm of the central clock in the suprachiasmatic nucleus(SCN) and affected by meal time and dietary composition[47].The microbiota with circadian rhythm oscillations accounts for about 60%of the gut microbiota[26].In this study,compared with the microbial population that normally undergoes the light-dark cycle,constant darkness changed the oscillation of some microbes,and this situation can be prominently alleviated by supplementing OTP.KEGG analysis presented that DEGs obviously have the highest levels in “protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum”,“endocytosis”,and “MAPK signaling pathway” after OTP supplementation.It can be seen that after OTP interferes with mice with circadian rhythm disorders,cell transcription and translation activities become active,and can regulate circadian rhythm disorders by participating in the formation of proteins.
Circadian rhythm can be found at the intracellular level and is coordinated by the SCN master clock located in the hypothalamus[48].Patients with different degrees of Alzheimer’s disease were considered to have circadian rhythm disorders,which were specifically manifested as delayed attenuation of amplitude and phase[49].Circadian rhythms influence host metabolic homeostasis by regulating various metabolic processes,including protein synthesis and secretion,glucose,lipid and energy metabolism,and DNA damage repair[6].For example,the clock geneBmal1can act directly on genes encoding rate-limiting enzymes such as long-chain fatty acid extensae and triacylglycerol hydrolase[50].GeneClockplays a crucial role in regulating lipid absorption,biosynthesis and decomposition[51].The lack or disorder of clock gene expression in astrocytes can lead to neuroinflammation which was the main manifestation factor of neurodegeneration[3].For instance,the absence ofBmal1in the mouse brain disrupted the function of the biological clock and also caused the degeneration of the synapses of astrocytes[52].Astrocytes can selectively remove synapses,fine-tune and reshape the brain’s neural circuits during host learning,memory and exercise[48].It has been confirmed that transplantation of human astrocytes into newborn mice can enhance the memory and learning ability of mice[38].It has been confirmed that transplantation of human astrocytes into newborn mice can enhance the memory and learning ability of mice[53].Oligodendrocytes provided metabolic support and nerve repair functions for neurons and axons,which were thought to be related to some mental diseases[54].Neurons have always been considered a crucial part of SCN.The latest research shows that neurons cannot only participate in the regulation of clock gene expression and maintain circadian rhythmic oscillations to coordinate the biological clocks of tissues and organs throughout the body,but also have the ability to autonomously encode circadian rhythms,so as able to initiate and maintain biological rhythmic activities and behaviors[55].Among the 8 hypothalamic cell types identified in this study,we revealed that fibroblasts only exist in the VF group,and the number of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes was up-regulated.Rhythmic genes such asClock,Cry2,Per3,Bhlhe41,Nr1d1,Nr1d2,Dbp,etc.indicated better expression after OTP intervention.Notably,the expression percentage and the average expression level of the rhythm geneClockin the VF group neurons were both the highest.All support the perspective that OTP can improve the negative effects of circadian rhythm disorders by increasing the number of cells and gene expression associated with the circadian rhythms.
5.Conclusion
In this study,the intervention of OTP reduced the ratio of F/B,the diurnal oscillation of the intestinal microbiota tended to be regular,and the intestinal microecological status was also better than that in the CD environment.OTP ameliorated the dysbiosis caused by continuous darkness,and increased the content of important metabolites such as Trp,Gln,Thr,Pro,alanine and 2-indolecarboxylic acid.In addition,scRNA-seq showed OTP significantly increased the number of hypothalamus cell clusters,up-regulated the number of astrocytes and fibroblasts,and enhanced the expression of circadian rhythm genesCry2,Per3,Bhlhe41,Nr1d1,Nr1d2,DbpandRorbin hypothalamic cells.Our results indicated that OTP can improve the metabolic imbalance caused by the circadian rhythm disorder,maintain the host’s homeostasis and make the contribution to improvements in health.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by the Ningbo Natural Science Foundation (2021J107).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at http://doi.org/10.26599/FSHW.2022.9250064.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Protective effects of oleic acid and polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil on cardiovascular diseases
- Diet and physical activity inf luence the composition of gut microbiota,benef it on Alzheimer’s disease
- Inf luence of nitrogen status on fermentation performances ofnon-Saccharomyces yeasts: a review
- Ganoderma lucidum: a comprehensive review of phytochemistry,eff icacy,safety and clinical study
- Resveratrol combats chronic diseases through enhancing mitochondrial quality
- Demonstration of safety characteristics and effects on gut microbiota of Lactobacillus gasseri HMV18

