超声检查视神经鞘直径预测颅内压增高的研究进展及其临床意义
王丽娟,陈盈,邢英琦
颅内压(intracranial pressure,ICP)增高是神经科常见的临床病理综合征,也是导致病情恶化、预后不良或死亡的最常见原因之一。引起ICP增高的常见病因有:脑血管疾病、颅内炎症、颅脑损伤、颅内占位性病变等。尤其大量颅内出血或大面积脑梗死的患者,常常伴有高颅压,此时病情严重者可出现脑疝,危及生命[1]。所以早期诊断至关重要。
有创性ICP监测目前仍然是评估ICP的“金标准”。然而,这项检查费用昂贵,有多种禁忌证及并发症,可导致出血、感染等。故有创性ICP监测在临床上未能得到广泛应用。故临床急需无创性ICP检测技术来有效地帮助医生早期、快速地筛查ICP增高的患者。随着超声技术的发展,这项无创、床旁、快捷、低廉的检查技术得到了广泛的应用。如今,运用超声技术检测视神经鞘直径(optic nerve sheath diameter,ONSD)又为早期有效诊断ICP增高提供了依据,在国外的临床工作中为患者及医生提供了莫大的帮助[2]。本文将对超声测量ONSD相关结构在早期诊断ICP增高中的应用做一综述。
1 视神经及其周围相关结构的解剖
视神经是胚胎发生时间脑向外突出形成视器过程中的一部分,故视神经外面包绕着由三层脑膜延续而来的三层被膜,脑蛛网膜下腔也随之延续到视神经周围。视神经鞘是硬脑膜的延续,内有横梁式的蛛网膜下腔[3](图1)。
在视神经鞘内的蛛网膜下腔里内包含了脑脊液以及由小梁、间隔和支柱组成的复杂结构。视神经的蛛网膜下腔与颅内的蛛网膜下腔内的脑脊液是自由相通的。当ICP增高时颅内充盈的脑脊液通过视神经管进入视神经蛛网膜下腔,使得视神经鞘内间隙扩张,即理论上讲视神经鞘内间隙的扩大与ICP增高呈时相一致性[3]。以上述的解剖特点为基础,学者们通过多个实验证实上述理论的真实性。有些学者通过动物模型,新鲜的人类尸体标本以及人类视神经鞘离体实验,均发现ICP增高导致ONSD扩张[4-6]。这些现象证实了视神经及其周围组织特殊的解剖结构,同时也提示了视神经鞘本身可能具有弹性而允许在ICP增高时视神经鞘能够迅速地扩张。
2 超声测量ONSD的临床研究进展
早在1968年,Hayreh提出视神经鞘内的蛛网膜下腔与颅内蛛网膜下腔的脑脊液压力一致[7]。随着A型超声及B型超声的问世,学者们可以通过超声技术识别视神经及其周围组织,现代高频率转换器使得上述结构能够更清晰地显示。Galetta等人发现超声技术可以检测到ICP增高的患者ONSD增粗[8]。随后,Hansen通过腰椎穿刺注入或抽出液体来改变ICP,发现ONSD的扩张与ICP增高有明确的相关性[9]。随后有研究将此项技术运用于临床,选择眼球后3 mm的位置测量ONSD(图2),得出ONSD与ICP有相关性,相关系数为0.46~0.74[10-15],认为ONSD增粗是ICP增高早期的敏感指标[16-17]。国内相关领域的研究较国外少,但是近几年也有研究报道超声测量ONSD可以有效诊断我国高ICP患者[18-22]。
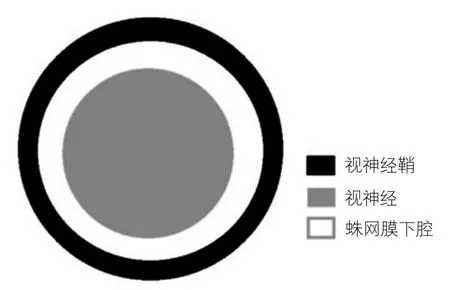
图1 视神经及其周围组织横断面示意图(作者原创)
3 超声检测ONSD评估ICP增高的临界值
西方国家在该领域的研究较多,不同研究得出的临界值有些差别,多数研究结果显示评估ICP增高的ONSD的临界值为5.0~5.9 mm[14,23-25]。表1总结了几项较具有国际影响力的研究结果[10-15,22,26-27]。国外研究多推荐ONSD>5 mm作为诊断高ICP的标准[28-29]。国内此领域的研究相对较少,仅有几项研究针对颅脑损伤患者进行了ONSD超声检测。张锐等[21]对35例颅脑损伤患者进行研究,得出5 mm为ONSD诊断ICP增高的最佳临界值。黎君彦等[30]运用计算机断层扫描(computed tomography,CT)影像及临床表现为标准对ICP进行计分,得出诊断ICP增高患者的ONSD临界值为5.3 mm。

图2 ONSD测量[22]
但是近几年国外有研究提出临界值应稍低于5.0 mm[10,27,31]。有研究证实当ICP升至13 mmHg时ONSD就已经出现扩张[32],当ICP超过15 mmHg时,4.5 mm作为ONSD临界值时敏感性及特异度较高[33]。王丽娟等对我国279例可疑高ICP患者进行了研究,每例患者均在发病早期进行了腰椎穿刺测量脑脊液压力值作为对照,结果显示早期诊断ICP增高的ONSD最佳临界值是4.1 mm[22]。此外国外有研究证实当ICP升高至20 mmHg时已经进入临床必须给予降ICP治疗的时期,此时ONSD已经扩张至5.2~5.9 mm[12,14,26]。可见在ICP增高早期时ONSD已经开始扩张,待ONSD扩张到5 mm甚至5.9 mm时,患者已进入急需降颅压治疗的阶段,此时脑容量极少的增加即可造成ICP急剧上升。而且既往的研究是多针对病情较严重需要在重症监护室治疗的患者,此时测得ONSD已经极度扩张,并且有研究表明重症监护、镇静或机械通气都有可能会影响ONSD的改变[34],上述原因均可导致研究结果中求得评估高ICP的ONSD诊断值变大。由于高ICP容易导致重要的不良预后及死亡,所以临床更需要的是早期发现ICP增高,即敏感度更高的诊断值。如果能够在早期发现ICP增高,就可以及时预防及纠正ICP继续增高。
此外有研究结果显示成人正常的ONSD明显小于5 mm。Ballantyne等[35]报道英国正常成人ONSD的平均值为3.2~3.6 mm。Soldatos等[13]发现希腊正常成人ONSD平均值为(3.6±0.6)mm。国内也有相关的报道,李臻等学者[18]对82例成人视神经鞘的横断面进行测量,得出ONSD的均值为(4.06±0.58)mm。王丽娟等对230例健康受试者的ONSD均进行了矢状位和横断面的测量,得出ONSD平均值为(3.4580±0.2767)mm[36]。可见到目前为止,ONSD正常值范围以及ICP增高患者ONSD的诊断值尚无明确的统一标准,未来还需要我们进行多中心大样本量的研究。
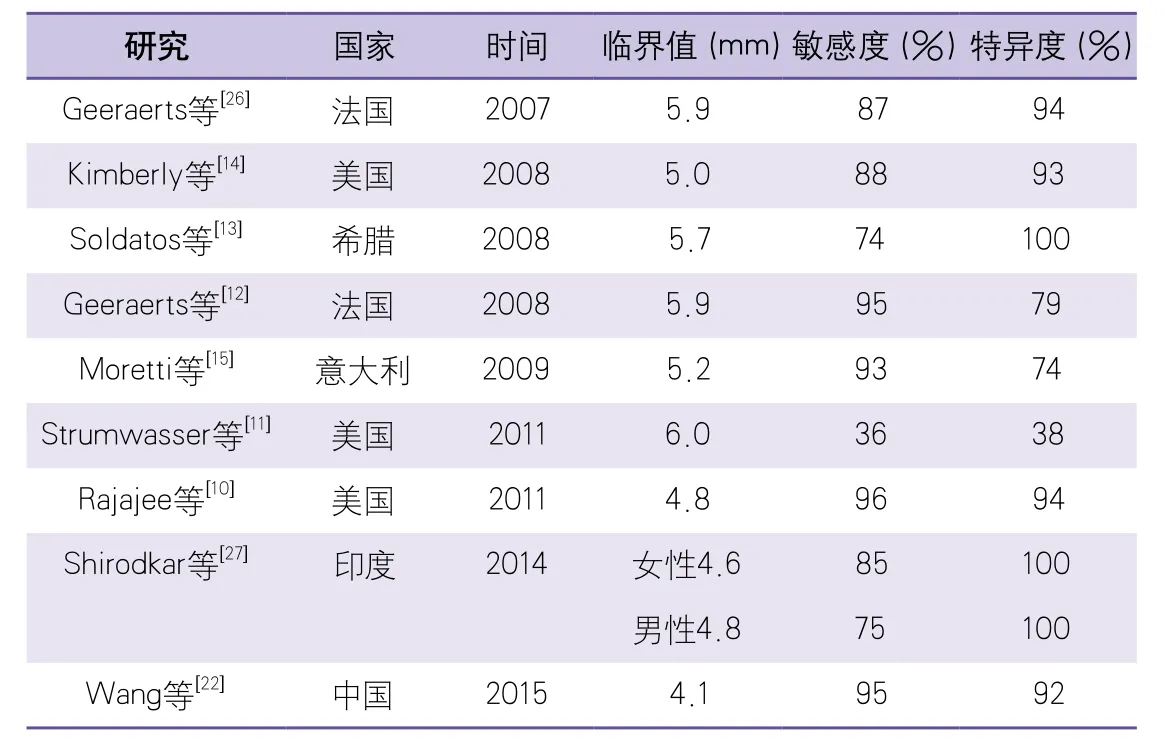
表1 评估ICP增高的ONSD最佳临界值
4 超声检测ONSD评估ICP增高的优点
超声检测ONSD评估ICP增高技术无创、简便、低廉,且可床旁进行检测。有研究证实此项技术不同观察者间的差异很小[34]。超声检测ONSD与磁共振成像[37]及CT[38]的测量值有较高的一致性,可以作为评估ICP增高首选的无创性筛查技术来初步评估患者ICP。并且ONSD的超声检测还可以动态观察ICP增高的变化,既可对患者的颅内压进行实时评估[39],又对临床治疗起到了重要的指导意义。超声成像技术已在各级医院及医疗机构、甚至社区健康中心普及。超声检测ONSD简单易学,操作者间的差异小,上述优点都使超声检查ONSD评估ICP增高能够被广泛地运用及推广,其可以作为评估ICP增高常用及首选的无创性检查,可以在患者入院之前或刚入院时进行此快捷无创的筛查,用以初步评估患者颅内压情况,提示临床医师,并为是否需要将患者转运至上级医院或患者是否需要有创性颅内压监测提供有效的指导作用。
5 超声检测ONSD未来的发展方向
运用超声检测ONSD评估ICP增高已在国外的医疗界得到了广泛的关注及推广。近期有研究报道ONSD可动态观察ICP增高的变化,了解高ICP的治疗效果,指导临床用药[40],在外科手术中此项技术可以帮助医生了解ICP的变化[41]。甚至有研究还证实ONSD可以预测患者的不良预后[42],未来我们还希望运用此项技术可以对卒中患者,例如出血或梗死患者的不良预后进行预测,可见超声ONSD具有广阔的研究前景,需要进行更深入的研究。
1 吴江. 神经病学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:385.
2 Irazuzta JE,Brown ME,Akhtar J. Bedside optic nerve sheath diameter assessment in the identification of increased intracranial pressure in suspected idiopathic intracranial hypertension[J].Pediatr Neurol,2016,54:35-38.
3 Killer HE. Architecture of arachnoid trabeculae,pillars,and septa in the subarachnoid space of the human optic nerve:anatomy and clinical considerations[J]. Br J Ophthalmol,2003,87:777-781.
4 Liu D,Kahn M. Measurement and relationship of subarachnoid pressure of the optic nerve to intracranial pressures in fresh cadavers[J]. Am J Ophthalmol,1993,116:548-556.
5 Hansen HC,Lagreze W,Krueger O,et al. Dependence of the optic nerve sheath diameter on acutely applied subarachnoidal pressure--an experimental ultrasound study[J]. Acta Ophthalmol,2011,89:528-532.
6 Helmke K,Hansen H. Fundamentals of transorbital sonographic evaluation of optic nerve sheath expansion under intracranial hypertension[J]. Pediatr Radiol,1996,26:701-705.
7 Hayreh SS. Pathogenesis of oedema of the optic disc[J]. Doc Ophthalmol,1968,24:289-411.
8 Galetta S,Byrne SF,Smith JL. Echographic correlation of optic nerve sheath size and cerebrospinal fluid pressure[J]. J Clin Neuroophthalmol,1989,9:79-82.
9 Hansen HC,Helmke K. Validation of the optic nerve sheath response to changing cerebrospinal fluid pressure:Ultrasound findings during intrathecal infusion tests[J]. J Neurosurg,1997,87:34-40.
10 Rajajee V,Vanaman M,Fletcher J,et al. Optic nerve ultrasound for the detection of raised intracranial pressure[J]. Neurocrit Care,2011,15:506-515.
11 Strumwasser A,Kwan RO,Yeung L,et al.Sonographic optic nerve sheath diameter as an estimate of intracranial pressure in adult trauma[J]. J Surg Res,2011,170:265-271.
12 Geeraerts T,Merceron S,Benhamou D,et al. Noninvasive assessment of intracranial pressure using ocular sonography in neurocritical care patients[J].Intensive Care Med,2008,34:2062-2067.
13 Soldatos T,Karakitsos D,Chatzimichail K,et al.Optic nerve sonography in the diagnostic evaluation of adult brain injury[J]. Critical Care,2008,12:R67.
14 Kimberly HH,Shah S,Marill K,et al. Correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with direct measurement of intracranial pressure[J]. Acad Emerg Med,2008,15:201-204.
15 Moretti R,Pizzi B,Cassini F,et al. Reliability of optic nerve ultrasound for the evaluation of patients with spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage[J].Neurocrit Care,2009,11:406-410.
16 Goel RS,Goyal NK,Dharap SB,et al. Utility of optic nerve ultrasonography in head injury[J]. Injury,2008,39:519-524.
17 Watanabe A,Kinouchi H,Horikoshi T,et al. Effect of intracranial pressure on the diameter of the optic nerve sheath[J]. J Neurosurg,2008,109:255-258.
18 李臻,刘大川,杨惠青,等. 中国健康成人球后视神经鞘直径的超声测量[J]. 临床超声医学杂志,2012,3:160-162.
19 苗雨露. 超声检查视神经鞘直径监测颅内压的研究进展[J]. 海南医学,2014,25:2882-2884.
20 赵万,苗雨露,王福明,等. 超声检查视神经鞘直径在颅脑损伤诊治中的应用价值[J]. 中国医师杂志,2012,14:1459-1462.
21 张锐,宋苏云,王丰,等. 床旁超声测量视神经鞘直径对颅脑损伤患者颅内压增高的诊断价值[J]. 医学临床研究,2012,29:707-709.
22 Wang L,Feng L,Yao Y,et al. Optimal optic nerve sheath diameter threshold for the identification of elevated opening pressure on lumbar puncture in a Chinese population[J]. PLoS One,2015,10:e0117939.
23 Soldatos T,Chatzimichail K,Papathanasiou M,et al.Optic nerve sonography:A new window for the noninvasive evaluation of intracranial pressure in brain injury[J]. Emerg Med J,2009,26:630-634.
24 Amini A,Kariman H,Arhami Dolatabadi A,et al.Use of the sonographic diameter of optic nerve sheath to estimate intracranial pressure[J]. Am J Emerg Med,2013,31:236-239.
25 Dubourg J,Javouhey E,Geeraerts T,et al.Ultrasonography of optic nerve sheath diameter for detection of raised intracranial pressure:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Intensive Care Med,2011,37:1059-1068.
26 Geeraerts T,Launey Y,Martin L,et al.Ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath may be useful for detecting raised intracranial pressure after severe brain injury[J]. Intensive Care Med,2007,33:1704-1711.
27 Shirodkar CG,Rao SM,Mutkule DP,et al. Optic nerve sheath diameter as a marker for evaluation and prognostication of intracranial pressure in Indian patients:An observational study[J]. Indian J Crit Care Med,2014,18:728-734.
28 Blaivas M,Theodoro D,Sierzenski PR. Elevated intracranial pressure detected by bedside emergency ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath[J]. Acad Emerg Med,2003,10:376-381.
29 Tsung JW,Blaivas M,Cooper A,et al. A rapid noninvasive method of detecting elevated intracranial pressure using bedside ocular ultrasound:Application to 3 cases of head trauma in the pediatric emergency department[J]. Pediatr Emerg Care,2005,21:94-98.
30 黎君彦,谭鸿,姜伟,等. 超声测量视神经鞘直径预测颅脑损伤患者颅内压增高的价值[J]. 海南医学,2014,25:1124-1126.
31 Maude RR,Hossain MA,Hassan MU,et al.Transorbital sonographic evaluation of normal optic nerve sheath diameter in healthy volunteers in Bangladesh[J]. PLoS One,2013,8:e81013.
32 Gangemi M,Cennamo G,Maiuri F,et al.Echographic measurement of the optic nerve in patients with intracranial hypertension[J].Neurochirurgia (Stuttg),1987,30:53-55.
33 Rosenberg JB,Shiloh AL,Savel RH,et al. Noninvasive methods of estimating intracranial pressure[J]. Neurocrit Care,2011,15:599-608.
34 Bäuerle J,Lochner P,Kaps M,et al. Intra- and interobsever reliability of sonographic assessment of the optic nerve sheath diameter in healthy adults[J]. J Neuroimaging,2012,22:42-45.
35 Ballantyne S,O'Neill G,Hamilton R,et al. Observer variation in the sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter in normal adults[J]. Eur J Ultrasound,2002,15:145-149.
36 Wang L,Feng L,Yao Y,et al. Ultrasonographic evaluation of optic nerve sheath diameter among healthy Chinese adults[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol,2016,42:683-688.
37 Bauerle J,Schuchardt F,Schroeder L,et al.Reproducibility and accuracy of optic nerve sheath diameter assessment using ultrasound compared to magnetic resonance imaging[J]. BMC Neurol,2013,13:187.
38 Hassen GW,Bruck I,Donahue J,et al. Accuracy of optic nerve sheath diameter measurement by emergency physicians using bedside ultrasound[J]. J Emerg Med,2015,48:450-457.
39 Maissan IM,Dirven PJ,Haitsma IK,et al.Ultrasonographic measured optic nerve sheath diameter as an accurate and quick monitor for changes in intracranial pressure[J]. J Neurosurg,2015,123:743-747.
40 Launey Y,Nesseler N,Le Maguet P,et al. Effect of osmotherapy on optic nerve sheath diameter in patients with increased intracranial pressure[J]. J Neurotrauma,2014,31:984-988.
41 Whiteley JR,Taylor J,Henry M,et al. Detection of elevated intracranial pressure in robotassisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy using ultrasonography of optic nerve sheath diameter[J]. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol,2015,27:155-159.
42 Sekhon MS,McBeth P,Zou J,et al. Association between optic nerve sheath diameter and mortality in patients with severe traumatic brain injury[J].Neurocrit Care,2014,21:245-252.

